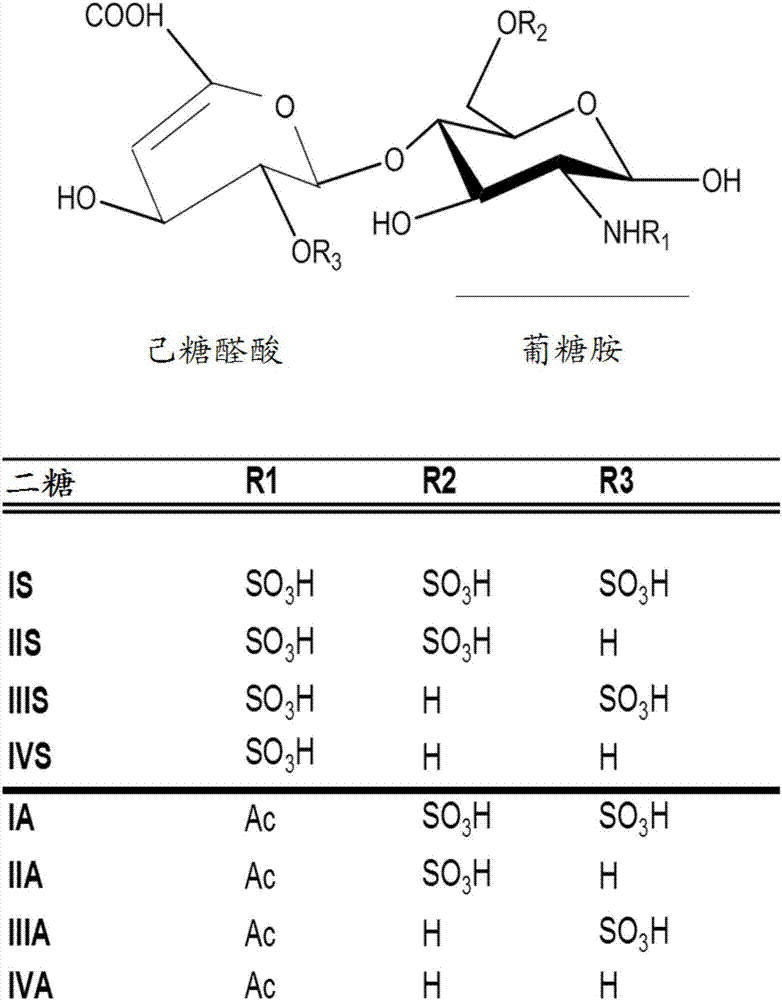
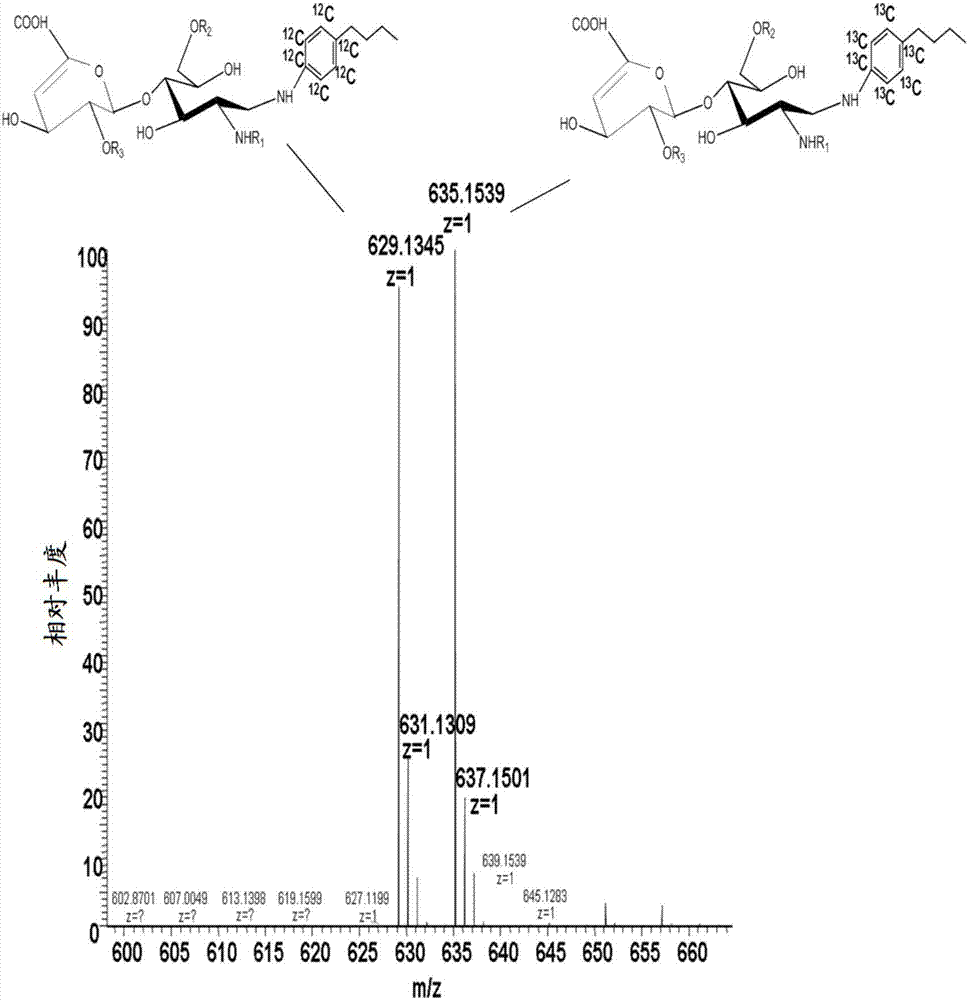
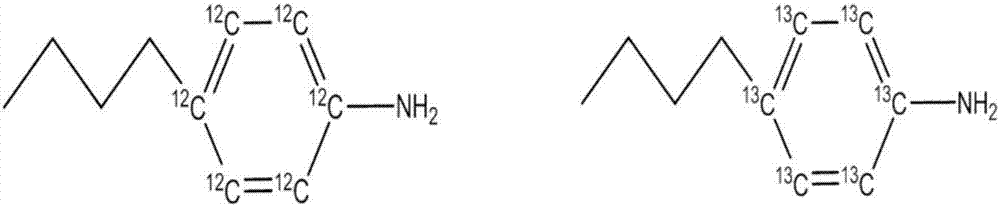Determination of glycosaminoglycan levels by mass spectrometry
A glycosaminoglycan and level technology, which is applied in the field of measuring the level of glycosaminoglycans in biological samples, and can solve problems such as difficulty in quantification or characterization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0239] Example 1: Liquid chromatography / mass spectrometry (LC / MS) assay for the quantification of heparan sulfate in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with mucopolysaccharidosis.
[0240] Heparan sulfate was quantified in human cerebrospinal fluid samples by a method for the quantification of heparan sulfate-derived disaccharides in samples using a multi-step protocol. Specifically, the multi-step protocol of this example includes ion-exchange solid-phase extraction, size-exclusion desalting, digestion with heparinase, chemical derivatization, and glycan-specific solid-phase extraction. After glycan-specific solid-phase extraction, use an API 5000 operating in electrospray negative ion mode TM Triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for the analysis of disaccharides by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.
[0241] Extraction of HS from CSF
[0242] Diethylaminoethyl (DEAE) resin (175 μL) was added to wells of a 96-well plate with a 20 μm frit. The re...
Embodiment 2
[0319] Example 2: Cerebrospinal fluid heparan sulfate concentrations in untreated Sanfilippo syndrome A patients.
