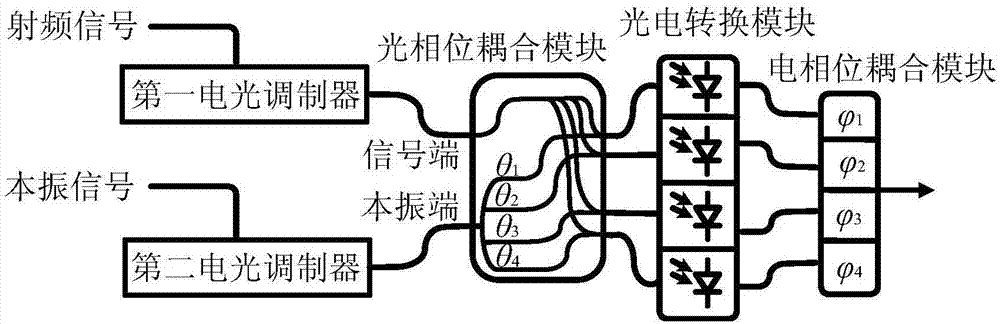
Microwave photonic image frequency rejection mixing method and device
A technology of image frequency suppression and microwave photonics, which is applied in the directions of multi-frequency modulation and conversion, optical fiber transmission, optical fiber radio, etc. It can solve the problem of inseparability, reduce complexity and cost, realize frequency conversion efficiency, and realize flexible and changeable methods. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
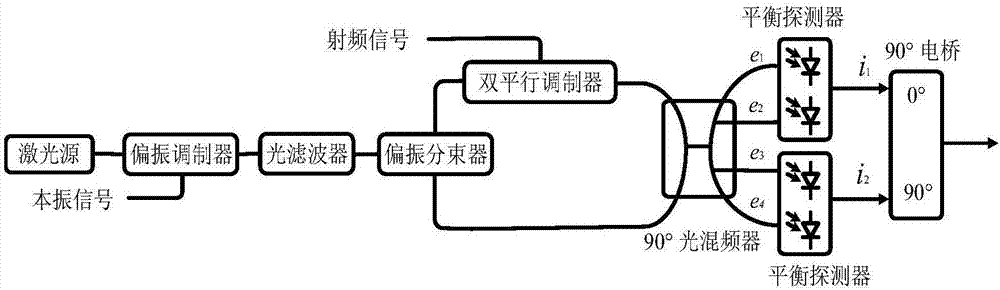
[0075] Such as figure 2 As shown, the frequency mixing device of this embodiment includes a light source (continuous wave laser), a polarization modulator, an optical filter, a polarization beam splitter, a dual parallel modulator, a 90° optical mixer, two balanced detectors, 90 °Microwave bridge.
[0076] The optical carrier ω output by the continuous wave laser c Injected into the polarization modulator, the local oscillator signal ω to be mixed L It is modulated on the optical carrier through the polarization modulator, and the output signal is injected into the optical filter, and the optical filter outputs the optical signal including the carrier and the upper sideband. After the optical signal passes through the polarization beam splitter, the optical carrier and the upper sideband are respectively output from two output ports of the polarization beam splitter.
[0077] The upper sideband of the local oscillator output by the polarizing beam splitter is expressed as ...
Embodiment 2
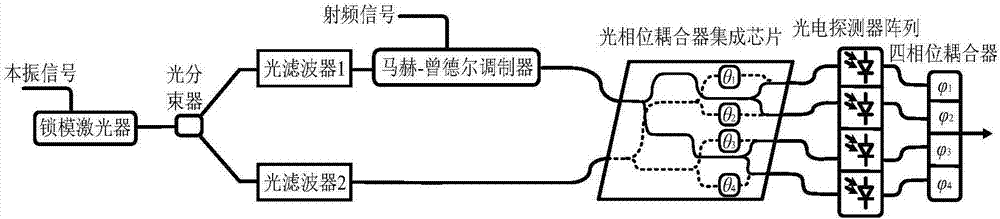
[0107] Such as image 3 As shown, the frequency mixing device in this embodiment includes: a mode-locked laser, an optical beam splitter, an optical filter 1, an optical filter 2, a Mach-Zehnder modulator, an optical phase coupling module, and four photodetectors A photodetector array (that is, a photoelectric conversion module) and a four-phase coupler are formed.
[0108] First set the frequency to ω L The local oscillator signal is injected into the mode-locked laser to generate an optical frequency comb whose comb tooth interval is the local oscillator frequency, and then its output is divided into two paths through the optical beam splitter, and two channels are selected by optical filter 1 and optical filter 2 respectively. frequency is ω c and ω c +ω L frequency components. Set the frequency to ω c The optical signal is double-band modulated by the radio frequency signal through the Mach-Zehnder modulator. The frequency of the modulated RF signal is ω s , while ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com