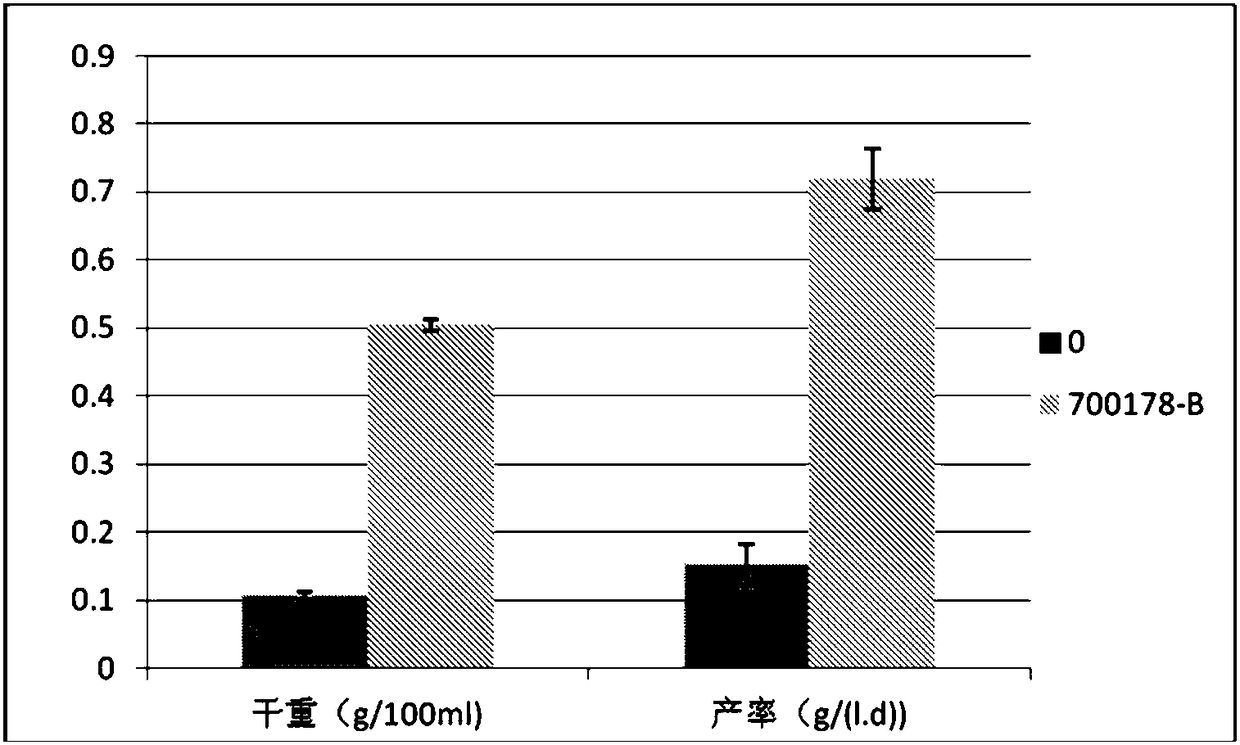
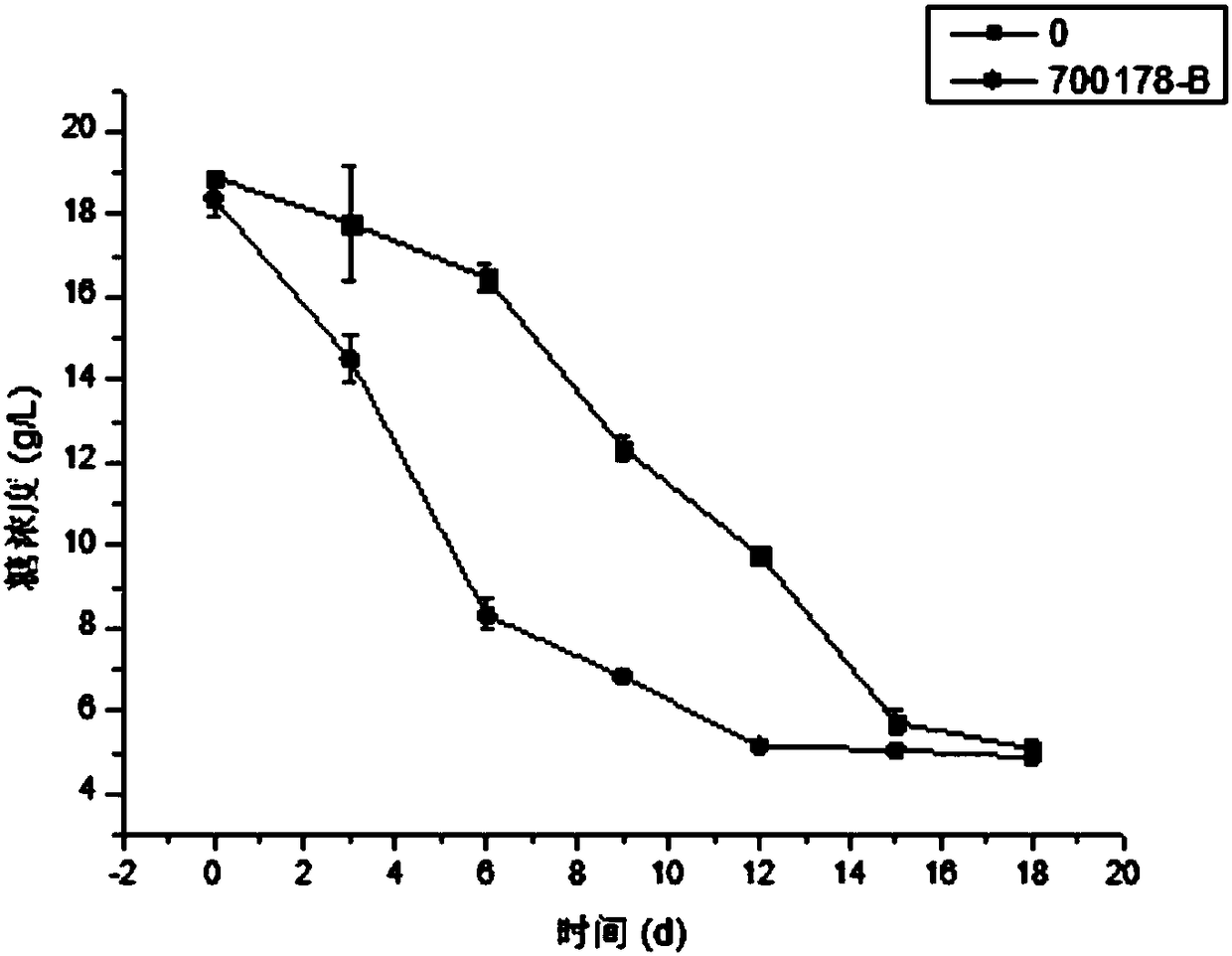
Bacterial cellulose producing bacterial strain and construction method and application thereof
A bacterial cellulose and a technology for producing strains, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as low yield and long fermentation time, and achieve the effects of increased yield, shortened fermentation time, and increased yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: Cloning of Acetobacter xylinum cellulose synthase subunit bcsB gene
[0025] First, the subunit (bcsB) related to bacterial cellulose secretion in the cellulose synthase of Acetobacter xylinum was amplified and sequenced, and a 470bp DNA fragment was obtained after amplification. The specific process is as follows:
[0026] Firstly, the genome of Acetobacter xylinum ATCC700178 was extracted, the primer pair bcsB-FA and bcsB-RC were designed, and the extracted genome of Acetobacter xylinum ATCC 700178 was used as a template for PCR amplification. The PCR reaction system was 5×PrimeSTARbuffer (Mg 2+ ) 20.0 μl, dNTP Mixture (2mM) 10.0 μl, bcsB-FA 1.0 μl, bcsB-RC 1.0 μl, PrimeSTAR 1.0 μl, template 0.5 μl; supplemented with sterile water to 100.0 μl, then aliquoted into 25.0 μl / Tube. Reaction conditions: 95°C for 5min; 95°C for 10sec; 60°C for 30sec; 72°C for 3min;
[0027] The above required primers are as follows:
[0028] bcsB-FA: tatgaccatgattacgaattc...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Construction and verification of recombinant plasmid pSA19-bcsB.
