Application of glucosamine in preparation of drug for preventing and treating ionizing radiation induced pulmonary injury
A radiation-induced lung injury and ionizing radiation technology, applied in the direction of drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of glucosamine and other problems, achieve the effect of protecting lung tissue, significant curative effect, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Cell culture: RLE-6TN cells were cultured in RMPI medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum. All cells were placed at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured in an incubator, subcultured every 2-3 days, and the cells in the logarithmic growth phase were used for experiments.
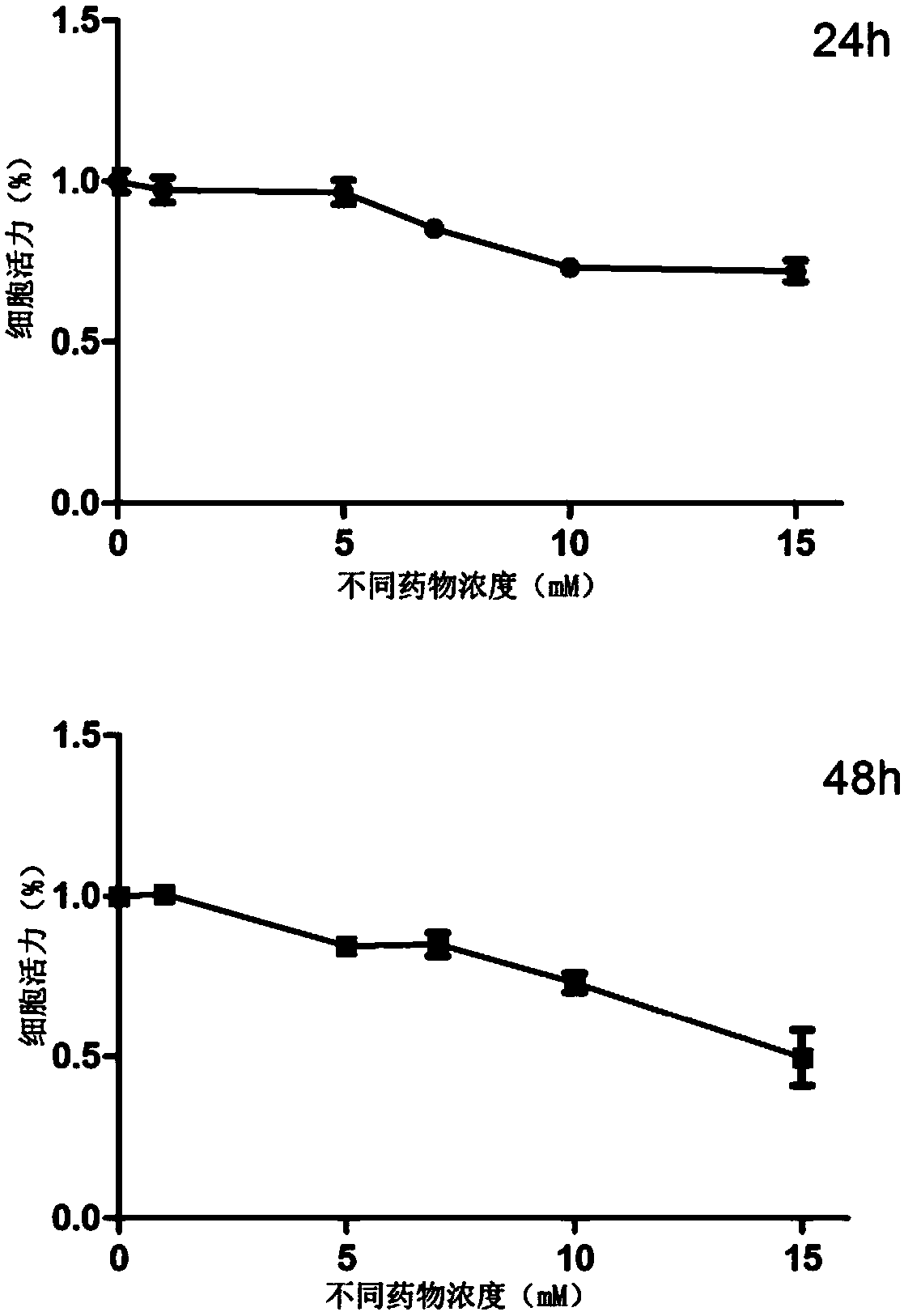
[0034] (2) CCK-8 colorimetric method: cells in logarithmic growth phase (5*10 4 / mL) were inoculated into 96-well plates, and 6 parallel wells were set up for each concentration. Different concentrations of glucosamine were added to continue culturing for 24 and 48 hours. Add 10 μL CCK-8 reagent to the cell culture medium and continue culturing for 1-4 hours. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader. Finally, the formula of cell survival rate=dosage group value / control group value×100% was used to calculate the cell survival rate.
