Fabrication of nanostructured substrates comprising a plurality of nanostructure gradients on a single substrate
A nanostructure and substrate technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for information processing, can solve the problems of optical path realignment, complex replacement process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0093] Formation of multiple nanostructure gradients on the same single substrate
[0094] 1. Provide composite substrate
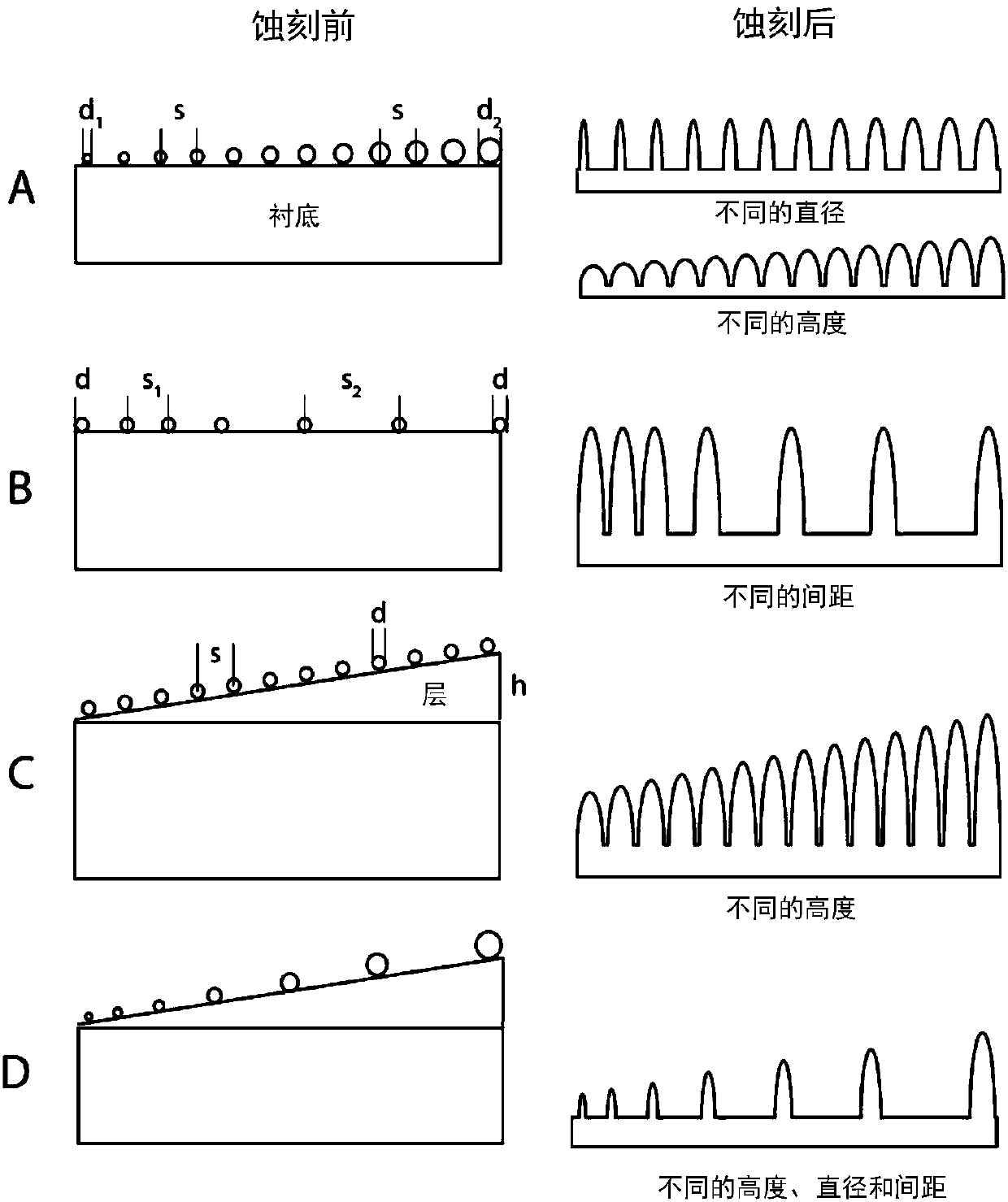
[0095] Primary substrates, such as transparent quartz glass, are coated by sputtering (UHV systems; target 99.995% SiO 2 , 3.00 inches in diameter, 0.125 inches thick, using 2*10 with 150W RF power -3 O of mbar 2 and Ar room temperature sputtering, base pressure: 10 -6 mbar) is coated with at least one layer of a material easily etched by RIE, such as SiO 2 formed.
[0096] By slowly tilting the substrate during deposition, a gradient of thickness variation can be deposited on the substrate. By choosing an appropriate deposition method and varying the tilt orientation during deposition, simple 2D gradients or more complex 3D gradients with linearly or otherwise increasing layer thicknesses can be formed ( figure 2 comparison in ).
