InGaN-based MSM visible light photoelectric detector with groove-type electrode structure
A photodetector and electrode structure technology, applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems of epitaxial layer dislocation, phase separation, uneven distribution of In, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
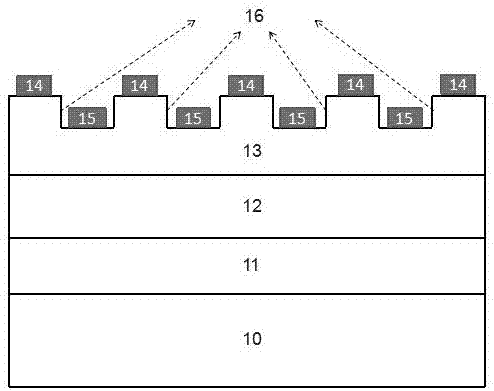
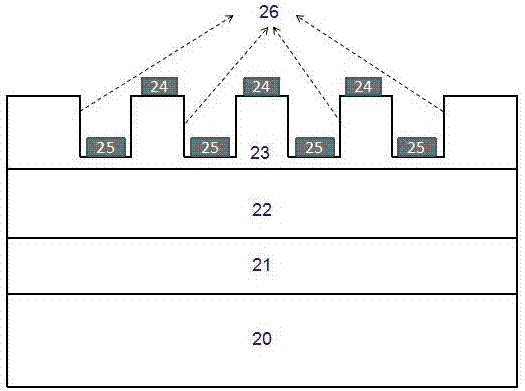
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, this method mainly provides an InGaN-based MSM visible light photodetector with a grooved electrode structure. layer, wherein the order of the epitaxial layer from bottom to top is the low-temperature GaN buffer layer 21, the unintentionally doped GaN layer 22, and the unintentionally doped In x Ga 1-x N active layer 23, deposited on In by electron beam evaporation x Ga 1-x The electrode 24 on the N layer 23 and the electrode 25 in the groove 26 . where the unintentional doping of In x Ga 1-x The wavelength range corresponding to the bandgap width in the N layer is 380-780 nm, and the thickness of the InGaN layer is 60-300 nm.
[0029] The process flow includes the following steps:
[0030] (1) Surface cleaning: Place the samples in acetone and isopropanol respectively, and ultrasonically oscillate for organic cleaning, then place the samples in 50% hydrochloric acid to remove the oxide layer on the surface, and dry them with a pure ni...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com