Red monascus alpha-amylase gene as well as preparation method and application thereof
A kind of Monascus rubrum, amylase technology, applied in its preparation, genetic engineering technology and fermentation of mold, Monascus rubrum α-amylase gene field, can solve the problem of lack of α-amylase high-efficiency expression gene and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] 1. Determination of the target gene
[0058] This section describes the finding and cloning of effective amylase genes from the 13 α-amylase genes predicted by the Monascus ruberum NRRL1597 genome-wide database.
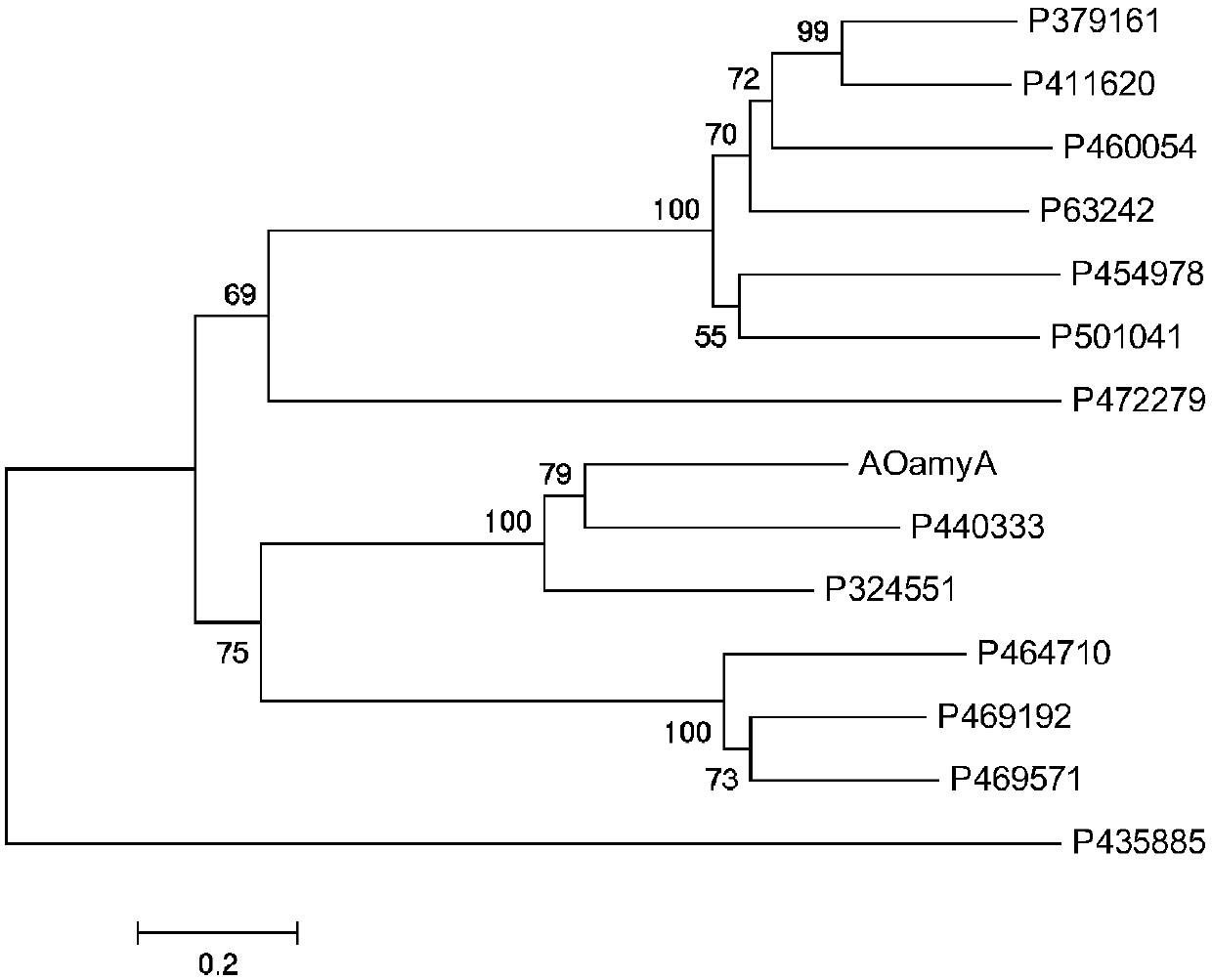
[0059] In the Monascus ruber database (https: / / genome.jgi.doe.gov / Monru1 / Monru1.home.html), the protein numbers (Protein ID) of the predicted 13 α-amylase genes are: P324551, P379161, P411620 , P435885, P63242, P440333, P454978, P460054, P464710, P469192, P469571, P501041, P472279. Through experiments, it was found that the expression of Aspergillus oryzae α-amylase A gene in Monascus can significantly promote starch degradation and increase the yield of Monascus pigment. Therefore with the protein (AOamyA) sequence of Aspergillus oryzae α-amylase A gene, and above-mentioned 13 kinds of α-amylases, construct phylogenetic tree, pattern is as follows figure 1 shown. Among them, the homology relationship between protein number P 440333 and AOamyA is 79%. Acco...
Embodiment 2
[0114] A Monascus ruberus CICC41233α-amylase gene, the DNA sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0115] The amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the α-amylase gene of Monascus ruberus is shown in SEQ ID NO:3.
[0116] The preparation method of the above-mentioned Monascus ruber α-amylase gene comprises the following steps: extracting the total DNA of the Monascus ruber strain as a template, and carrying out PCR amplification with a pair of primers whose sequences are SEQ ID No:4 and SEQ ID No:5 , the amplified product is the Monascus ruber α-amylase gene.
[0117] The method for constructing a high-yielding strain of Monascus pigment by applying the above-mentioned Monascus ruber α-amylase gene comprises the following steps:
[0118] 1) Take the Monascus rubra α-amylase gene and the pNeo0380 vector, respectively digest the two with restriction endonucleases HindIII and Sac I, and connect the digested products with T4DNA ligase to obtain a binary plasmid Expre...
Embodiment 3
[0125] A Monascus ruberus CICC41233α-amylase gene, the DNA sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0126] The method for constructing a high-yielding strain of Monascus pigment by the above-mentioned Monascus ruber α-amylase gene comprises the following steps:
[0127] 1) Take the Monascus α-amylase gene and the pNeo0380 vector, respectively digest the two with restriction endonucleases Hind III and Sac I, and connect the digested products with T4DNA ligase to obtain a binary plasmid Expression vector pNeo0380-440333;
[0128] 2) The binary plasmid expression vector pNeo0380-440333 was mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105, transformed into a Monascus ruber strain, and positive clones were screened to obtain the high-yielding strain of Monascus pigment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com