[0097] 2. Provide nanoparticle arrays on the substrate surface
[0098] The surface of the graded "sacrificial" la...
example 2
[0139] Characterization of nanostructured composite or primary substrates
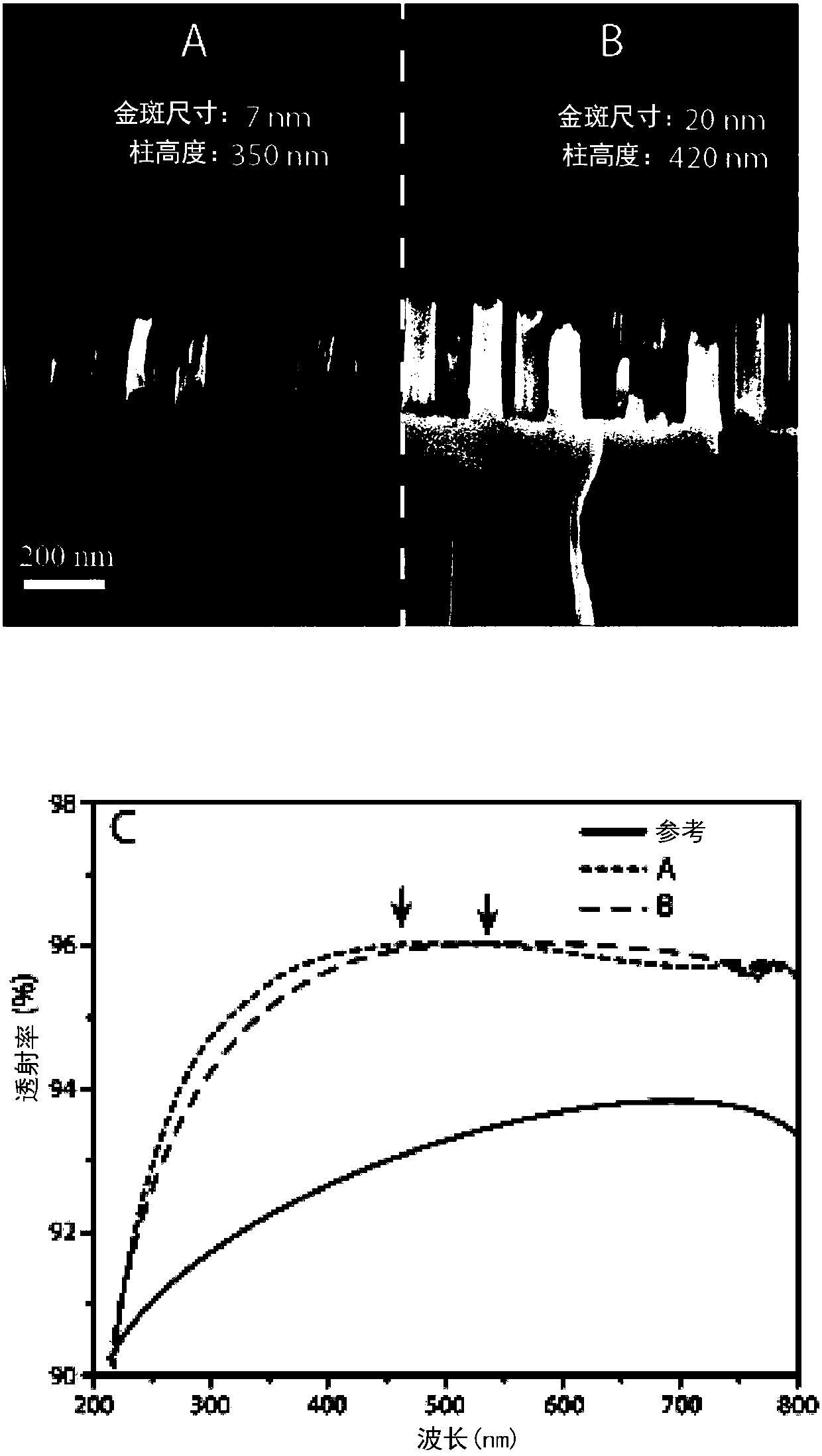
[0140] with gradient SiO 2 layer and electroless treated BCML patterned clear quartz samples were etched on one side using the RIE process as described above. The transmittance was then measured as a function of wavelength using a spectrometer device at ~1 mm beam size. The sample was split after measurement to take SEM pictures of the column cross-section. figure 1 A shows the geometry of the pillar structure on one side of the sample (~42 nm in diameter and 350 nm in height), figure 1 B shows the geometry on the opposite side of the same sample (~78 nm in diameter and 420 nm in height). figure 1 C shows the corresponding improved total transmission (compared to common transparent quartz substrates) and the shift in maximum projection.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com