Method for producing siniperca chuatsi infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus and siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus through microcarrier suspension culturing CPB cells
A spleen and kidney necrosis virus and microcarrier culture technology, applied in the field of cell engineering, can solve the problems of high cost, high titer virus technical difficulties, long time, etc., and achieve the effects of low production cost, low pollution probability and small labor force.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
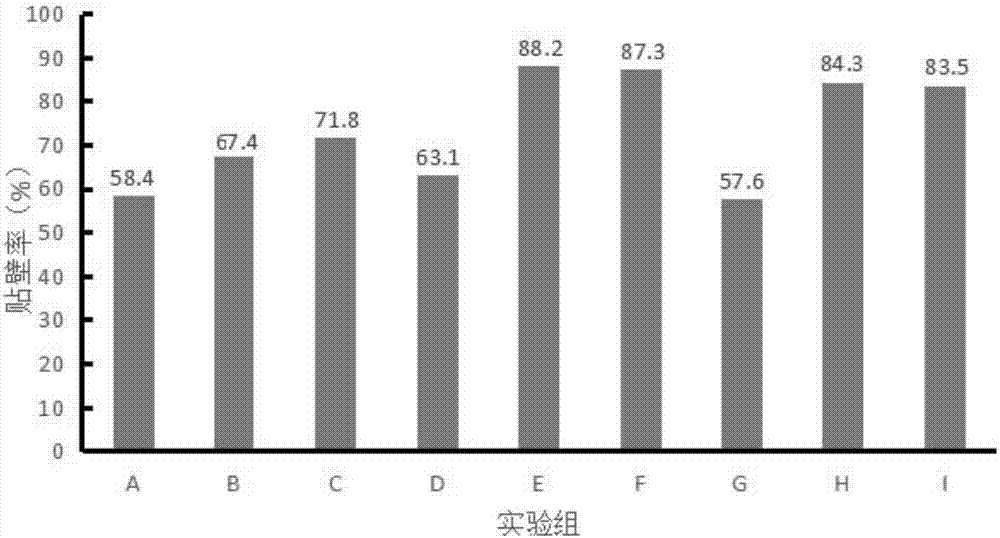
[0054] Preparation of seedling liquid for Siniperca infectious spleen-kidney necrosis virus: 71-73 hours after the second scale-up culture of CPB cells, let the microcarriers settle down, remove the supernatant, wash with an equal volume of incubation solution, and use the multiplicity of infection (MOI) after washing From 4.8 to 5.2, add mandarin fish infectious spleen-kidney necrosis virus to infect the cells, and add serum-free incubation solution to make the system volume half of the final volume, stir at 39-41r / min every 11-13min for 2.5-3.5min, and continue After 1.8 to 2.2 hours, add the remaining serum-containing incubation solution to the final volume, settle the microcarriers at 118 to 122 hours after inoculation, collect the supernatant, freeze and thaw, centrifuge to take the supernatant, and filter the filtrate to obtain virus seedlings liquid;
[0055] Preparation of mandarin rhizoma virus seedling preparation: 95-97 hours after the second scale-up culture of CPB...
Embodiment 1
[0078] Embodiment 1: A kind of method that utilizes stirred bottle and bioreactor microcarrier to cultivate CPB cell to produce mandarin fish infectious spleen-kidney necrosis virus and mandarin fish shell virus
[0079] Main experimental materials:
[0080] 1. Cells: CPB cells (see CN 104694483A);
[0081] 2. Virus species: Mandarin Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus ISKNV (QY) strain, Mandarin SCRV;
[0082] 3. Microcarrier: Cytodex1, product of GE Healthcare;
[0083] 4. Stirring bottle: double arm stirring bottle, Wheaton, USA;
[0084] 5. Bioreactor: BC type 3L bioreactor, Guangzhou Qizhi Bioengineering Equipment Co., Ltd.