[0031] The plasmid fragment pAH4 was synthesized according to the endogenous plasmid sequence of Acetobacter xylinum on NCBI, and the plasmid pAH4 and plasmid pUC18 were digested with hindIII and recombined to obtain the recombinant plasmid pSA19 with ampicillin resistance. The pSA19 plasmid was digested with EcoRI and SalI, and the gel was recovered. The target fragment recovered from the above gel was connected to the pSA19 plasmid by one-step cloning, thereby constructing the vector pSA19-bcsB with ampicillin resistance as a selectable marker. Then, the pSA19-bcsB vector was verified by double enzyme digestion, and the verification result was in line with the expectation. The plasmid with the double enzyme digestion result in line with the expectation was sent for sequencing, which was in line with the expectation, proving that the vector was successfully constructed.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Construction and molecular verification of transformants of Acetobacter xylinum 700178 transformed with pSA19-bcsB vector.
[0033] 1 μg of pSA19-bcsB vector was transformed into Acetobacter xylinum ATCC700178 by electroporation. The transformants were screened on the selection medium containing ampicillin resistance, and finally a genetically stable Acetobacter xylinum bcsB transformant was obtained. It was verified by PCR that the above transformants were successfully inserted into the pSA19-bcsB plasmid.
[0034] The concrete method of above-mentioned electroconversion is as follows:
[0035] Competent state preparation:
[0036] 1. Scrape a ring of Acetobacter xylinum seeds from the flat plate in a 500ml Erlenmeyer flask with 100ml of seed solution, and add cellulase that has been sterilized through the membrane at the same time so that the amount of cellulase in each milliliter of medium is 0.5U. 30°C, 150rpm, culture for 18h, so that the OD value of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com