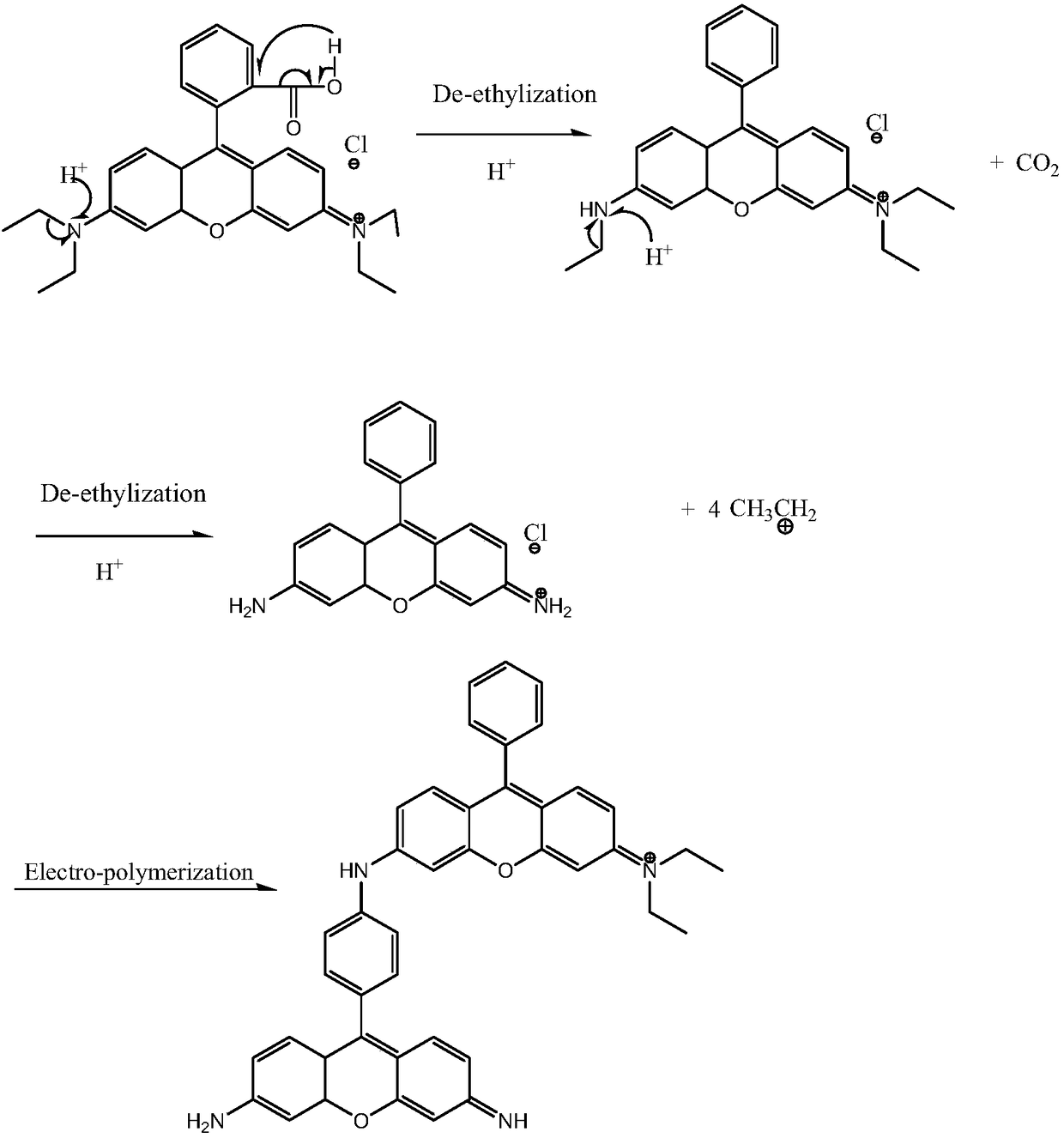
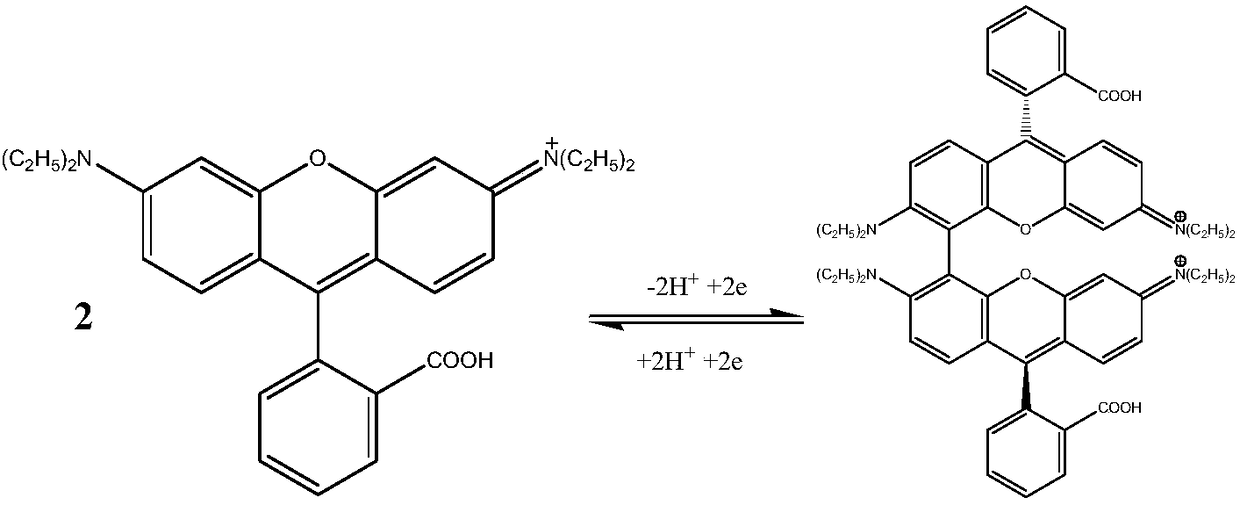
Method for decomposing rhodamine B wastewater
A wastewater and electrolyte technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor COD removal efficiency, long degradation time, high energy, etc., to reduce electrolysis energy consumption, The effect of reducing degradation time and COD value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] (1) Rhodamine B (C=100mg·dm -3 ) waste water grate sedimentation;
[0023] (2) Heating the rhodamine B wastewater treated in step (1) to 35°C, adjusting the pH to 4, and filtering after 1 hour; Fe in the wastewater 2+ , Fe 3+ , Ca 2+ Wait to form precipitate, and be filtered off, and the filtrate obtained by filtering is processed in the next step;
[0024] (3) take the filtrate after step (2) processing as electrolyte, adopt platinum electrode as oxidation electrode, adopt saturated calomel electrode as reference electrode, oxidation 5 minutes under the condition that oxidation voltage is 1.3V, rhodamine B waste water Electropolymerization occurs, resulting in a precipitate. Filter the oxidized electrolyte membrane to obtain a clear solution;
[0025] Obtain clear liquid after degrading by this embodiment, and the detection COD is 15mg·dm -3 .
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) Rhodamine B (C=100mg·dm -3 ) waste water grate sedimentation;