[0085] 1. Handling of experimental equipment
[0086] 1. Treatment of the stirring bottle: Rinse the stirring bottle with tap water for more than 3 times, rinse with ultrapure water for more than 3 times, and sterilize with high-pressure steam at 121°C;
[0087] 2. Processing of 3L Bioreactor
[0088] (1) cleaning
[0089] a. Tanks and...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Embodiment 2: A kind of method that utilizes stirred bottle and bioreactor microcarrier to cultivate CPB cell to produce mandarin fish infectious spleen-kidney necrosis virus and mandarin fish shell virus
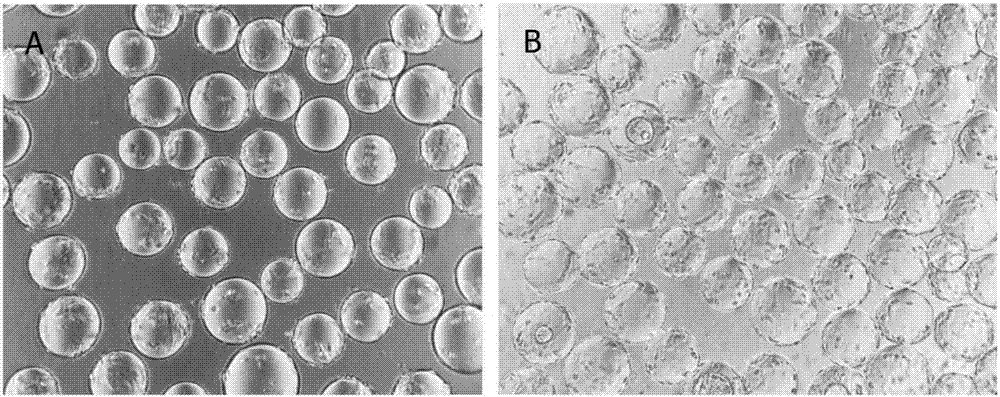
[0113] 1) Microcarrier pretreatment; put Cytodex 1 microcarrier powder into a common glass bottle siliconized with dichlorodimethylsilane, add Ca-free 2+ , Mg 2+ Hydrate in PBS at room temperature, then settle the microcarriers statically, remove PBS, wash with fresh PBS, add fresh PBS at last, cover the bottle and carry out high-pressure steam sterilization, after cooling to room temperature, use serum-containing L15 medium After washing, the serum-containing L15 medium was added, and transferred to a stirring bottle siliconized with dichlorodimethylsilane to equilibrate overnight.
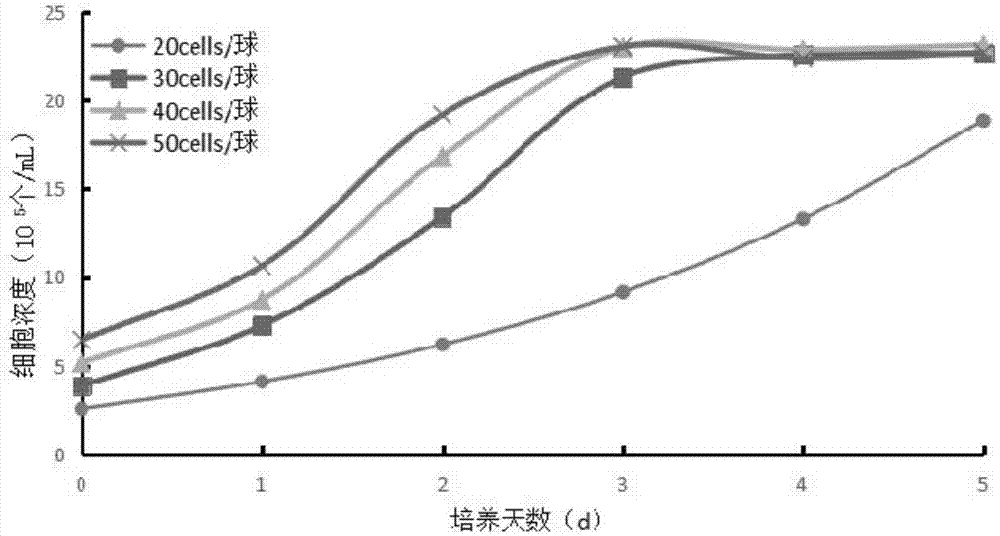
[0114] 2) Initial culture of CPB cells on microcarriers in 125ml stirring flasks: microcarriers and CPB single cell suspensions are inoculated into cell culture stirring flasks contain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com