Interface control method of grain boundary diffusion neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A technology of grain boundary diffusion and interface regulation, which is applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inductors/transformers/magnets, etc., can solve the problems of magnet grade reduction, achieve the effect of eliminating the reduction of residual magnetism and inhibiting diffusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
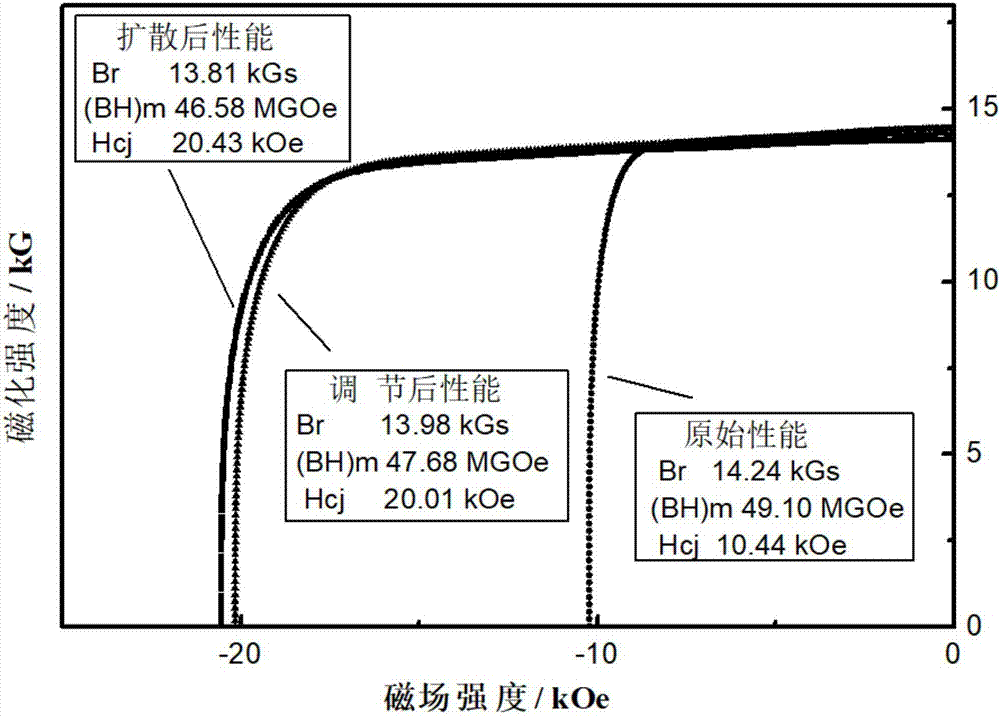
[0019] Grain boundary diffusion of a commercial N50 magnet with magnetic properties Br 14.24kGs, (BH) m 49.10MGOe, H cj The main component of 10.44kOe is Nd 26.6 Fe Bal B 1.01 Dy 0.03 Pr 4.7 Co 0.92 Cu 0.09 Al 0.27 .
[0020] (1) The block N50 magnets were cut into cylindrical samples of Φ10×10 by wire cutting.
[0021] (2) DyF 3 The powder (particle size is less than 10μm) is mixed with high-purity alcohol according to the mass ratio of 1:1, and then the mixed solution is ball-milled and stirred by a ball mill to obtain DyF 3 Mixed slurry with alcohol.
[0022] (3) DyF 3 The slurry mixed with alcohol is coated on the surface of the sample and thoroughly dried, and a layer of DyF is obtained on the surface of the sample. 3 coating.
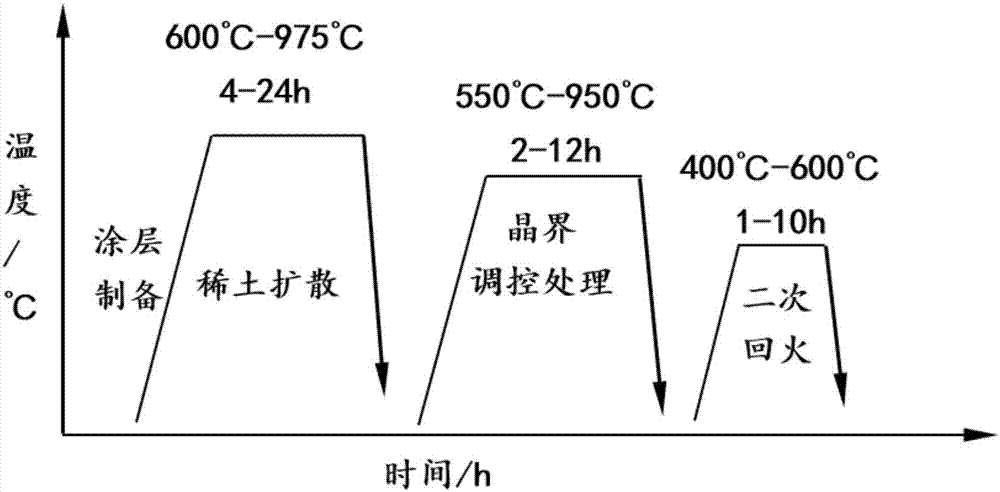
[0023] (4) The sample was subjected to grain boundary diffusion treatment for 10 h under an argon atmosphere at 900 °C. After the diffusion is completed, the sample is subjected to secondary tempering treatment for 4 hours in an ar...
