Ferroelectric thin-film transistor and preparation method thereof
A ferroelectric thin film and transistor technology, applied in the direction of transistor, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuit, etc., can solve the problems of increasing process difficulty, increasing chip manufacturing cost, incompatibility, etc., and achieves the improvement of CMOS logic circuit application, less leakage and Excellent breakdown and thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
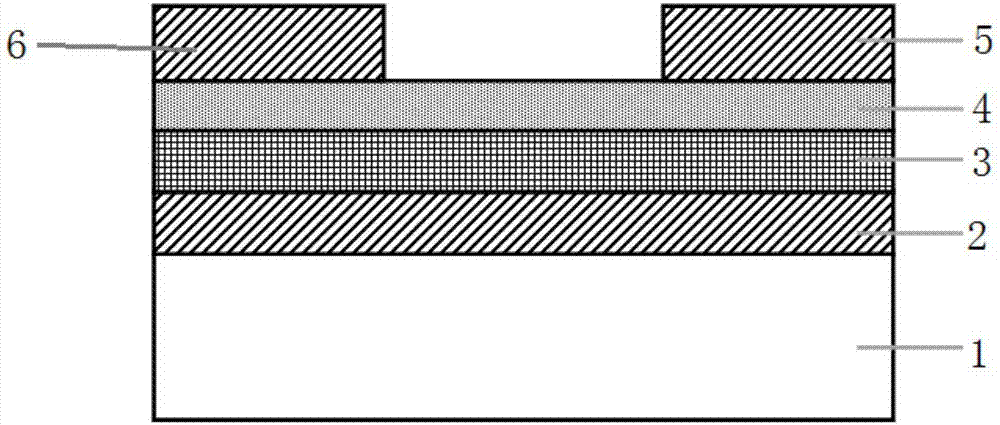
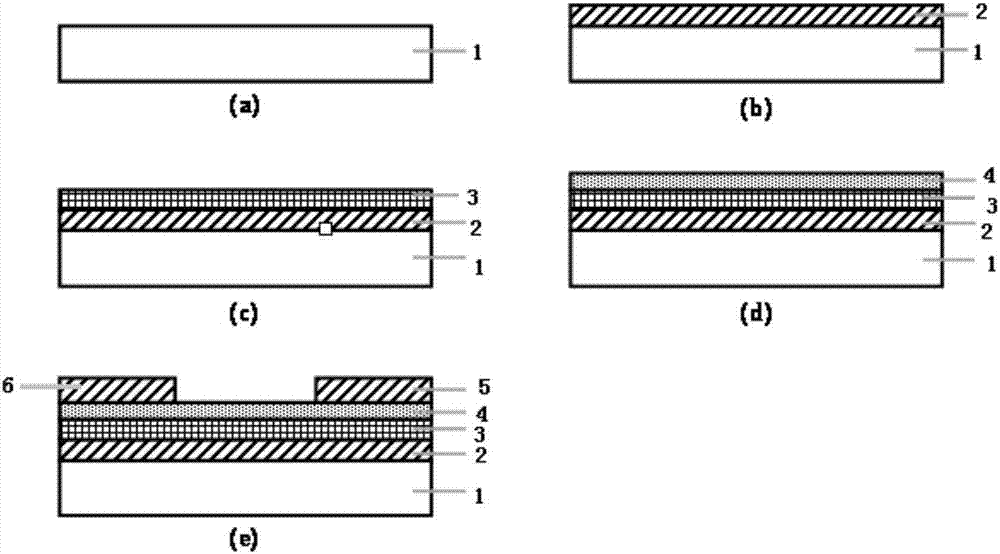
[0041] An embodiment of the ferroelectric thin film transistor of the present invention, a cross-sectional structure diagram of the ferroelectric thin film transistor described in this embodiment is shown in the attached figure 1 shown, including:
[0042] substrate1;
[0043] A bottom gate electrode 2 formed on the substrate 1;
[0044] A ferroelectric thin film layer 3 formed on the bottom gate electrode 2;
[0045] A channel layer 4 formed on the ferroelectric thin film layer 3;
[0046] a source electrode 5 formed on the channel layer 4;
[0047] as well as
[0048] A drain electrode 6 formed on the channel layer 4 and separated from the source electrode 5 .
[0049] The ferroelectric thin film layer 3 is composed of a hafnium oxide-based material, and the hafnium oxide-based material is Zr-doped HfO 2 Material; the thickness of the ferroelectric film layer 3 is 10nm; the substrate 1 is made of silicon material, and the thickness of the bottom gate electrode 2 is 120...
Embodiment 2
[0057] An embodiment of the ferroelectric thin film transistor of the present invention, a cross-sectional structure diagram of the ferroelectric thin film transistor described in this embodiment is shown in the attached figure 1 shown, including:
[0058] substrate1;
[0059] A bottom gate electrode 2 formed on the substrate 1;
[0060] A ferroelectric thin film layer 3 formed on the bottom gate electrode 2;
[0061] A channel layer 4 formed on the ferroelectric thin film layer 3;
[0062] a source electrode 5 formed on the channel layer 4;
[0063] as well as
[0064] A drain electrode 6 formed on the channel layer 4 and separated from the source electrode 5 .
[0065] The ferroelectric thin film layer 3 is composed of a hafnium oxide-based material, which is Si-doped HfO 2 Material; the thickness of the ferroelectric film layer 3 is 5nm; the substrate 1 is made of silicon material, and the thickness of the bottom gate electrode 2 is 100nm; the channel layer 4 is made ...
Embodiment 3
[0073] An embodiment of the ferroelectric thin film transistor of the present invention, a cross-sectional structure diagram of the ferroelectric thin film transistor described in this embodiment is shown in the attached figure 1 shown, including:
[0074] substrate1;
[0075] A bottom gate electrode 2 formed on the substrate 1;
[0076] A ferroelectric thin film layer 3 formed on the bottom gate electrode 2;
[0077] A channel layer 4 formed on the ferroelectric thin film layer 3;
[0078] a source electrode 5 formed on the channel layer 4;
[0079] as well as
[0080] A drain electrode 6 formed on the channel layer 4 and separated from the source electrode 5 .
[0081] The ferroelectric thin film layer 3 is composed of a hafnium oxide-based material, and the hafnium oxide-based material is Al-doped HfO 2 Material; the thickness of the ferroelectric thin film layer 3 is 20nm; the substrate 1 is made of silicon material, and the thickness of the bottom gate electrode 2 i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com