Primers, probes and kit for rapidly detecting mycobacterium paratuberculosis on site
A technology for mycobacteria and paratuberculosis, applied in the field of microbial detection, to achieve the effects of convenient use, high sensitivity and strong specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
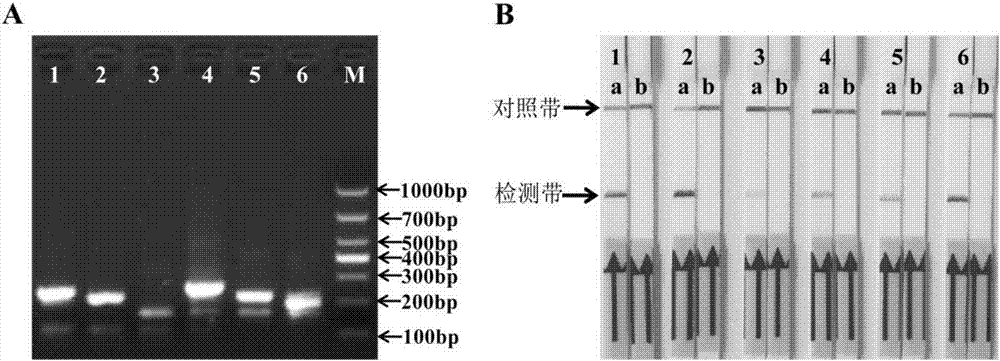
[0062] Example 1: Design and screening of primers and probes
[0063] 1. Design of primers and probes
[0064] At present, there are no specific operating rules for the design of RPA-nfo primers and probes. The specificity and amplification efficiency must be tested after the RPA reaction, in order to screen and obtain primers and probes that can be used in clinical testing. In the experiment, it is necessary to design multiple pairs of primers and probes from both ends of the target sequence for optimization and screening, and the substitution or increase or decrease of individual bases will have an important impact on the experimental results.
[0065] The present invention designs forward primers, reverse primers and probes according to the specific IS900 gene (GengBank No. S74401) of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, as shown in Table 1 respectively. There are 6 sets of RPA combinations of primers and probes. When designing the primers, the conservation of the IS900 gene in...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Embodiment 3: the kit that is used for the detection of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis
[0108] 1. The composition of kit: the primer and probe combination of embodiment 1 screening, positive quality control standard substance, negative quality control standard substance, rehydration buffer, magnesium acetate (280mM), ddH 2 O and lateral flow chromatography test strips.
[0109] 2. Amplification system and detection method:
[0110] The RPA-nfo reaction system is 25 μL:
[0111]
[0112] Add 23.75 μL of the above mixture into the RPA-nfo reaction tube, mix well and dissolve, and finally add 1.25 μL of 280 mM magnesium acetate solution, mix upside down and directly place it in a 37°C constant temperature water bath for 25 minutes.
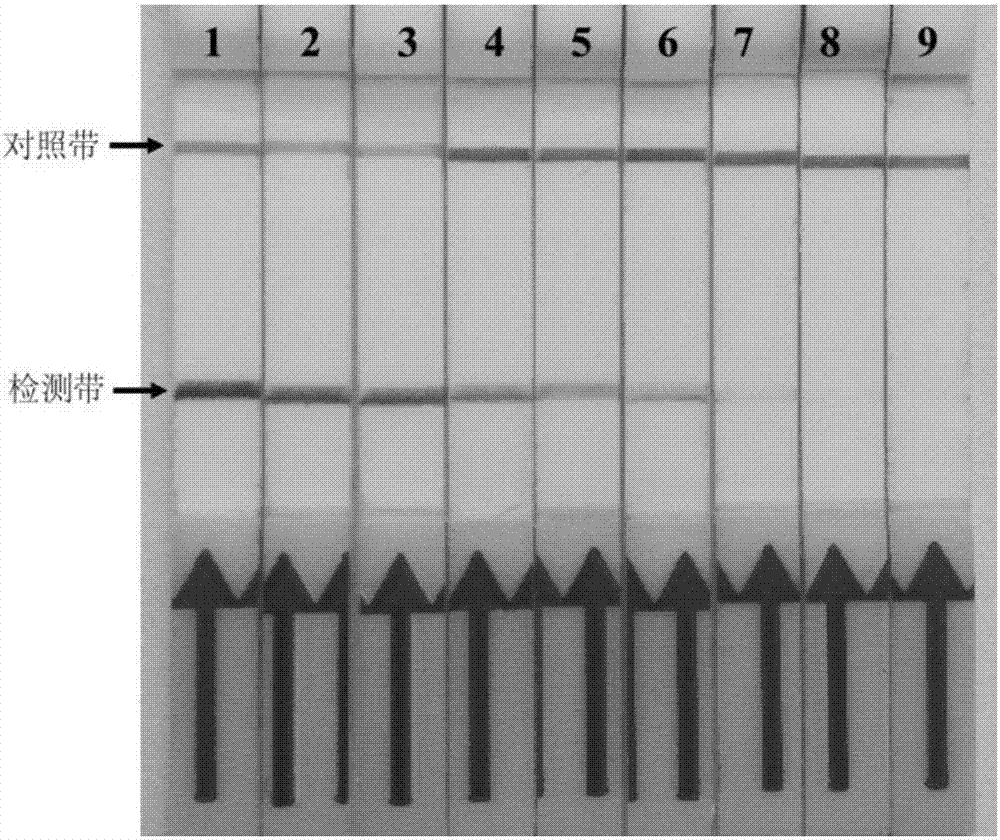
[0113] After the reaction, mix 1 μL with 49 μL LFD detection buffer, immerse the LFD vertically in the above mixed buffer, observe the result within 5 minutes, and interpret it through the display of the test strip. If the detection ban...