[0035] The result is as figure 1 As shown, the results show that glucosamine less than 10mmol / L does not inhibit the growth and proliferation of RLE-6TN...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Cell culture is the same as in Example 1;
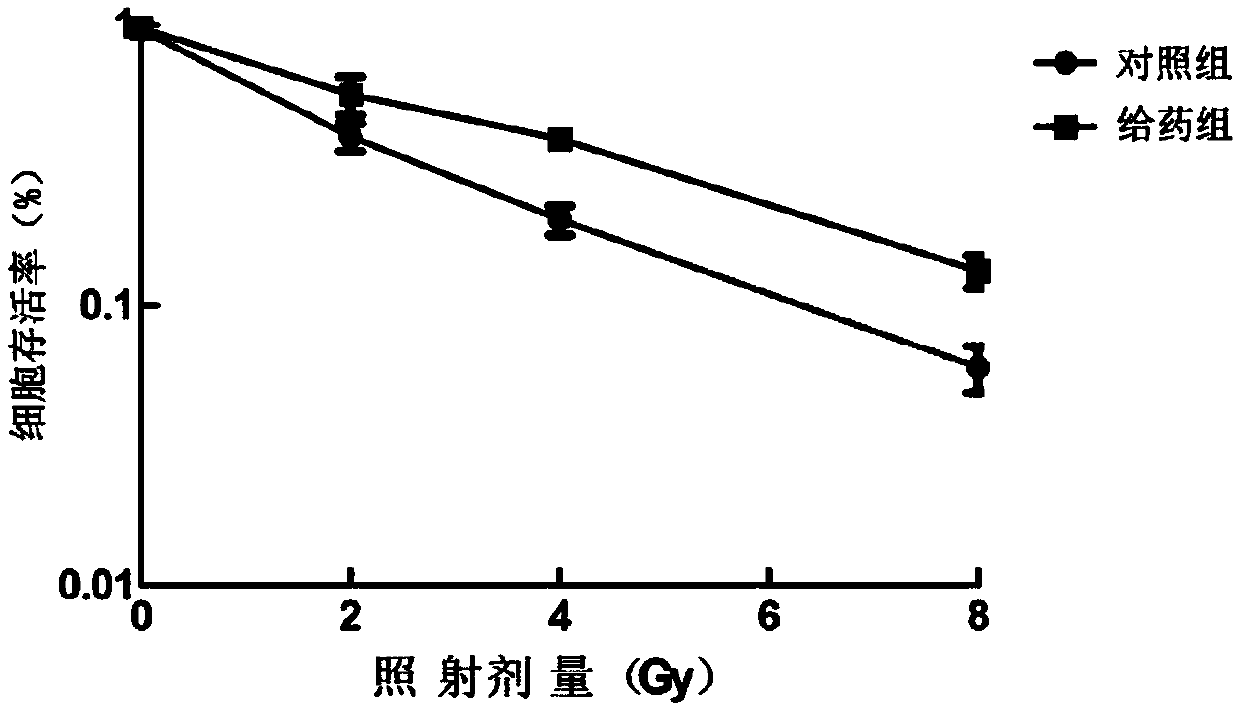
[0038] (2) Cell clone formation method: Take RLE-6TN cells in the logarithmic growth phase, and inoculate different numbers of cells into six-well plates according to different irradiation dose requirements (0, 2, 4, and 8 Gy doses inoculated with 200 cells, respectively. 400, 800 and 1600). After 24 hours, the glucosamine combined with radiation group was treated with 5 mmol / L glucosamine for 1 hour, and the control group was treated with the same amount of PBS as a negative control. Two groups of cells received different doses (0-8Gy) of 60 Coγ-rays were irradiated, and culture continued for 24 hours after irradiation. Both groups were replaced with ordinary medium, and the culture was continued until obvious cell clones visible to the naked eye appeared in