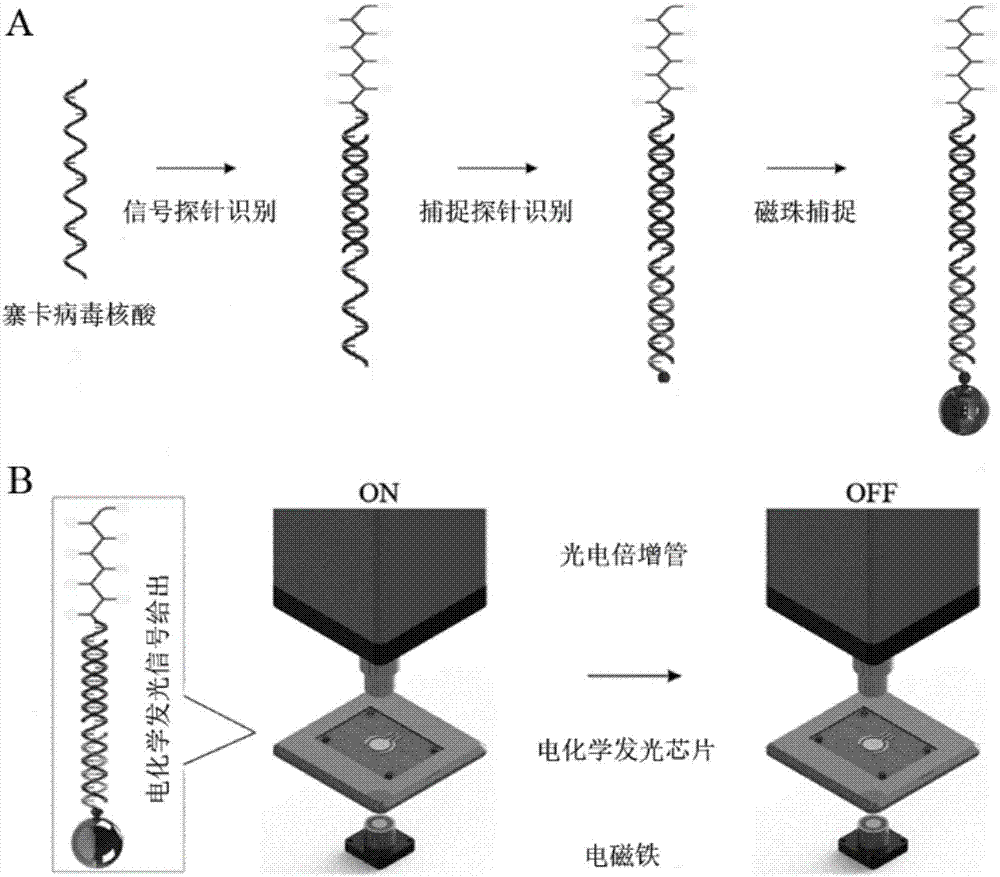
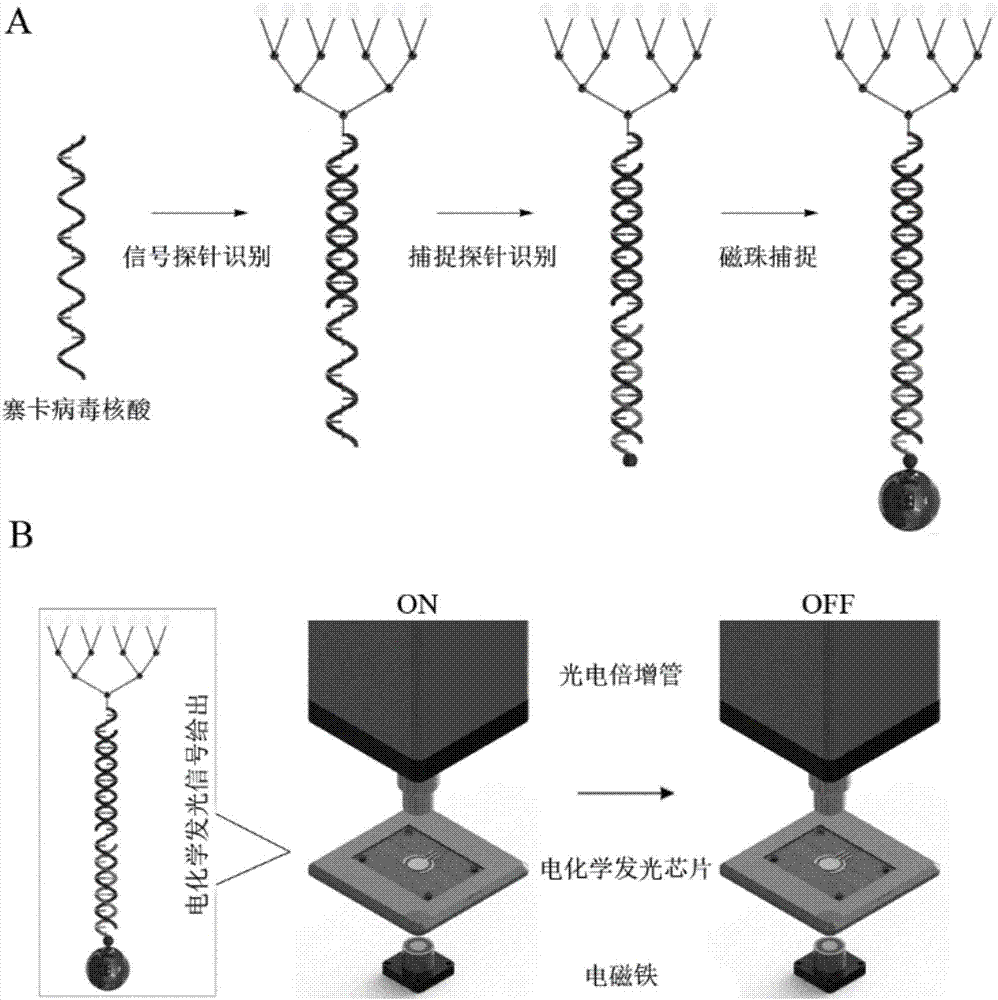
Zika virus nucleic acid detection method based on electrochemical luminescence amplification principle
A Zika virus and detection method technology, which is applied in the field of Zika virus nucleic acid detection based on the principle of electrochemiluminescence amplification, can solve the problems of Zika virus detection mode, time-consuming, and cumbersome detection process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Example 1 Zika virus detection technical route
[0111] (1) Zika virus nucleic acid extraction
[0112] ①Collect certain tissue or cell samples. The tissue and cell samples must be samples infected with Zika virus. The weight of a single extracted tissue should be less than 0.1g. 7 cells, to avoid too many samples resulting in ineffective cell lysis;
[0113] ② Sample pretreatment:
[0114] a. Tissue samples
[0115] Grind the tissue into powder in liquid nitrogen, add 1mL of sample protector, shake it 3-5 times with an oscillator (1-2 seconds each time), let it rest for 30 minutes, remove the RNase in the cells, centrifuge for 30 minutes, and remove the supernatant. clear;
[0116] b. Monolayer adherent cell sample
[0117] Remove the liquid medium in the culture plate, add trypsin to the culture plate, digest the cells for 1 min, add the medium to stop the digestion, collect the cells by centrifugation and discard the supernatant, add 1 mL of sample protector, sh...
