HN-VP233-221aa fusion protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of fusion protein and bursa, which is applied in the field of HN-VP233-221aa fusion protein and its preparation, can solve the problems of reduced immune effect of traditional vaccines, increased susceptibility to other diseases, impaired lymphocyte function, etc., and achieve enhanced body fluid and cellular immune response, good immune protection rate, good protective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
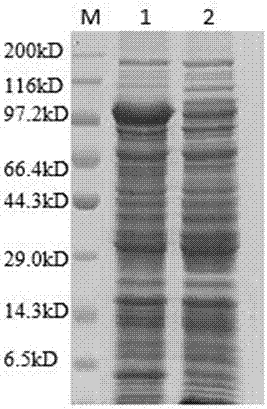
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
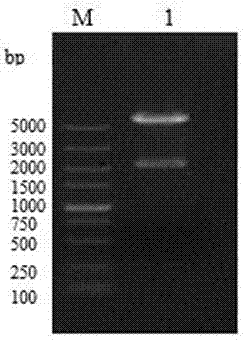
[0049] Recombinant HN-VP2 of the present invention 33-221aa The preparation method of fusion protein, its production comprises the following steps:
[0050] (a) HN-VP2 33-221aa and HN gene sequence acquisition
[0051] ①IBDV VP2 33-221aa Obtaining the gene sequence:
[0052] According to the nucleotide sequence of IBDV VP2 in GenBank (No:AF508177), design a pair of primers to amplify VP2 33-221aa Gene fragment.
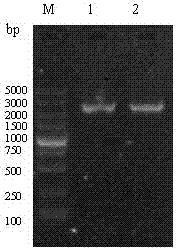
[0053] Using the previously constructed pMD18-T-VP2 as a template, PCR amplifies IBDV VP2 33-221aa fragment. After the amplified product was identified by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, the target band was excised, recovered and purified using a common agarose gel DNA recovery kit, and the purified product was VP2 33-221aa Gene fragments were sent to Dalian Bao Biological Engineering Co., Ltd. for sequencing;
[0054] ② Acquisition of NDV HN gene
[0055] According to the nucleotide sequence of NDV HN gene in GenBank (No: JF343538), a pair of primers were de...
Embodiment 1
[0066] 1. HN-VP2 33-221aa Acquisition of fusion protein coding gene sequence
[0067] (1) Acquisition of Newcastle disease virus HN gene
[0068] According to the nucleotide sequence of the HN gene of Newcastle disease virus in GenBank (No: JF343538), a pair of specific primers were designed using DNA Star7.0 and Primer premier6.0 software to amplify the HN gene fragment of Newcastle disease virus.
[0069] P1 and P2 amplify the HN gene of Newcastle disease virus, and the 5' end of primer P1 is introduced Bam HI endonuclease site, P2 5' end introduces a flexible linker. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0070] Table 1 Primer sequences used in PCR amplification
[0071]
[0072] The frozen NDV strain was thawed in a 37°C water bath, and then inoculated into 9-10 day-old non-immune chicken embryos (0.2 mL per embryo) through the allantoic cavity, and incubated at 37°C. Aseptically collect the allantoic fluid of dead chicken embryos within 24 to 48 hours (discard th...
Embodiment 2
[0092] rHN-VP2 33-221aa Applications of fusion proteins:
[0093] 1) Animal immunity
[0094] With above recombinant HN-VP2 33-221aa Chickens were immunized with the fusion protein, and its immune characteristics were evaluated. 240 14-day-old healthy chicks were randomly divided into 4 groups, 60 per group. Group 1 was a negative control, immunized with 200 μL PBS; group 2 was immunized with 200 μg of HN-VP2 recombinant fusion protein (diluted with 200 μL PBS), and immunized by chest muscle injection. Groups 3 and 4 were immunized with Newcastle disease IV vaccine and bursa vaccine (B87 strain) respectively as the traditional vaccine control group, and 200 μL were immunized by nasal drops and eye drops; all experimental groups were immunized once every 2 weeks. A total of 3 times of immunization. And on the 7th, 21d, and 35th day after the first immunization, 8 chicks were randomly selected from each group for heart blood collection and serum separation. At the same tim...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com