Pesticidal composition for killing root-knot nematode
A root-knot nematode and composition technology, applied in the direction of nematicides, biocides, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of easy occurrence of drug-resistant pests in insecticidal effects, differences in pest resistance and drug resistance, etc., which are not easy to achieve Drug resistance, no environmental toxicity, good biodegradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] This example provides a pharmaceutical composition for killing root-knot nematodes, including pumpkin seed extract, arsenic stone extract, morning glory seed extract, radish extract, radish seed extract, chamaejasma chamaejasme extract, tiger’s leg extract Extract, Boa Bougainvillea Extract, Ficus Barbadensis Extract and Veratrine in the following quantities:
[0024]
[0025]
[0026] Its preparation method: decoct pumpkin seeds, arsenic stones, and morning glory seeds twice with water, each time for 2 hours, combine the decoction, add ethanol to filter and concentrate, add 3 times the amount of water, fully stir, refrigerate for 48 hours, filter, and the filtrate reduces Concentrate under pressure until the relative density is about 1.15, and prepare the medicinal solution for later use; add radish, radish, chamaejasma chamaejasme, tiger's leg, anaconda, and banyan to decoct twice, each time for 1 hour, combine the decoction, filter, and concentrate Let the filt...
Embodiment 2
[0029] This example verifies the killing rate of root-knot nematodes of the pharmaceutical composition compared with common insecticides on the market.
[0030] Select the common insecticides on the market: P. lilacinus water agent, nematicide, special root thread agent, and thiamethoxam insecticide.
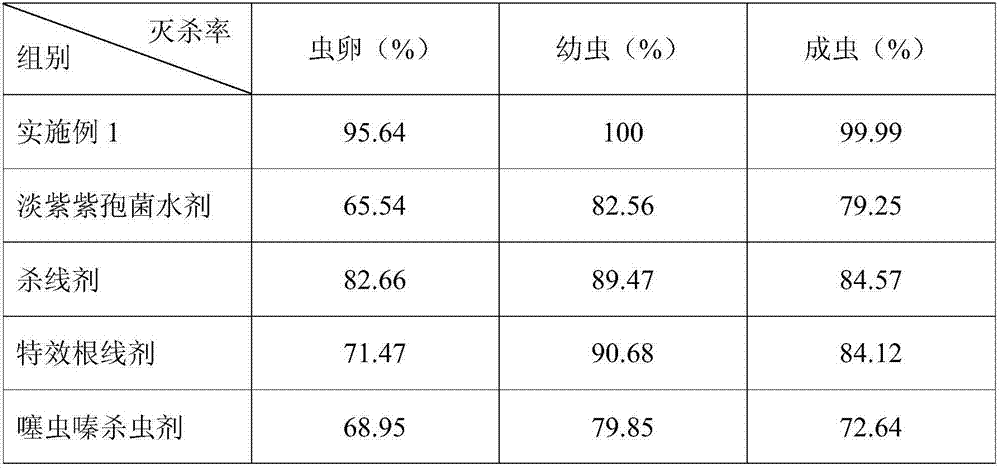
[0031] Grouping according to different insecticides, each group prepares 1000 root-knot nematodes in the three stages of eggs, larvae, and adults respectively, and then uses insecticides on the root-knot nematodes in each stage respectively, and tests each group to kill the root-knot nematodes. Insecticide kill rate, as shown in the table below:
[0032] Table 1 The killing effect of insecticides on root-knot nematodes
[0033]
[0034] It can be seen from the above table that each group of insecticides has the highest killing rate on root-knot nematodes in the larval state, and this product has the best insecticidal effect, and the killing effect is remarkable, and it can k...
Embodiment 3
[0036] This example verifies the killing rate of the pharmaceutical composition on various pests.
[0037] Select 10,000 scarabs, beetles, leafhoppers, borers, pear psyllids, scale insects, spodoptera, mole crickets, vetch, and root-knot nematodes, and group them respectively, and use the medicines prepared in Example 1 to make medicines of the same concentration. liquid, spray the pests of each group respectively, and after 1 hour, check the killing rate of various pests, the results are shown in the following table:
[0038] Table 2 The killing effect of the drug on various pests
[0039] group
[0040] As can be seen from the above table, the medicine prepared in Example 1 only has a good killing effect on root-knot nematodes, and has a very limited killing effect on other pests. This proves that this product is highly targeted and can only be used to kill root-knot nematodes. Used for killing root-knot nematodes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com