the culture dish, and the culture was terminated. Discard the medium, wash twice with PBS, fix with anhydrous methanol for 30 minutes, stain with Gimsa stain for 30...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) Cell culture is the same as in Example 1;
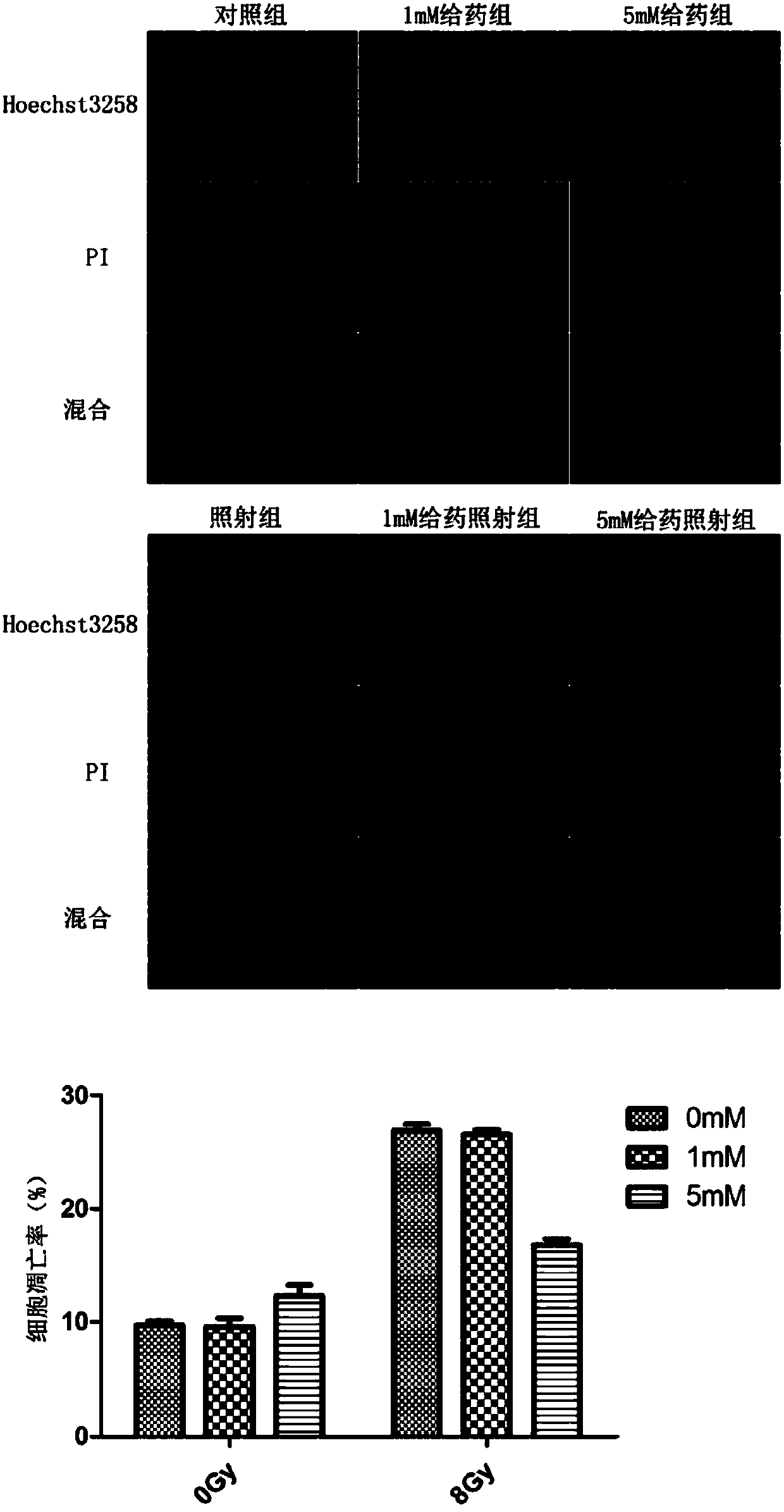
[0041] (2) Hoechst33342 staining method for detecting cell apoptosis: take RLE-6TN cells in the logarithmic growth phase (1*10 5 / mL) were inoculated into six-well plates overnight, treated with 5mmol / L glucosamine, and then irradiated with 8Gy of 60Coγ-rays, then cultured for 24h, washed three times with PBS, and fixed with paraformaldehyde. Cell apoptosis was detected after staining with Hoechst33342 and PI. The result is as image 3 It was shown that pretreatment with glucosamine (5mmol / L) at a concentration without toxic side effects can significantly reduce the apoptosis rate of RLE-6TN cells induced by radiation therapy, and the concentration of glucosamine used has no effect on RLE-6TN.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com