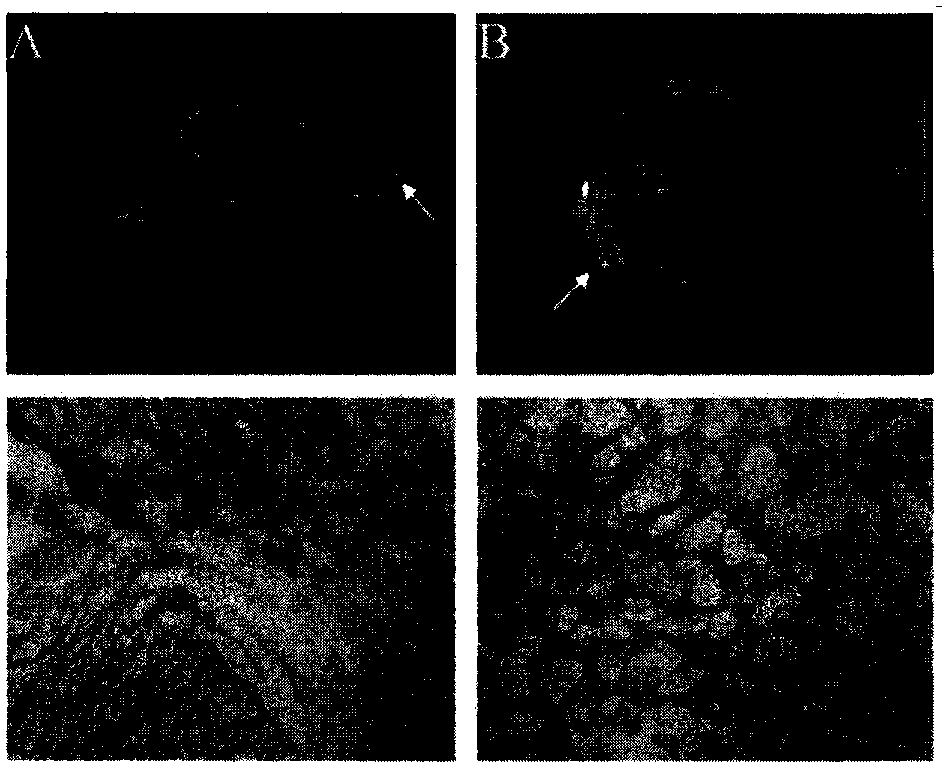
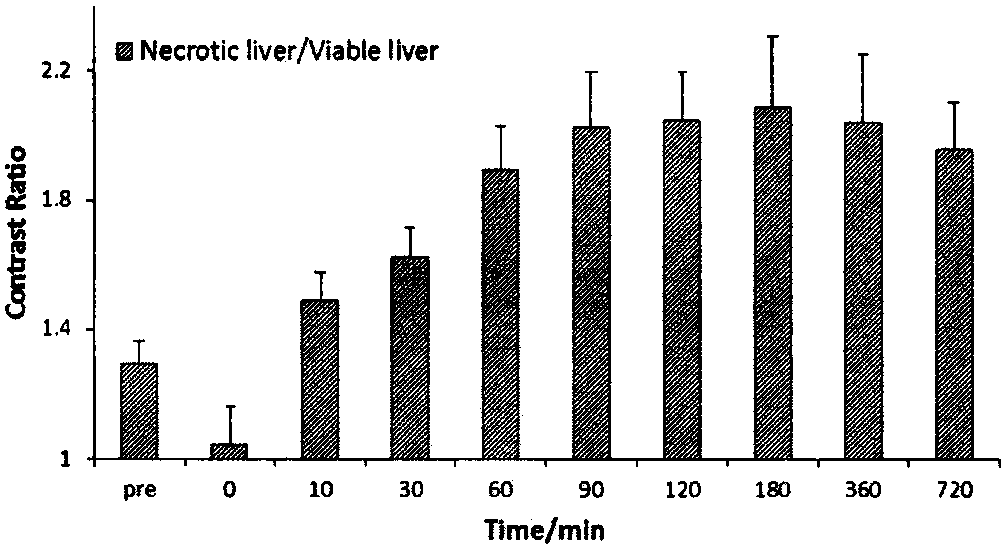
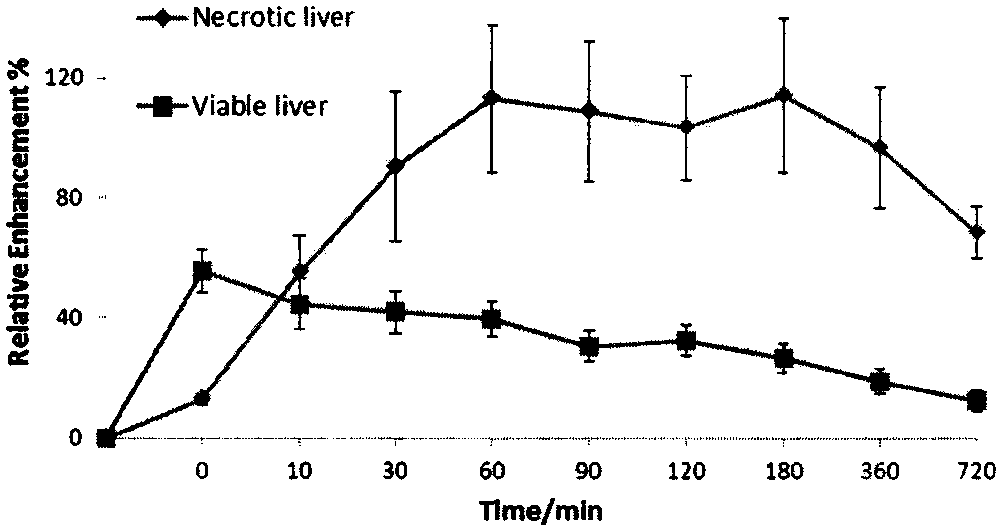
Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent
A magnetic resonance contrast agent and magnetic resonance imaging technology, applied in the field of biological imaging, can solve the problems of short residence time, narrow imaging time window, low relaxation rate, etc., and achieve stable imaging time window, long imaging time window, biological good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1
[0042] Embodiment 1-1: the synthesis of formula (I) contrast agent
[0043] Add 200mg (0.70mmol) rhein and 148mg (0.77mmol) EDC to 100mL dichloromethane solution, stir at room temperature for 30min, then add 88mg (0.77mmol) NHS, react at room temperature for 24h until the reaction system is clear, add 100μLN -Boc-Ethylenediamine was added dropwise to the reaction solution, stirred at room temperature for 24 h, filtered to obtain a yellow solid, and washed with methanol to obtain pure intermediate 1.
[0044] 200 mg (0.47 mmol) of intermediate 1 was added to 15 ml of dichloromethane / trifluoroacetic acid (10:1), reacted at room temperature for 12 h, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain intermediate 2.
[0045] Add 421mg (0.74mmol) DOTA-tris(tBu)ester, 280mg (0.74mmol) HBTU to 50mL acetonitrile, then add 100μL DIPEA, react at room temperature for 30min, then put 241mg (0.74mmol) intermediate 2 into the reaction system, Reaction 24h. The solvent was re...
Embodiment 1-2
