Recovery process for waste zinc ions in viscose production
A technology of viscose fiber and zinc ions, which is applied in the field of recovery process of waste zinc ions in the production of viscose fiber, can solve the problems of zinc waste and environmental pollution, and achieve the effect of effective recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] A recovery process for waste zinc ions in viscose fiber production, comprising the steps of:
[0022] (1) Viscose fiber wastewater treatment: add lime powder to the wastewater generated in the production of viscose fiber, react and settle to obtain sediment;
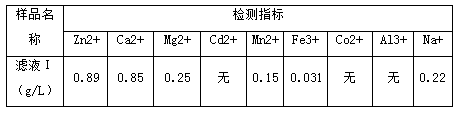
[0023] (2) Add sulfuric acid solution to the sediment obtained in step (1), stir and dissolve, then filter to obtain filtrate I, set aside,
[0024] (3) adding sodium hydroxide to the filtrate I obtained in step (2), so that the pH of the filtrate I is 7, after the reaction, filter to obtain the filtrate II for subsequent use;
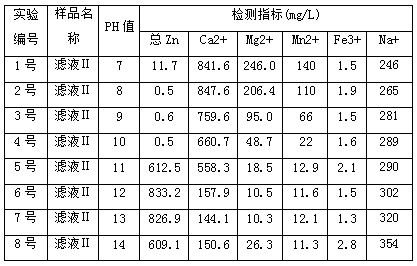
[0025] (4) Adjust the filtrate II to be acidic with a sulfuric acid solution, and then use a macroporous chelating type divinylbenzene polymerized ion exchange resin to absorb zinc ions in the filtrate II;
[0026] (5) Use sulfuric acid solution to rinse the macroporous chelated divinylbenzene polymer ion exchange resin that has absorbed zinc ions in the filtrate II in step (4) to desorb ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A recovery process for waste zinc ions in viscose fiber production, comprising the steps of:
[0029] (1) Viscose fiber wastewater treatment: add lime powder to the wastewater generated in the production of viscose fiber, react and settle to obtain sediment; wherein, the amount of lime powder added is 30kg per ton of wastewater.
[0030] (2) Add sulfuric acid solution to the sediment obtained in step (1), stir and dissolve, then filter to obtain filtrate I, set aside,
[0031] (3) adding sodium hydroxide to the filtrate I obtained in step (2), so that the pH of the filtrate I is 8, after the reaction, filter to obtain the filtrate II for subsequent use;
[0032] (4) adjust the pH of filtrate II to 3.5 with sulfuric acid solution, and the concentration of said sulfuric acid solution is 5g / L; then adopt macroporous chelating type divinylbenzene polymerized ion exchange resin to adsorb zinc ions in filtrate II;
[0033] (5) Use sulfuric acid solution to rinse the macropor...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A recovery process for waste zinc ions in viscose fiber production, comprising the steps of:
[0036] (1) Viscose fiber wastewater treatment: add lime powder to the wastewater generated in the production of viscose fiber, react and settle to obtain sediment; wherein, the amount of lime powder added is 35kg per ton of wastewater.
[0037] (2) Add sulfuric acid solution to the sediment obtained in step (1), stir and dissolve, and filter to obtain filtrate I, for subsequent use, the concentration of the sulfuric acid solution is 2g / L; wherein, the volume of the sulfuric acid solution and the sediment The mass ratio is 5:1.
[0038] (3) adding sodium hydroxide to the filtrate I obtained in step (2), so that the pH of the filtrate I is 9, after the reaction, filter to obtain the filtrate II for subsequent use;
[0039] (4) adjust the pH of filtrate II to 4 with sulfuric acid solution, and the concentration of said sulfuric acid solution is 5g / L; then adopt macroporous chela...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com