Embodiment 4
[0114] Embodiment 4: the application of RPA-LFD detection method of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis
[0115] 1. Experimental steps
[0116] (1) On-site preparation of clinical samples
[0117] Use 200μL of TE buffer [1.0M Tris-HCl (pH8.0) 10mL, 0.5M Na 2 EDTA·2H 2 O (pH8.0) 2mL, add distilled water to 1000mL] resuspend, blood, serum and other liquid samples directly take 200μL, then add 30μL 10% (w / v) SDS and 3μL 2% (w / v) proteinase K, mix Then incubate at 37°C for 1 hour, during which time it was turned upside down several times.
[0118] (2) Detection of clinical samples
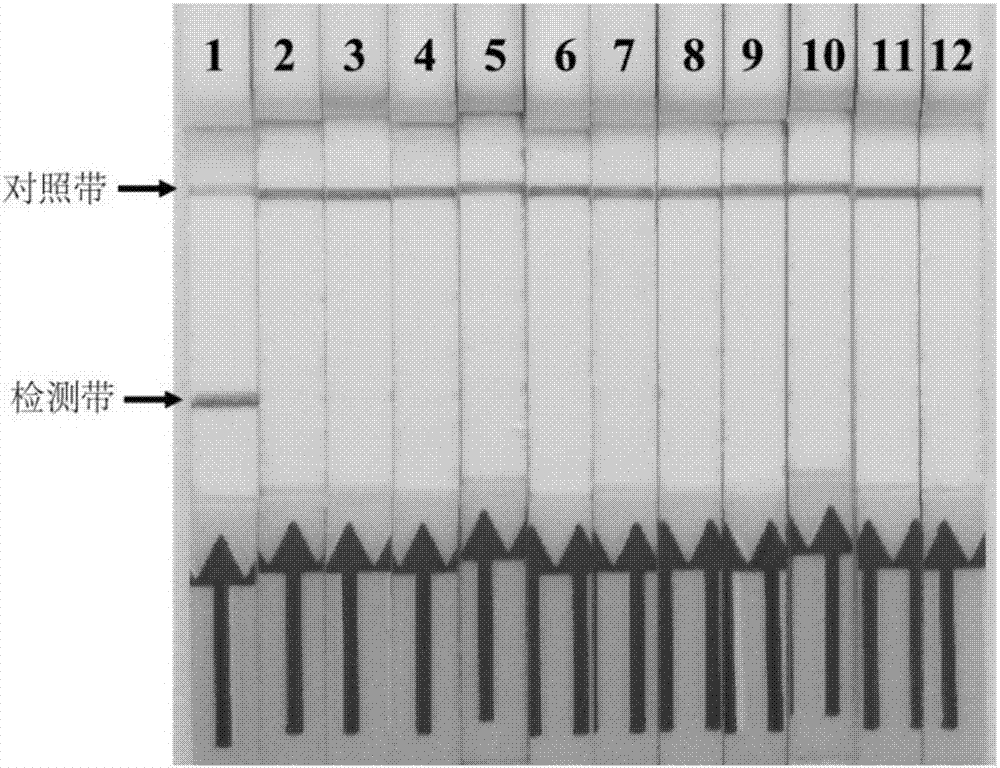
[0119] According to the method of on-site cracking and processing of clinical samples in step (1), 9 stool samples, 1 serum sample, and 4 blood samples that have been amplified with Mycobacterium paratuberculosis-specific PCR primers and sequenced correctly are stored in our laboratory. Samples and 1 milk sample were tested for Mycobacterium paratuberculosis RPA-LFD. At the same time, 1 negative sample...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com