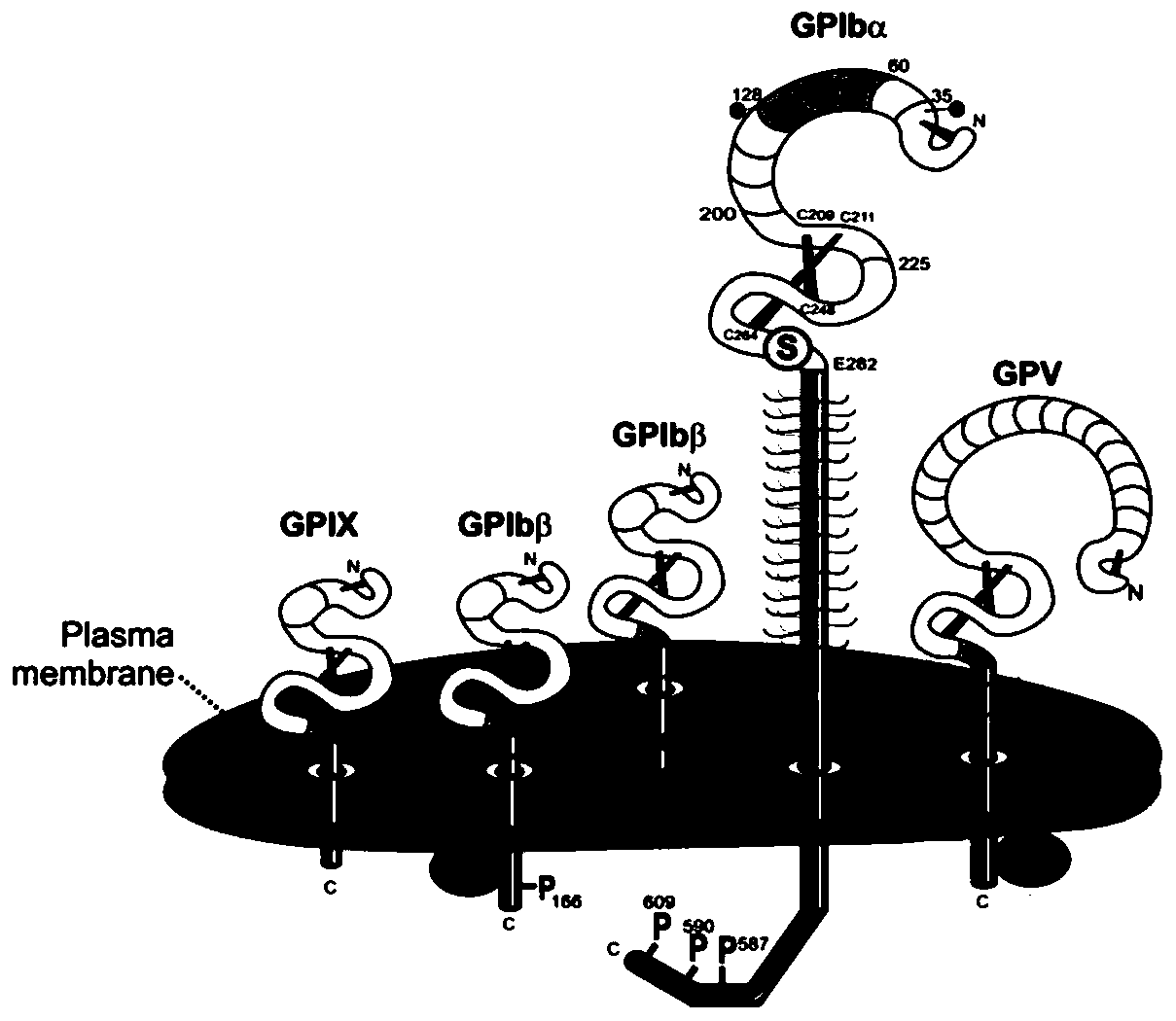
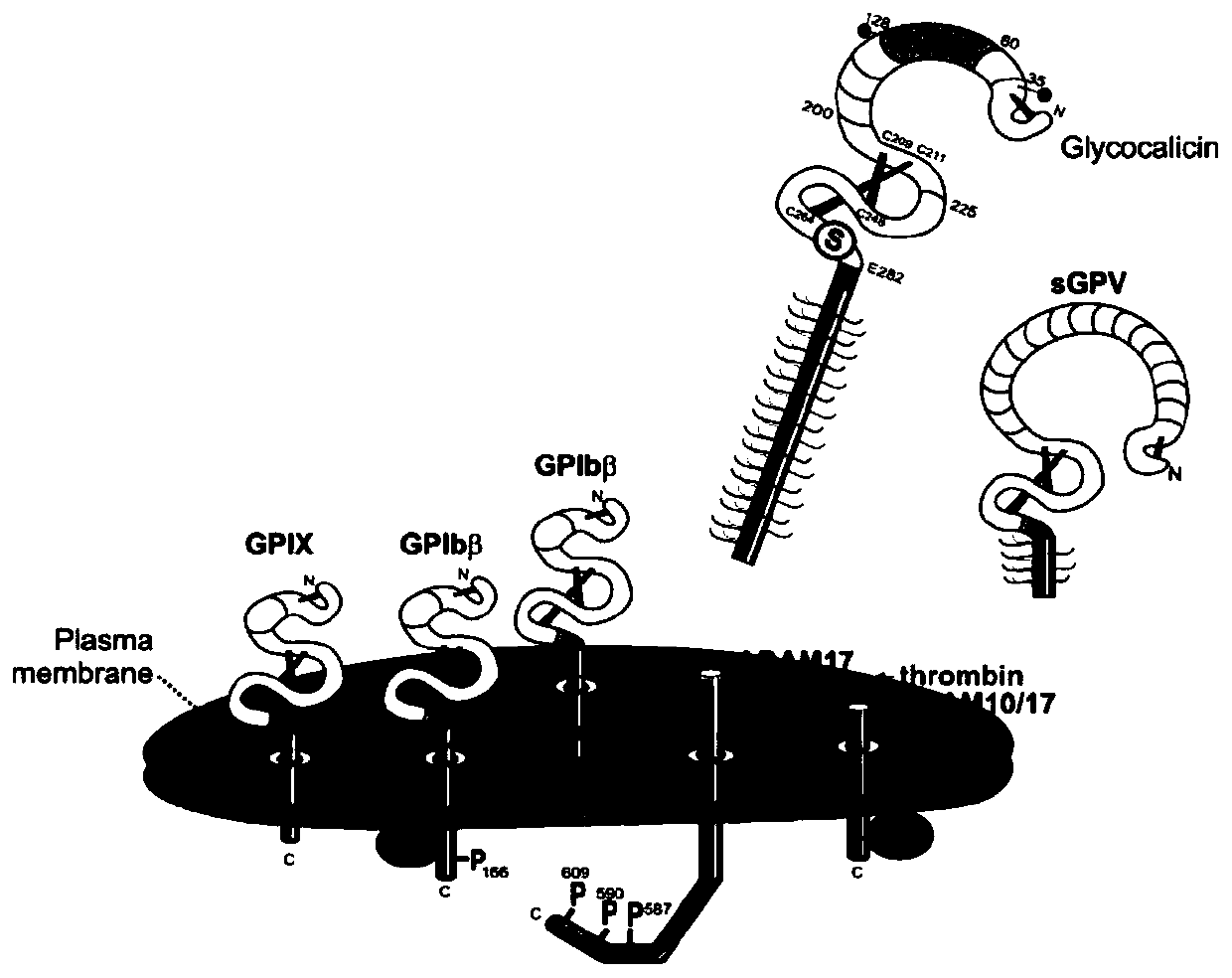
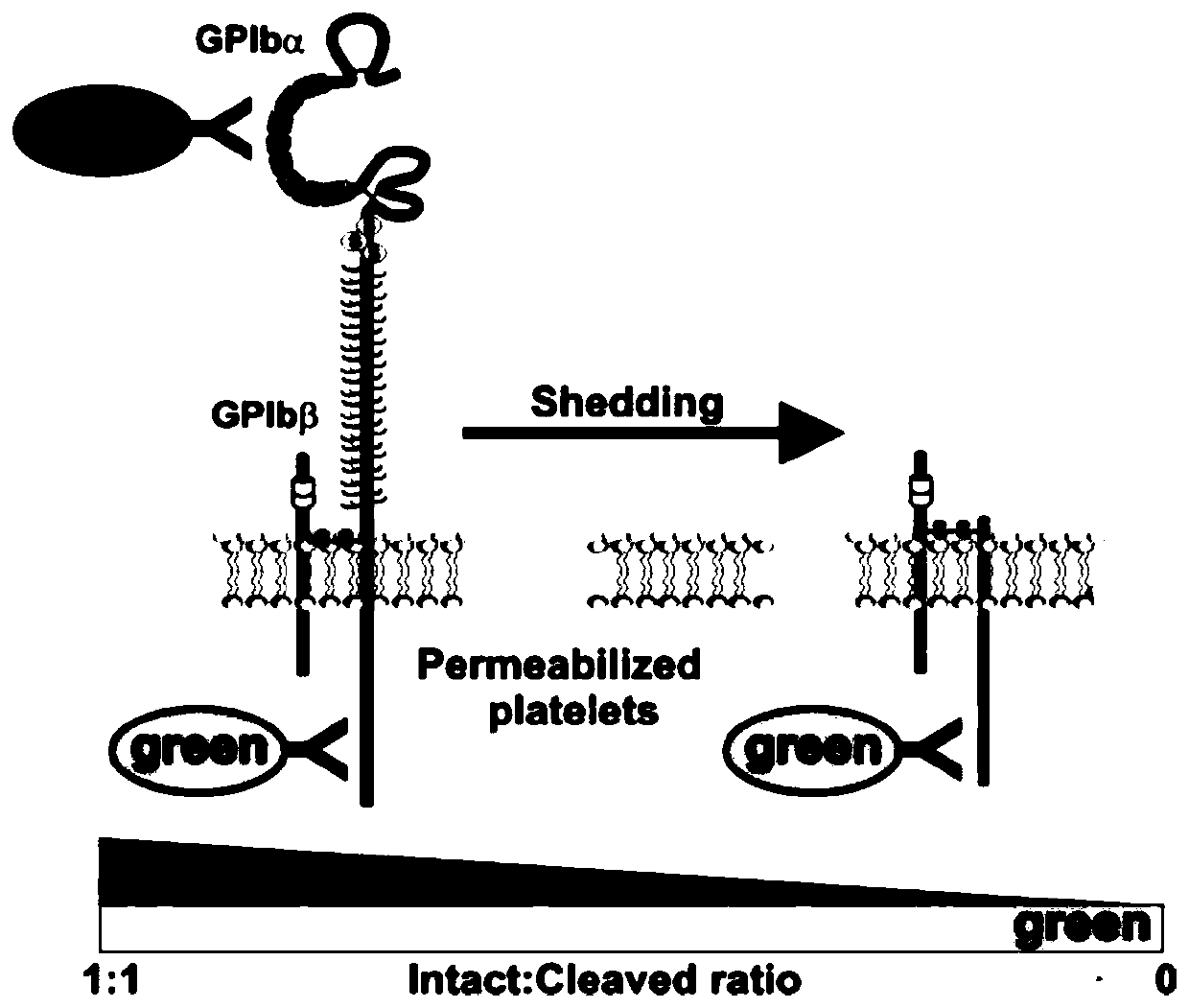
A flow cytometry-based method for detecting the cleavage of the extracellular segment of the platelet receptor gpiba
A technology of flow cytometry and platelets, applied in the field of medical biology, can solve the problems of high background value of ELISA, high level of soluble fragments, lower reliability and stability of test results, etc., and achieve high reliability and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1: Detection of enzyme cleavage of the extracellular segment of GPIba in healthy human platelets
[0041] A method for detecting platelet receptor GPIba ecto-digestion enzymes based on flow cytometry, comprising the following steps:
[0042] (1) Sample preparation and processing
[0043] a. Collect 5ml of venous blood from healthy people and collect it in a test tube containing the anticoagulant trisodium citrate aqueous solution (1.6 grams of trisodium citrate dissolved in 50ml distilled water). The blood is mixed slowly and gently according to the volume ratio of 1:9;
