Manufacturing method of brake drum, and brake drum
A manufacturing method and technology of brake drums, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, brake drums, casting molding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the total weight of the braking system, endangering the safety of vehicles, and poor thermal fatigue resistance, etc., and achieve a good social benefits, overall weight reduction, and strength-enhancing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
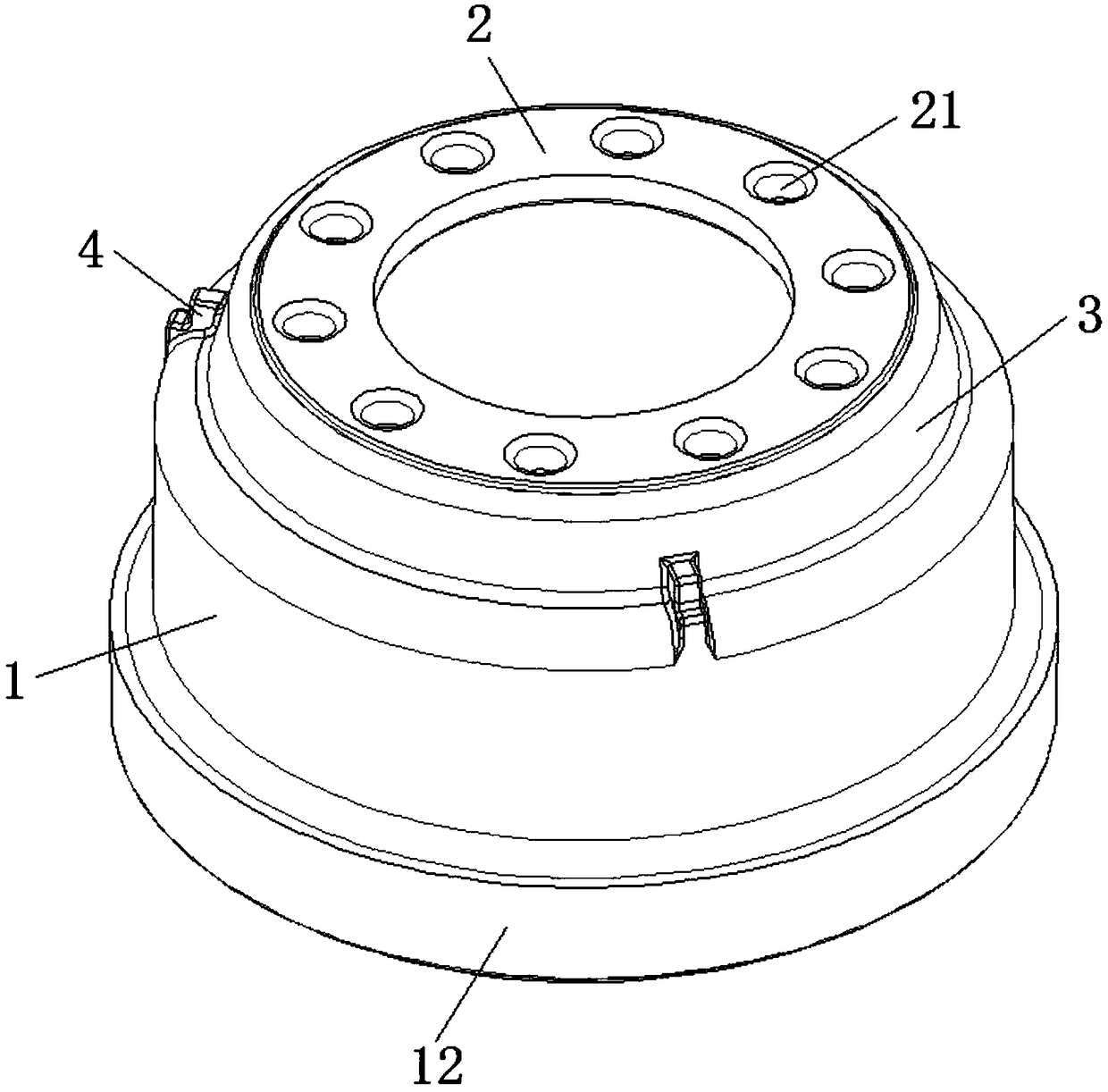
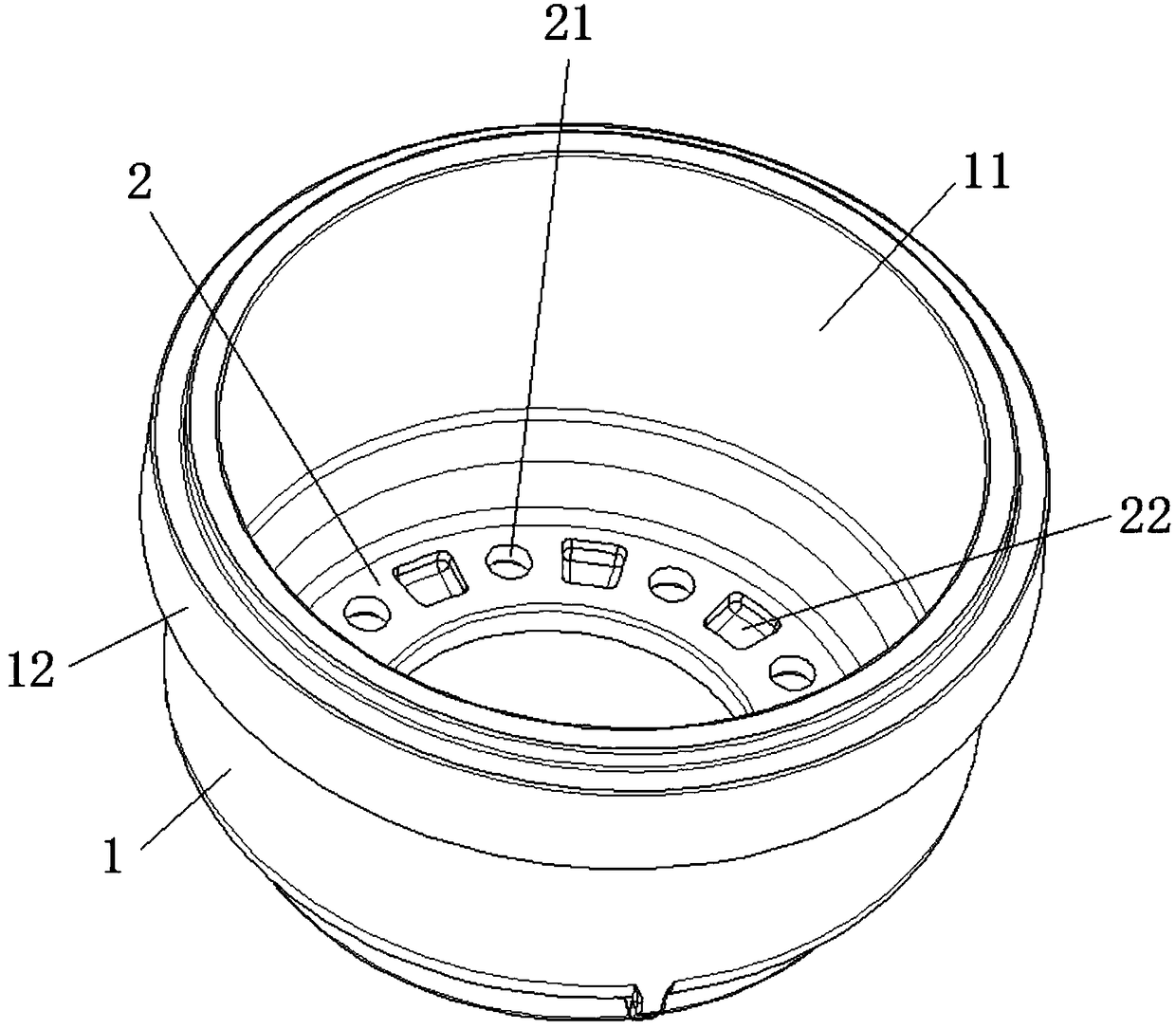
[0048] A method for manufacturing a brake drum provided by the present invention, as well as the manufacture of the brake drum of this embodiment, all include the following steps:
[0049] S1. Preparation of raw materials:
[0050] The following materials are prepared according to mass percentage: 30% of pig iron, 60% of steel scrap, 10% of recycled materials; molybdenum and copper are added, and their mass is equivalent to 0.25-0.5% and 0.4-0.8% of the total mass of the raw materials.
[0051] The mass of molybdenum added in this embodiment is equivalent to 0.25% of the total mass of the raw materials.
[0052] The mass of copper added in this embodiment is equivalent to 0.5% of the total mass of the raw materials.
[0053] The percentage of molybdenum and copper added in this embodiment to the total mass of the raw materials is the best implementation mode, which can make the creep rate of molten iron reach the highest, and improve the thermal fatigue resistance and mechani...
Embodiment 2
