Manufacturing method of metal-ceramic composite substrate and composite substrate manufactured through manufacturing method
A technology of ceramic composite and manufacturing method, applied in the field of ceramic metallization, can solve the problems of decreased overcurrent capability of metal-ceramic composite substrate, increased manufacturing cost, increased electrical impedance, etc., and achieves tight bonding, decreased manufacturing cost, and reduced The effect of silver content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
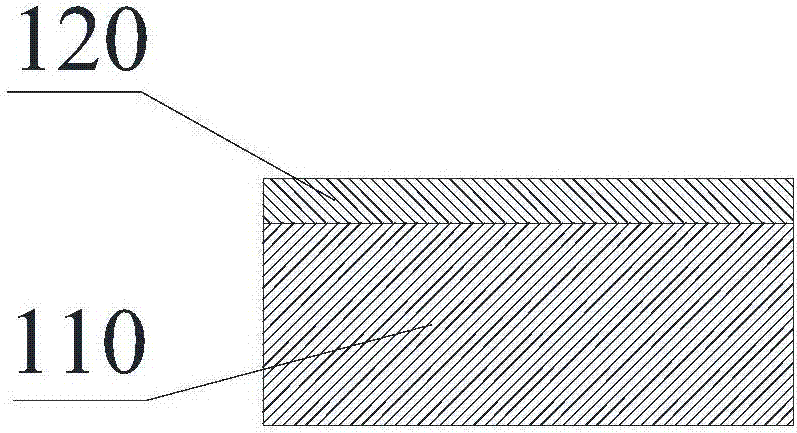
[0047] see figure 1 , printing the first brazing material (6% active metal content, 20% silver content) on the surface of the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate 110 , and drying at 100° C. for 10 minutes to obtain the first brazing material layer 120 .
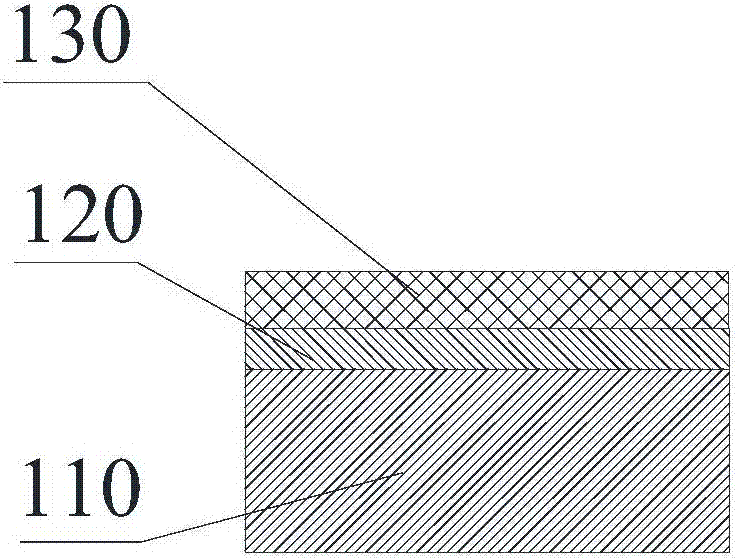
[0048] see figure 2 , printing the second brazing material (active metal content 0%, silver content 72%) on the surface of the first brazing material layer 120 away from the ceramic substrate 110, and drying at 100° C. for 10 minutes to obtain the second brazing material Material layer 130.
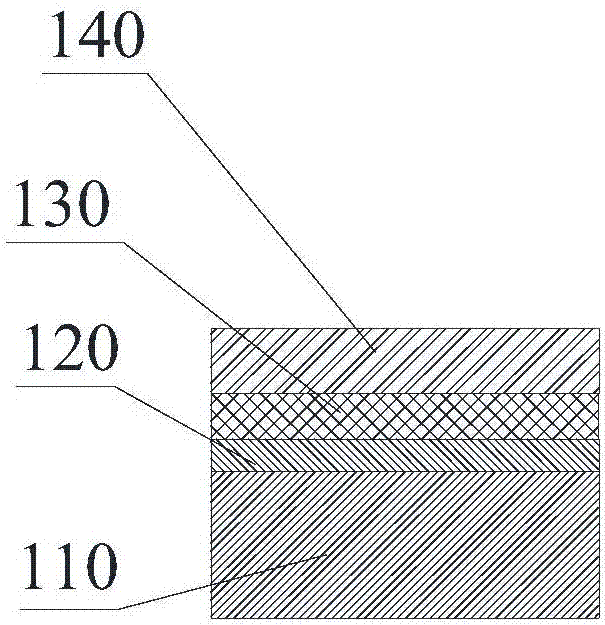
[0049] see image 3 , soak the copper foil at 60°C with 5wt% sodium hydroxide solution for 10 minutes, and wash it twice with distilled water; Second, blow dry. The treated copper foil is placed on the surface of the second solder layer 130 away from the first solder layer 120 to form a copper layer 140 .
[0050] see Figure 4 , the metal-ceramic composite substrate precursor is placed in a vacuum sintering furnace for vacuum sint...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Except that the silver content in the second layer of brazing material was increased to 78%, the rest were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 to produce a metal-ceramic composite substrate, and the same analysis was carried out. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0079] The first copper paste with a viscosity of 300 mPa·s was coated on the surface of the ceramic substrate 110 and dried at 110° C. for 10 minutes to obtain the first solder layer 120 .
[0080] The second copper paste with a viscosity of 50 mPa·s was coated on the surface of the first solder layer 120 away from the ceramic substrate 110 , and dried at 90° C. for 15 minutes to obtain the second solder layer 130 .
[0081] Soak the copper strip in 5wt% sodium hydroxide solution for 5 minutes at 60°C, wash it twice with distilled water; then soak it in 10wt% sulfuric acid solution at room temperature for 1min, and wash it with distilled water twice. The treated copper strip is placed on the surface of the second solder layer 130 away from the first solder layer 120 to form the copper layer 140 .
[0082] The metal-ceramic composite substrate precursor was vacuum sintered in a vacuum sintering furnace at 800° C. for 40 min to obtain a metal-ceramic composite substrate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| peel strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com