Soybean gene copy number variation analysis method
A technology for gene copy number and variation analysis, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of researchers with extremely high requirements for operation techniques and analysis experience, unsuitable for large sample analysis, and high experimental costs , to achieve the effect of low technical and experience requirements, large sample analysis and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Using this method to verify the copy number variation regions obtained by high-throughput sequencing
[0047] 1) Plant material and DNA extraction
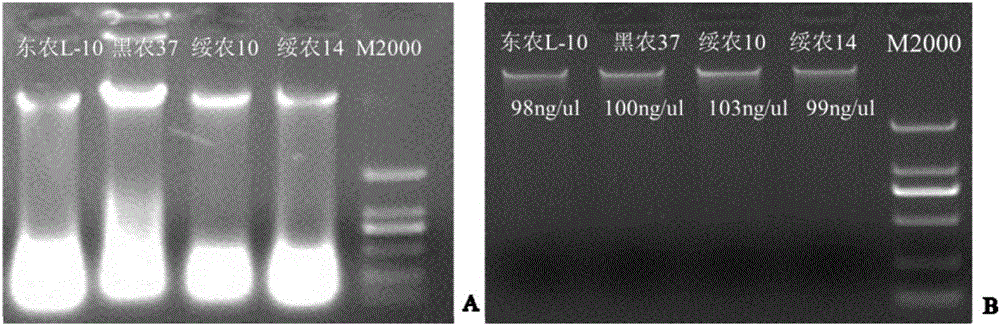
[0048] Soybean genomic DNA was extracted by SDS method, detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and The Lite UV spectrophotometer was used to jointly detect the DNA concentration and achieve uniform concentration by dilution. The genomic DNA concentration was adjusted to 50ng / μL and stored at -20°C for later use. Soybean cyst nematode multi-race resistant soybean germplasm Dongnong L-10 was used as reference material, and susceptible soybean varieties Heinong 37, Suinong 10 and Suinong 14 were used as reference materials.
[0049] 2) Target gene primer design and specificity analysis
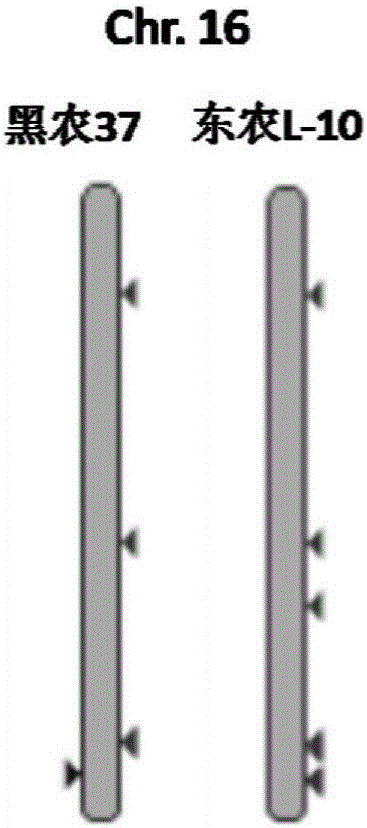
[0050] By resequencing the soybean genome (sequencing depth 30x), the copy number difference region between the resistant variety Dongnong L-10 and the susceptible variety Heinong 37 was obtained ( figure 2 ,Table 1).
[0051] Table ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com