Method for extracting free nucleic acid from large-volume cell-free body fluid
A cell-free body fluid and free nucleic acid technology, applied in the direction of DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of skin corrosion, human body damage, and low extraction efficiency, and achieve the effect of increasing versatility, improving efficiency, and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
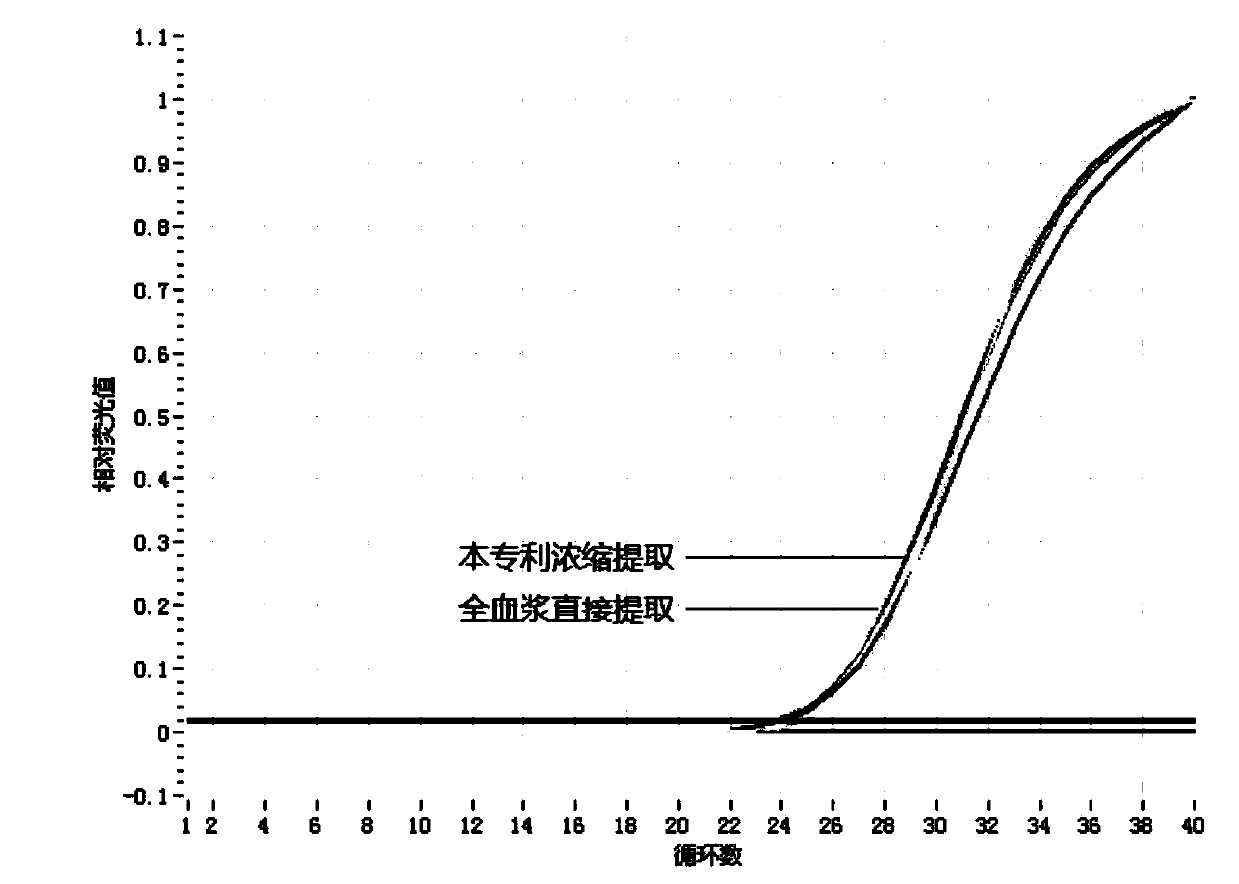
[0049] Example 1: Comparison of non-concentrated and concentrated plasma cfDNA extraction
[0050] 1) Extract plasma cfDNA without concentration
[0051] 1. Take 1ml of plasma and add it to a 2ml centrifuge tube, then add 1ml of lysate and 50ul of proteinase K, mix well, resuspend the mixture and incubate at 58°C for 1 hour;
[0052] 2. Add 400ul of isopropanol to the resuspension, mix it upside down; draw 700ul of the sample into a spin column with a 2ml collection tube, lightly cover the lid, centrifuge at 12000 r / min in a high-speed centrifuge for 1min, and discard the flow-through. Pipette the remaining samples into the spin column and repeat this operation until all the samples are transferred;
[0053] 3. Add 700ul protein-removing solution to the spin column, centrifuge at 12000 r / min for 1min in a high-speed centrifuge, discard the flow-through solution, and repeat this step once;
[0054] 4. Add 700ul of 80% ethanol to the spin column, centrifuge at 12000 r / min for ...
