Method for evaluating toxicity of organic pollutants of reclaimed water based on caenorhabditis elegans
A technology for Caenorhabditis elegans and organic pollutants, applied in the field of toxicity evaluation of organic pollutants in reclaimed water, can solve the problems of low biological sensitivity, high detection cost, general sensitivity, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the drawings and embodiments. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but not to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
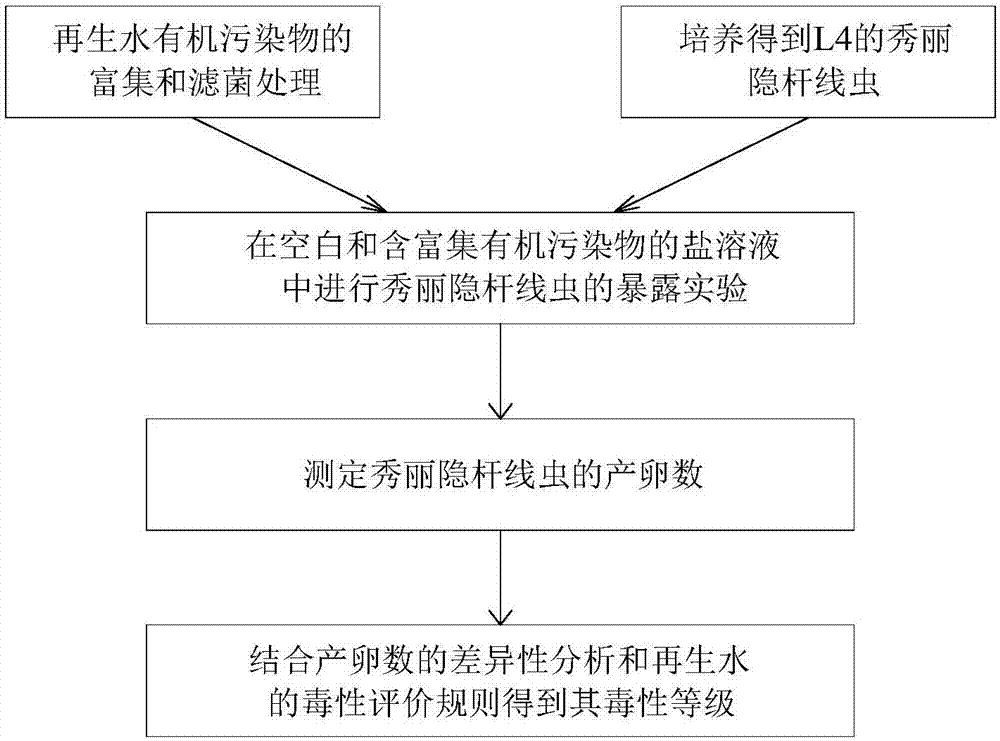
[0032] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for evaluating the biological toxicity of organic pollutants in reclaimed water based on Caenorhabditis elegans, which includes the following steps:
[0033] S1. Enrichment of organic pollutants in reclaimed water and filter bacteria treatment, including:
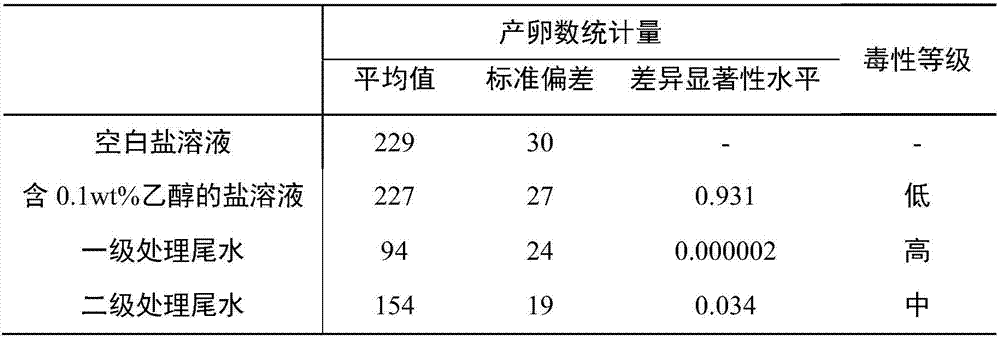
[0034] Collect the tail water after primary treatment and secondary treatment from Xiaohongmen Sewage Treatment Plant of Beijing Urban Drainage Group for use;
[0035] Prepare salt solution, weigh 0.308g sodium chloride and 0.242g potassium chloride, dissolve in 100mL pure water, sterilize at 121℃ and 100kPa high pressure for 20min;
[0036] Enrichment and filter bacteria treatment, the 500...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com