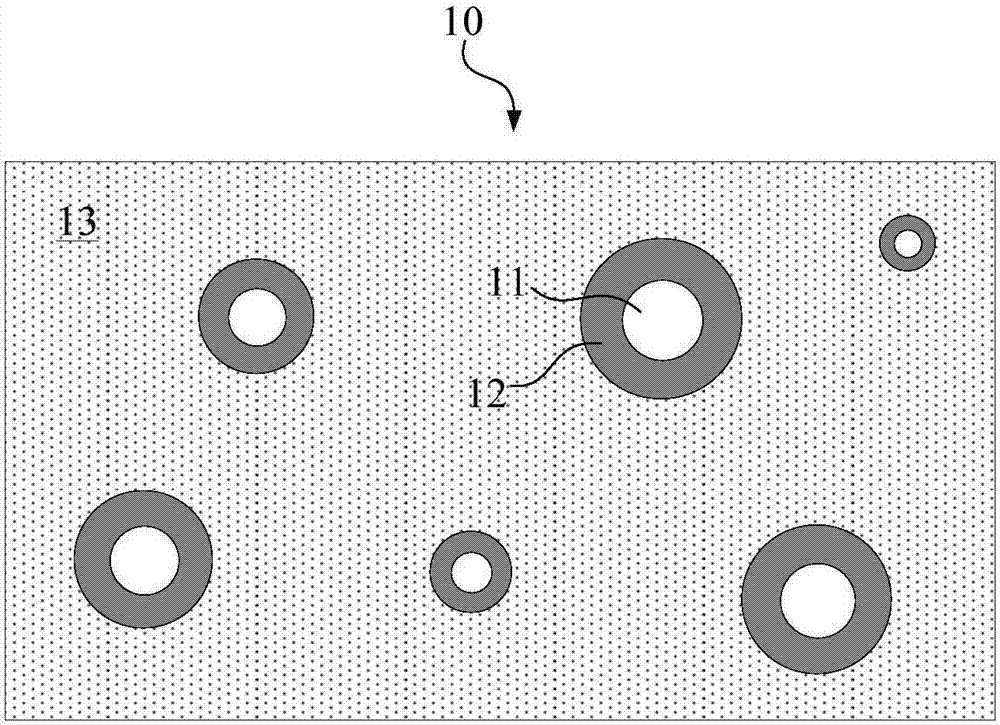
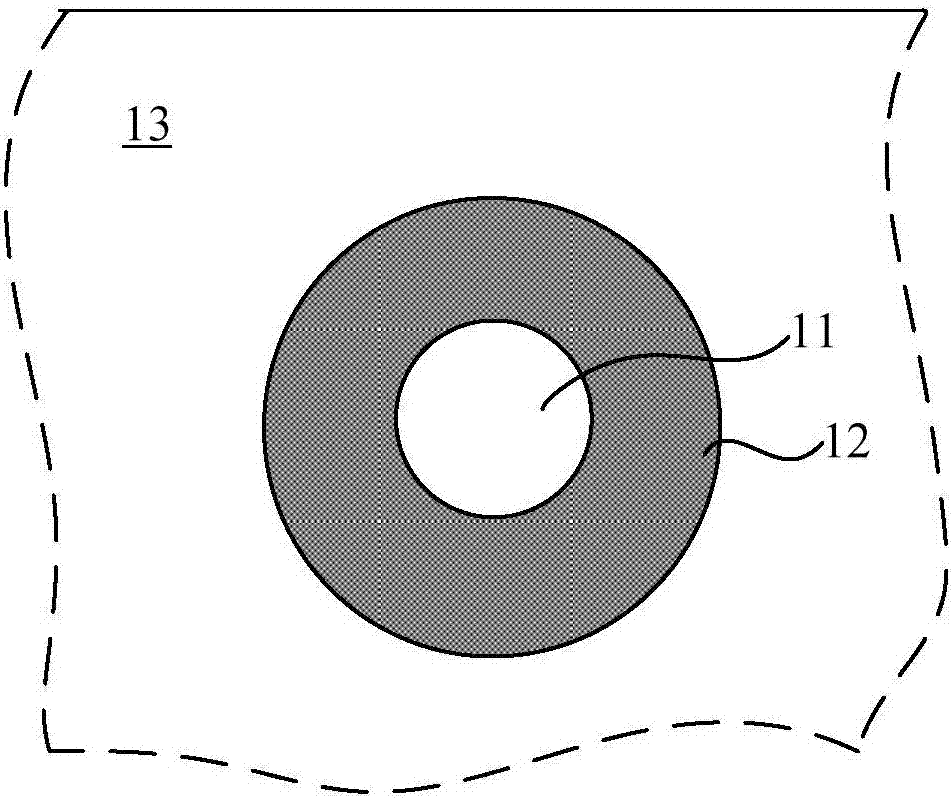
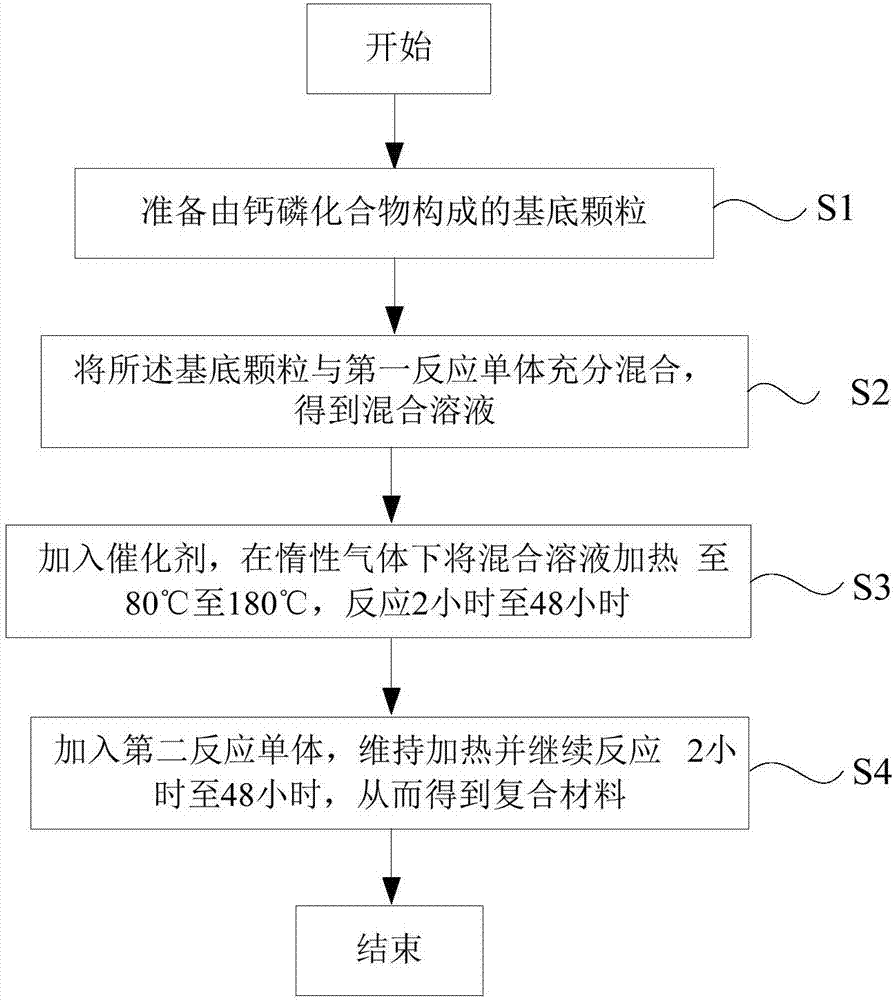
Absorbable biomedical composite material and preparation method thereof
A composite material and biomedical technology, which is applied in the field of biomedical composite materials, can solve the problems of unfavorable application, damaged toughness of composite materials, and easy brittle fracture, etc., and achieve the effect of inhibiting the decline of strength, improving toughness, and alleviating microcracks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Mix 0.1g of hydroxyapatite with a particle diameter of 5nm, 0.06g of L-lactide monomer and 0.06g of caprolactone monomer evenly, add 40ul of stannous octoate, then stir and heat to 180°C under nitrogen protection , after the reaction mixture melted evenly, the stirring reaction was continued for 2 hours to form a hydroxyapatite-rubber layer. Then, 10 g of L-lactide was added to the reaction system, and the reaction was continued at 180° C. for 2 hours.
[0081] After the reaction, the reaction mixture was dissolved in chloroform, then precipitated in methanol, and washed three times with methanol to obtain a hydroxyapatite-rubber layer-polylactic acid composite material.
[0082] The resulting hydroxyapatite-rubbery layer composite material and hydroxyapatite-rubbery layer-polylactic acid composite material were dissolved in chloroform respectively, and then centrifuged at a speed of 15000rpm, and the supernatant was precipitated in methanol and After cleaning, the fre...