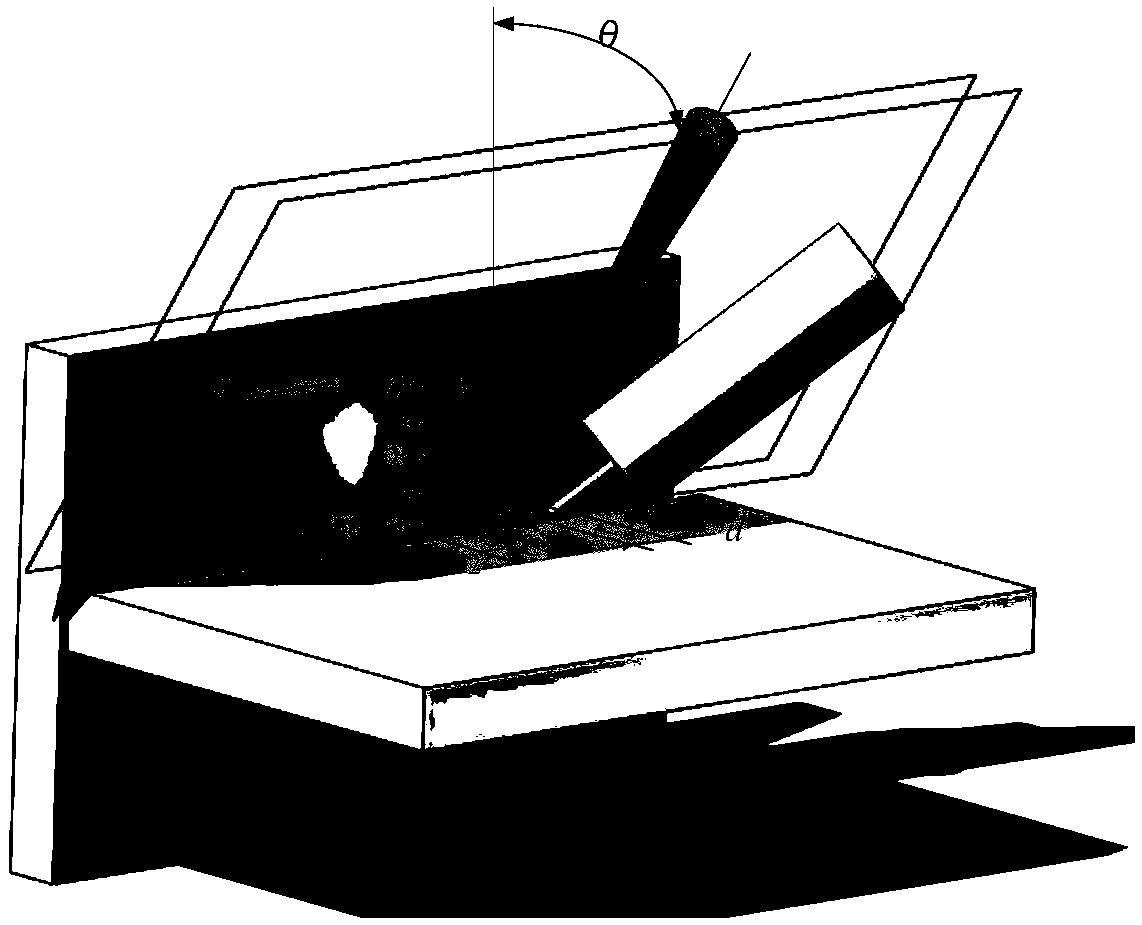
A beam-wire dislocation laser-mag composite welding method for corner joints of medium and thick plates
A composite welding and welding wire technology, which is applied in the field of beam-welding wire misalignment laser-MAG composite welding of medium and thick plate corner joints, can solve the problems of great influence on the preparation accuracy and welding quality, uneven surface welds, and incomplete penetration of back welds, etc. problems, to achieve the effects of improving mechanical properties and sealing performance, narrowing the heat-affected zone, and reducing residual deformation and residual stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0039] Specific implementation mode 1: using laser beam-welding wire dislocation laser-MAG composite welding medium and thick plate fillet joints, the laser can use CO 2 Gas lasers, YAG solid-state lasers, semiconductor lasers, fiber lasers, etc. Among them, YAG solid-state lasers, semiconductor lasers or fiber lasers that use optical fiber transmission have the best welding effect because they are more flexible and efficient. MAG adopts the Fronius TPS4000 MAG arc welding machine, and assembles and connects the fiber laser-MAG composite welding head with the Kuka robot.
[0040] Step 1: Process the part to be welded of the workpiece (horizontal plate in the fillet joint) into a single V-shaped groove, a single U-shaped groove, a single Y-shaped groove or a single U-shaped groove with a blunt edge as required, and Grind or clean the processed single-sided groove, the surfaces on both sides, and the surface of the vertical plate, and fix the polished or cleaned workpiece to be ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the laser is CO 2 Gas laser, YAG solid-state laser, semiconductor laser or fiber laser. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
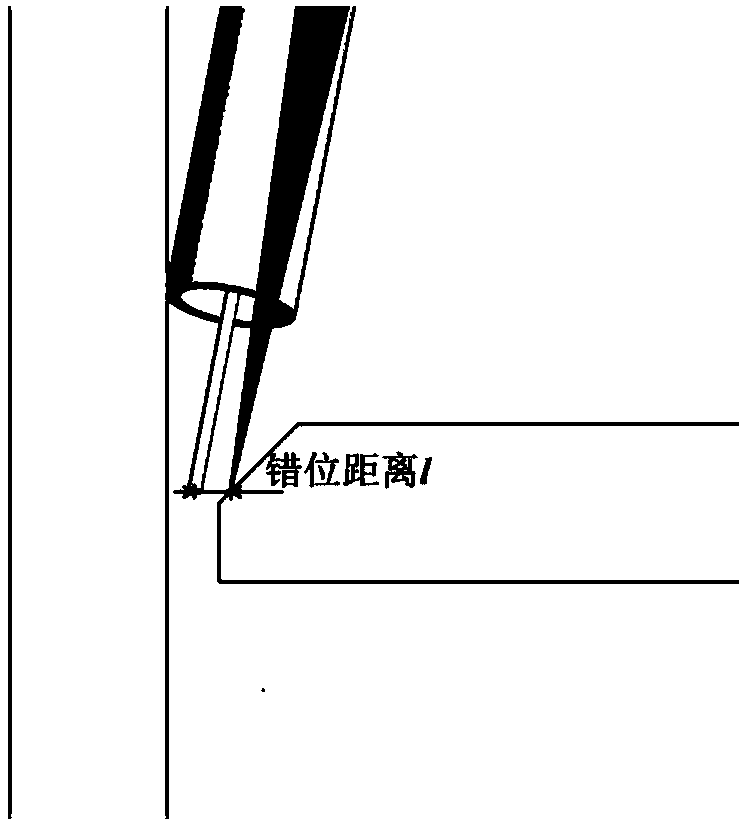
[0050] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the laser beam and the tip of the welding wire are staggered along the direction perpendicular to the weld seam, which means that the plane swept by the laser beam along the moving direction and the plane swept by the welding wire along the moving direction The planes are staggered along the direction perpendicular to the weld. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com