Laminated structure of a photovoltaic module and preparation method thereof, photovoltaic module
A laminated structure and photovoltaic module technology, which is applied in lamination, lamination devices, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, heavy weight of packaging materials, and affecting appearance, and achieve low manufacturing cost and weight reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
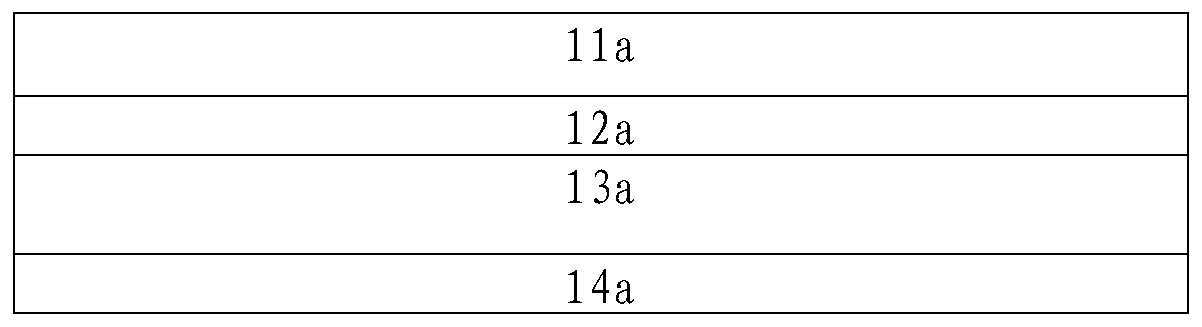
[0058] See figure 2 As shown, a laminated structure of a photovoltaic module, the laminated structure includes a first encapsulation layer 11a, a solar cell string 13a and a second encapsulation layer 14a, wherein,
[0059] Preferably, in order to further enhance weather resistance, the laminated structure includes a fluoroplastic film layer, and the fluoroplastic film layer is located above the first encapsulation layer. Preferably, in order to provide toughness protection for the solar cell strings, the laminated structure includes an encapsulation film layer, and the encapsulation film layer can be separately arranged between the first encapsulation layer and the solar cell strings or between the solar cell strings and the second encapsulation layer, It can also be arranged between the first encapsulation layer and the solar battery string and between the solar battery string and the second encapsulation layer at the same time. Further preferably, the encapsulation film l...
Embodiment 2
[0086] See image 3 As shown, in this embodiment 2, the laminated structure includes a fluoroplastic film layer 11b, a first encapsulation layer 12b, a first encapsulation adhesive film layer 13b, a solar cell string 14b and a second encapsulation layer 15b, and the fluoroplastic film layer 11b Located above the first encapsulation layer 12b, the rest of the technical solution of this embodiment 2 is the same as that of the above-mentioned embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
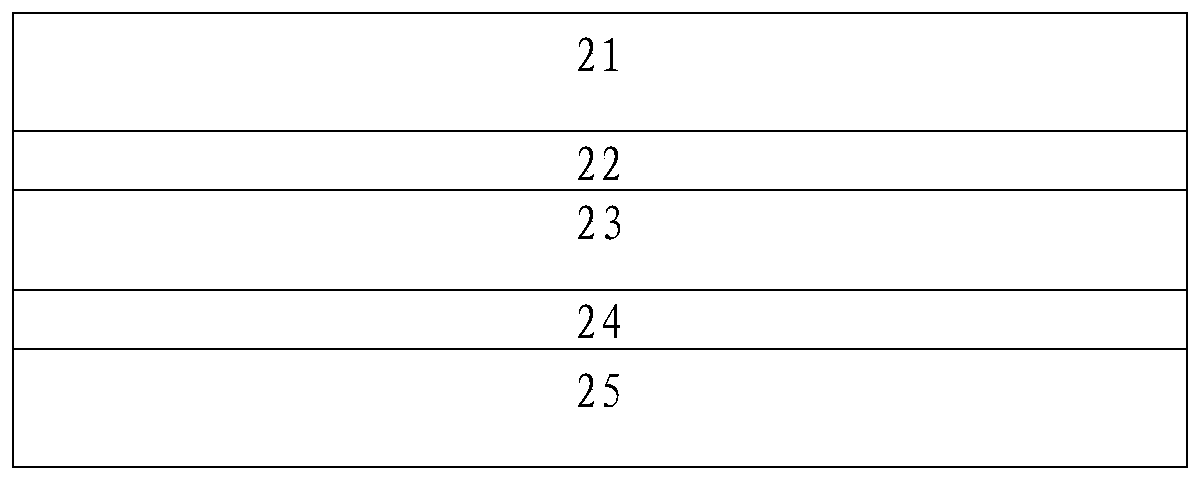
[0088] See Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment 3, the laminated structure includes a first encapsulation layer 11c, a first encapsulation film layer 12c, a solar cell string 13c, a second encapsulation layer 14c and a back sheet layer 15c, and the back sheet layer 15c is located at the second Underneath the second encapsulation layer 14c, the rest of the technical solution of the third embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment above.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com