[0049] Embodiment 1-2: the synthesis of formula (II) contrast agent
[0050] N-Boc-ethylenediamine in Example 1-1 was changed to N-Boc-butylenediamine, and the specific preparation method was the same as in Example 1-1 to obtain the magnetic resonance contrast agent of Ligand 2.
[0051] Ligand 2: 1 H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-d 6 ), δ(ppm): 11.81(s, 2H); 9.66(s, 1H); 8.18(s, 1H); 8.15(s, 1H); 7.90(s, 1H); 7.82~7.71(m, 2H) ;7.40(d, 1H, J=8.3Hz); 3.52~2.61(m, 28H); 1.57~1.55(m, 4H). 13 C NMR (75MHz, DMSO-d 6 ):δ:191.39,181.20,170.22,170.15,169.84,163.78,161.37,161.24,142.03,137.39,133.44,133.33,124.40,122.70,119.31,117.87,117.30,116.11,58.77,55.37,54.65,50.92,50.05, 49.94, 49.88, 37.93, 25.98, 25.65. ESI-MS m / z 777.2 for (M+K + -2H - ).
Embodiment 1-3
[0052] Embodiment 1-3: the synthesis of formula (III) contrast agent
[0053] N-Boc-ethylenediamine in Example 1-1 was changed to N-Boc-hexanediamine, and the specific preparation method was the same as in Example 1-1 to obtain the magnetic resonance contrast agent of Ligand 3.
[0054] Ligand 3: 1 H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-d 6 ), δ(ppm): 11.67(s, 2H); 9.14(s, 1H); 8.12(s, 2H); 7.83(s, 1H); 7.80~7.70(m, 2H); J=8.5Hz); 3.48~2.64(m, 28H); 1.56~1.32(m, 8H). 13 CNMR (75MHz, DMSO-d 6 ):δ:191.26,181.16,170.19,169.73,163.76,161.37,161.23,141.91,137.37,133.43,133.28,124.42,122.54,119.30,117.62,58.28,55.60,54.77,51.13,50.16,50.00,39.38,38.33, 28.74, 28.47, 25.95.ESI-MS m / z 805.3for ([M+K+2H] - ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com