[0075] The manufacturing method of the brake drum of this embodiment is substantially the same as the manufacturing method of the brake drum of Embodiment 1, the difference is that, in the S1 of this embodiment, the mass of molybdenum added is equivalent to the total mass of the raw materials 0.3%, the quality of adding copper is equivalent to 0.4% of the total mass of the raw materials.
[0076] The tapping temperature of the molten iron in S2 in this embodiment is 1480°C.
[0077] The pouring temperature in S3 of this embodiment is 1390°C.
[0078] The structure of the brake drum in this embodiment is the same as the structure of the brake drum in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0080] The manufacturing method of the brake drum of this embodiment is substantially the same as the manufacturing method of the brake drum of Embodiment 1, the difference is that, in the S1 of this embodiment, the mass of molybdenum added is equivalent to the total mass of the raw materials 0.5%, the quality of adding copper is equivalent to 0.8% of the total mass of the raw materials.
[0081] The tapping temperature of the molten iron in S2 in this embodiment is 1520°C.
[0082] The pouring temperature in S3 of this embodiment is 1400°C.
[0083] The structure of the brake drum in this embodiment is the same as the structure of the brake drum in Embodiment 1.
[0084] Compared with the prior art, the manufacturing method of the brake drum of the present invention carries out integrated casting on the brake drum, reduces secondary processing, reduces processing steps and costs; the brake drum produced by it is a vermicular graphite cast iron brake drum, Vermicular graphit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com