[0320] CSF samples from 25 untreated Sanfilippo syndrome A patients were analyzed using the LC / MS-based HS assay described above. HS concentrations were compared to those of 156 control healthy individuals whose CSF was obtained from a biobank and analyzed using the same method. In the patient group, HS concentrations ranged from 1.94 μM to 9.71 μM, with a mean HS concentration of 4.9 μM ( Figure 6 ). In contrast, 33% of control samples were characterized by HS levels below the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) of the assay. Those within the quantifiable range had an average concentration of 0.37 μM, with the lowest and highest concentrations being 0.229 μM and 0.648 μM, respectively. Thus, HS levels in CSF were significantly increased 13-fold in patients with Sanfilippo syndrome A compared with control subjects (t-test; P<0.001).
Embodiment 3
[0321] Example 3: Changes of HS concentration in patients with Sanfilippo syndrome A after intrathecal enzyme replacement therapy.
[0322] This example relates in part to the application of the method of the invention to monitoring patient status and treatment efficacy. Patients with Sanfilippo syndrome A were administered 10 mg, 45 mg, or 90 mg of recombinant heparan N-sulfatase intrathecally monthly for a period of 22 weeks. CSF samples were collected prior to each dose of recombinant heparan N-sulfatase, and HS in CSF was measured using the LC / MS-based HS assay described above. CSF HS changes during the 22-week treatment period as Figure 7 shown. At all doses, the concentration of HS in CSF samples was reduced by 50% relative to baseline (ie, samples collected prior to the first treatment dose). These data show in particular that CSF HS levels remained stable during treatment and that the lowest level of CSFHS was achieved at the 90 mg dose.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com