Chromatographic determination method of synthetic colorants in food
A technology for synthesizing colorants and measuring methods, applied in measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitability for batch sample detection, low sensitivity, and high detection concentration, and achieves reduction of manual labor, less reagent consumption, Accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
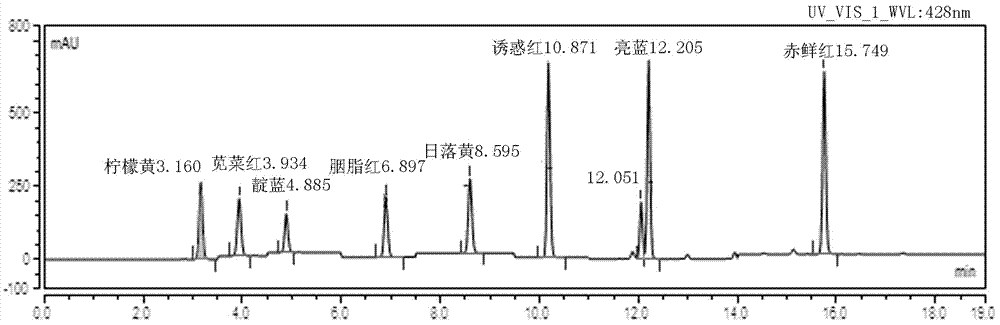
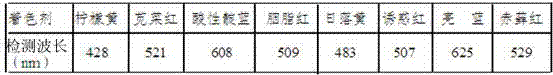
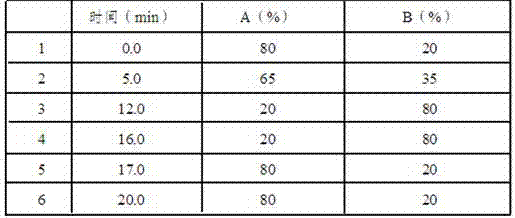
[0021] The invention provides a chromatographic determination method for synthetic coloring agents in food, which is suitable for high-efficiency liquids of eight synthetic colorants in foods: lemon yellow, amaranth, acid indigo, carmine, sunset yellow, allure red, brilliant blue and erythrosin Phase chromatography
[0022] The detection limit of lemon yellow, amaranth, acid indigo, carmine, sunset yellow, allure red, brilliant blue and erythrosin in this method is 0.025 mg / kg, and the limit of quantification is 0.075 mg / kg.
[0023] In order to describe the present invention more conveniently, the reagents used in the present invention are listed here. Unless otherwise specified, the reagents used in this example are all analytically pure, and the water is first-grade water that meets the requirements of GB / T 6682;
[0024] 3.1 Methanol (CH3OH): chromatographically pure;
[0025] 3.2 Ammonia (NH3•H2O);
[0026] 3.3 Citric acid (C6H8O7•H2O);
[0027] 3.4 Zinc acetate (C4H6O4Zn•2H2O);
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com