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Mix 1g of hydroxyapatite with a particle diameter of 200um, 0.4g of L-lactide monomer, 0.4g of p-dioxanone monomer and 0.4g of glycolide monomer in 100ml of dry toluene, add 160ul of octanoic acid Stinous, then stirred and heated to 80 degrees Celsius under the protection of argon, after the reactants were mixed and dissolved evenly, continued to stir and react for 48 hours to form a hydroxyapatite-rubber layer. Then, 8.5 g of glycolide was added to the reaction system, and the reaction was continued at 80 degrees Celsius for 48 hours.
[0090] After the reaction, the reaction mixture was precipitated in methanol and washed three times with methanol to obtain a hydroxyapatite-rubbery layer-polyglycolide composite material.
[0091] The obtained hydroxyapatite-rubbery layer composite material and hydroxyapatite-rubbery layer-polyglycolide composite material were respectively dissolved in chloroform, then centrifuged at a speed of 15000rpm, and the supernatant was taken i...
Embodiment 3
[0094]Mix 0.5g of hydroxyapatite with a particle diameter of 200nm and 0.3g of caprolactone monomer in 100ml of dry toluene, add 100ul of stannous octoate, then stir and heat to 120 degrees Celsius under the protection of argon, and wait until the reactants are mixed After dissolving evenly, continue to stir and react for 12 hours, then add 0.3 g of p-dioxanone monomer, and continue to react at 120 degrees Celsius for 12 hours to form a hydroxyapatite-rubber layer. Then add 4.6g of glycolide to the reaction system, continue to react at 130 degrees Celsius for 24 hours, then add 4.6g of L-lactide, continue to react at 130 degrees Celsius for 24 hours.
[0095] After the reaction, the reaction mixture was precipitated in methanol and washed three times with methanol to obtain a hydroxyapatite-rubber layer-polylactic acid glycolic acid composite material.
[0096] The obtained hydroxyapatite-rubbery layer composite material and hydroxyapatite-rubbery layer-polylactic acid glycoli...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com