Embodiment 2
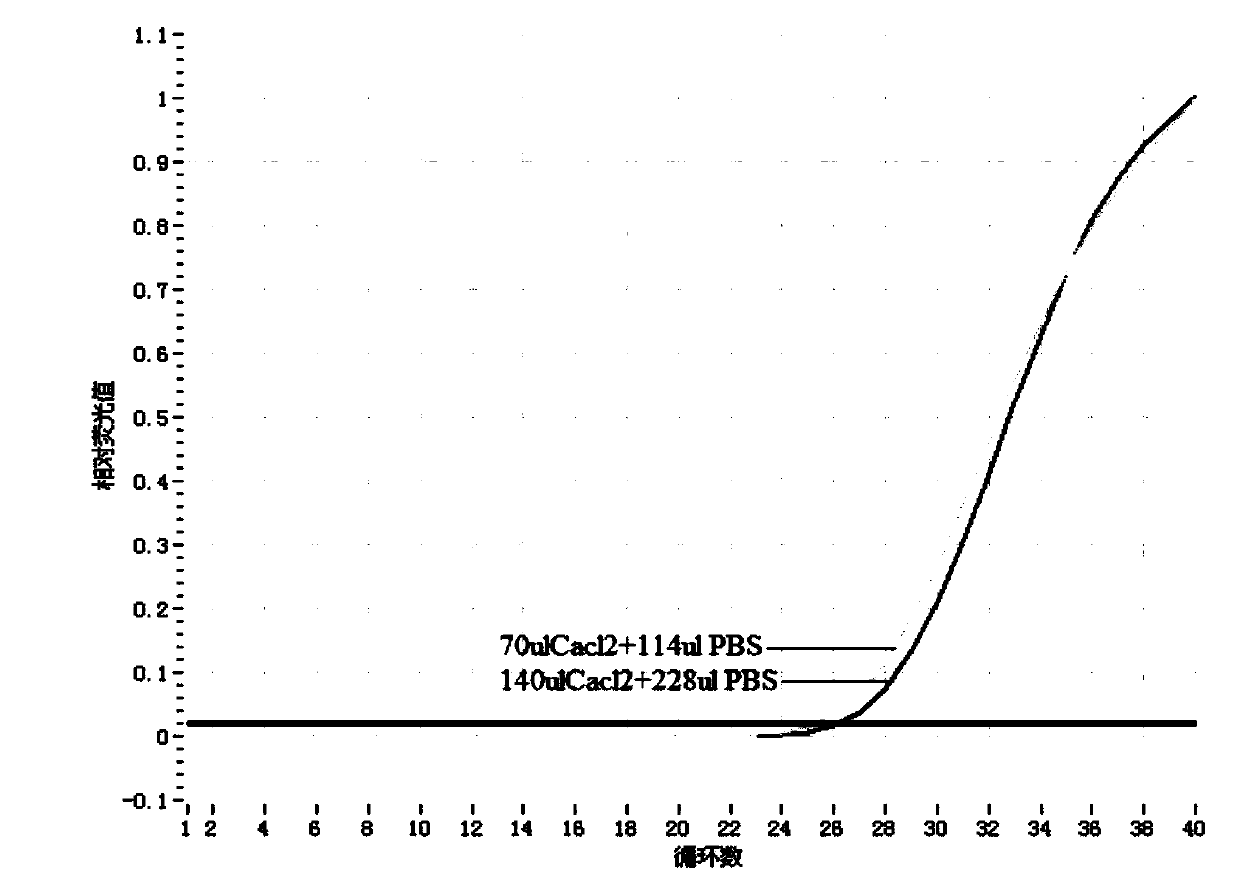
[0063] Example 2: Optimization of the amount of precipitating agent in the process of concentrating and extracting plasma cfDNA
[0064] 1. Divide 2ml of plasma into two 2ml centrifuge tubes, add 1ml of plasma in each tube, add 70ul of precipitant and 114ul of buffer, 140ul of precipitant and 228ul of buffer, and then centrifuge each The tube was vortexed, placed at room temperature for 1 min, centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 3 min in a high-speed centrifuge, and the supernatant was discarded;
[0065] Perform the following operations on the above two tubes of plasma respectively,
[0066] 2. Add 700ul of sterilized water to the sediment, mix it upside down three times, centrifuge with a high-speed centrifuge at 12000r / min for 3min, and discard the supernatant;
[0067] 3. Add 400ul lysate and 50ul proteinase K to the precipitate, resuspend the precipitate, and incubate at 58°C for 15min;
[0068] 4. Add 400ul of isopropanol to the resuspension, mix by inverting, draw 700ul o...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3: Optimization of the amount of lysate used in the process of concentrating and extracting plasma cfDNA
[0075] 1. Divide 4ml of plasma into four 2ml centrifuge tubes, add 140ul of precipitant and 228ul of buffer solution to each tube of 1ml of plasma, vortex and mix well, place at room temperature for 1min, and centrifuge at 10000r / min for 3min in a high-speed centrifuge , discard the supernatant;
[0076] 2. Add 700ul of sterilized water to the sediment of the above four centrifuge tubes, mix by inverting three times, centrifuge at 12000r / min for 3min in a high-speed centrifuge, and discard the supernatant;
[0077] 3. Add 4 different volumes of lysate to the sediment of the above 4 centrifuge tubes: 200ul lysate, 300ul lysate, 400ul and 500ul lysate, then add 50ul proteinase K to resuspend the precipitate, Incubate at 58°C for 15 minutes;
[0078] Perform the following operations on the resuspension in the above four centrifuge tubes respectively,
[007...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com