Embodiment 2
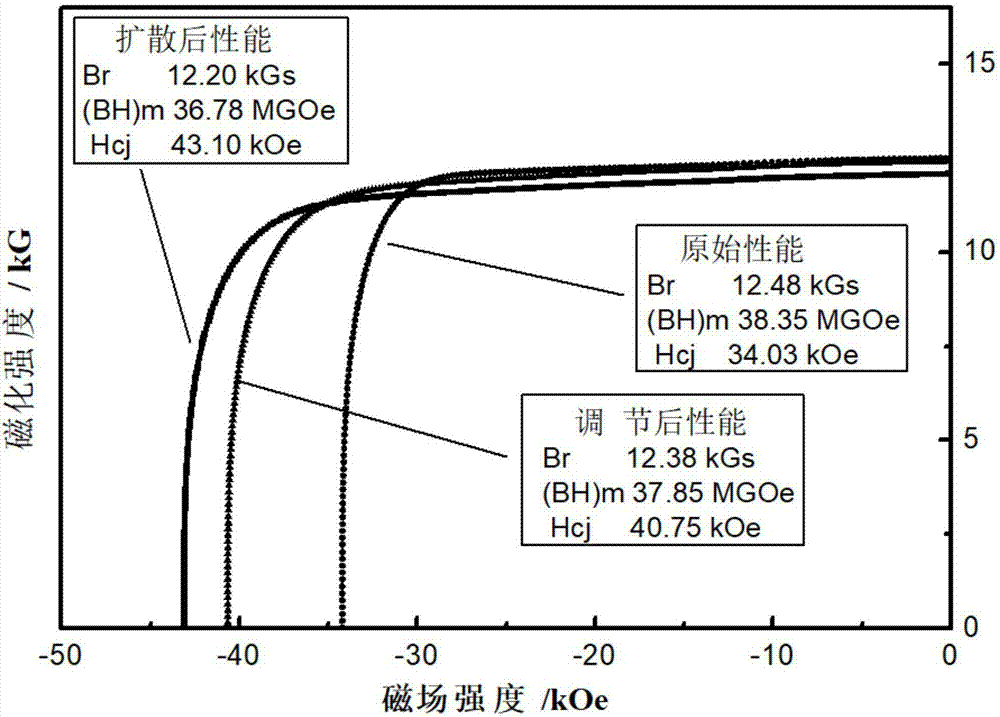
[0026] Grain boundary diffusion of commercial 38AH magnet, its magnetic properties Br 12.48kGs, (BH) m 38.35MGOe, H cj The main component of 34.03kOe is Nd 25.6 Fe Bal B 1.01 Dy 4.3 Tb 0.7 Pr 4.6 Co 0.92 Cu 0.09 .
[0027] (1) The block 38AH magnet was cut into cylindrical samples of Φ10×10 by wire cutting.
[0028] (2) Electroplating a layer of Tb on the surface of the sample by electrophoresis. The specific operation method is to clean and activate the surface of the sample, 2 (OH) 3 NO 3 ·H 2 Electroplating in O electrolyte for 4 min, so that the Tb electrophoresis layer is evenly coated on the surface of the sample, and the sample is thoroughly dried.
[0029] (3) The sample was subjected to grain boundary diffusion treatment at 900 °C in an argon atmosphere for 14 h. After the diffusion is completed, the sample is subjected to secondary tempering treatment for 4 hours in an argon atmosphere at 520 ° C. The magnetic properties of the sample are measured as B...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Grain boundary diffusion of a commercial N50 magnet with magnetic properties Br 14.24kGs, (BH) m 49.10MGOe, H cj The main component of 10.44kOe is Nd 26.6 FeBal B 1.01 Dy 0.03 Pr 4.7 Co 0.92 Cu 0.09 Al 0.27 .
[0033] (1) The block N50 magnets were cut into cylindrical samples of Φ10×10 by wire cutting.
[0034] (2) TbH 2 The powder (particle size is less than 10μm) is mixed with high-purity alcohol according to the mass ratio of 1:1, and then the mixed solution is ball-milled and stirred by a ball mill to obtain TbF 2 Mixed slurry with alcohol.
[0035] (3) TbH 2 The slurry mixed with alcohol is coated on the surface of the sample and dried thoroughly, and a layer of TbH is obtained on the surface of the sample. 2 coating.
[0036] (4) The sample was subjected to rare earth diffusion treatment for 10h under argon atmosphere at 875°C. After the diffusion is completed, the sample is subjected to secondary tempering treatment for 4 hours in an argon atmosph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com