[0028] (2) Heating the Rhodamine B wastewater treated in step (1) to 35°C, adjusting the pH to 2, and filtering after 1 hour; Fe in the wastewater 2+ , Fe 3+ , Ca 2+ Wait to form precipitate, and be filtered off, and the filtrate obtained by filtering is processed in the next step;
[0029] (3) take the filtrate after the treatment of step (2) as electrolyte, adopt BDD electrode as oxidation electrode, adopt saturated calomel electrode as reference electrode, oxidize 5 minutes under the condition that oxidation voltage is 1.1V, rhodamine B wastewater Electropolymerization occurs, resulting in a precipitate. Filter the oxidized electrolyte membrane to obtain a clear liquid;
[0030] Obtain clear liquid after degrading by this example, and the detection COD is 50mg·dm -3 .
Embodiment 3
[0032] (1) Rhodamine B (C=100mg·dm -3 ) water grid for sedimentation;
[0033] (2) Heating the rhodamine B wastewater treated in step (1) to 50°C, adjusting the pH to 3, and filtering after 1 hour; Fe in the wastewater 2+ , Fe 3+ , Ca 2+ Wait to form precipitate, and be filtered off, and the filtrate obtained by filtering is processed in the next step;
[0034] (3) take the filtrate after the treatment of step (2) as electrolyte, adopt gold electrode as oxidation electrode, adopt saturated calomel electrode as reference electrode, oxidize 5 minutes under the condition that oxidation voltage is 1.2V, rhodamine B waste water Electropolymerization occurs, and the oxidized electrolyte membrane is filtered to obtain a clear solution;
[0035] Obtain clear liquid after degrading by this example, and the detection COD is 45mg·dm -3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com