Embodiment 2
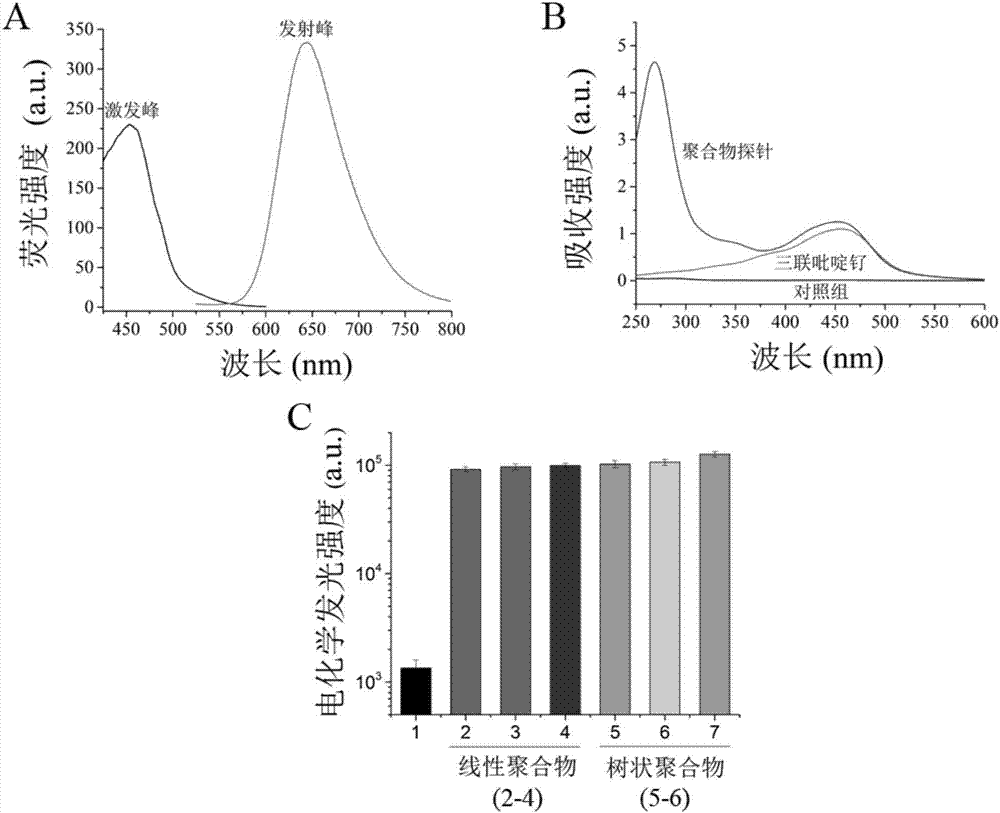
[0148] Example 2 Probe Characterization and Detection Principle Verification
[0149] In order to verify the feasibility of the construction of the probe of the present invention, the inventor characterized the labeling of the probe and the DNA connection (experimental results such as image 3 A, B shown). The inventor first detected the excitation and emission spectra of the terpyridine ruthenium polymer ( image 3 A), the experimental results show that the ruthenium terpyridine polymer has a maximum absorption peak at 460nm, and its emission peak is at 650nm, which is consistent with a single ruthenium terpyridine molecule. At the same time, the inventor characterized the product after the polymer was linked to the DNA nucleic acid, and the experimental results were as follows: image 3 As shown in B, a single ruthenium terpyridine polymer molecule has an absorption peak at 460nm, and when the ruthenium terpyridine polymer is connected with a DNA probe to construct an elec...
Embodiment 3
[0151] Example 3 Detection condition optimization and performance evaluation
[0152] The key point of the probe construction system of the present invention lies in the ratio and purification of the ruthenium terpyridine polymer and the DNA recognition domain when the polymer probe is constructed. The inventors set different molecular ratios and purified the product by ultrafiltration .
[0153] First, the inventors set different molecular ratio polymers, polymer: DNA recognition domain = 1:1, 1:10, 1:20, 1:30, 1:40, 1:50, 1:60, 1: 70, and in the case of sufficient reaction time, the electrochemiluminescent intensity after the probe captured the target nucleic acid was compared (the experimental results are as follows Figure 4 Shown in A), increases with the concentration of the DNA recognition domain and reaches a plateau when the ratio of polymer:DNA recognition domain is 1:50. Therefore, the present invention regards polymer:DNA recognition domain=1:50 as the optimal mo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com