[0044] b. At room temperature, centrifuge at 120×g for 20 minutes, use a plastic straw to gently absorb the platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in the upper layer, do not absorb the PRP near the middle layer, so as not to absorb white blood cells and cause pollution;
[0045] c. Add the aspirated PRP to 5 EP tubes respectively, and the number of platelets in each EP tube is 1×10 7 Add 1×TS buffer ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2: Detection of enzyme cleavage of GPIba extracellular segment of healthy human platelets treated with NEM
[0062] N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), a reagent that can artificially induce the cleavage of the extracellular segment of GPIba, was used to treat platelets to induce cleavage of GPIba.
[0063] from Figure 7 It can be seen that the abscissa is the binding of the intracellular antibody, and the ordinate is the binding of the extracellular antibody. The 4 boxes in the figure represent the binding of each antibody respectively. The lower left quadrant represents the negative area, which represents the percentage of platelets that have neither the binding of the extracellular fragment antibody nor the binding of the intracellular fragment antibody. The upper left quadrant represents the percentage of platelets bound only by antibodies to the extracellular domain. The lower right quadrant represents platelets bound by intracellular segment antibodies. The up...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3: Detection of enzyme cleavage of extracellular segment of platelet GPIba in patients with thrombocytopenia
[0067] Platelets from 5 patients with thrombocytopenia were collected, and the method of the present invention was used to detect the enzyme cleavage of the extracellular segment of GPIba. from Figure 9 As can be seen in the figure, the intact state of GPIba was significantly decreased in patients with thrombocytopenia, suggesting increased cleavage of the extracellular segment. In addition, through correlation analysis, it was found that the degree of cleavage of the extracellular segment of GPIba in patients with thrombocytopenia was not dependent on the change of platelet number (R2=0.021, P=0.815), which further verified the flow cytometry-based detection method of the present invention. The method of cleavage of the extracellular segment of GPIba does not depend on the change of platelet number.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com