Molecular marker TJcM02 for identifying separate flowers of muskmelons and application thereof
A molecular marker, unisexual flower technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of high cost, low efficiency, long life, etc., and achieve the effect of high accuracy, good specificity, and accurate distinction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1, the acquisition of molecular markers
[0031] The melon gene CmACS-7 is an important regulatory factor for regulating the flower type of melon. Using the resequencing information of the melon genome, an InDel molecular marker TJcM02 was obtained in the region near the position of the gene, and its sequence is shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing. In order to utilize the InDel site, suitable specific primers were designed, including upstream primer F and downstream primer R, and the primer sequences are as follows:
[0032] Upstream Primer F: TTCAAATTCTTCACAACTTTACCGTATTGATCC
[0033] Downstream primer R: GGTGGTCATTTTCATAGAACTTTCCCATAC
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2, the acquisition of melon materials Oa831, Oa808 and F2 generation segregated populations and the identification of material flower types
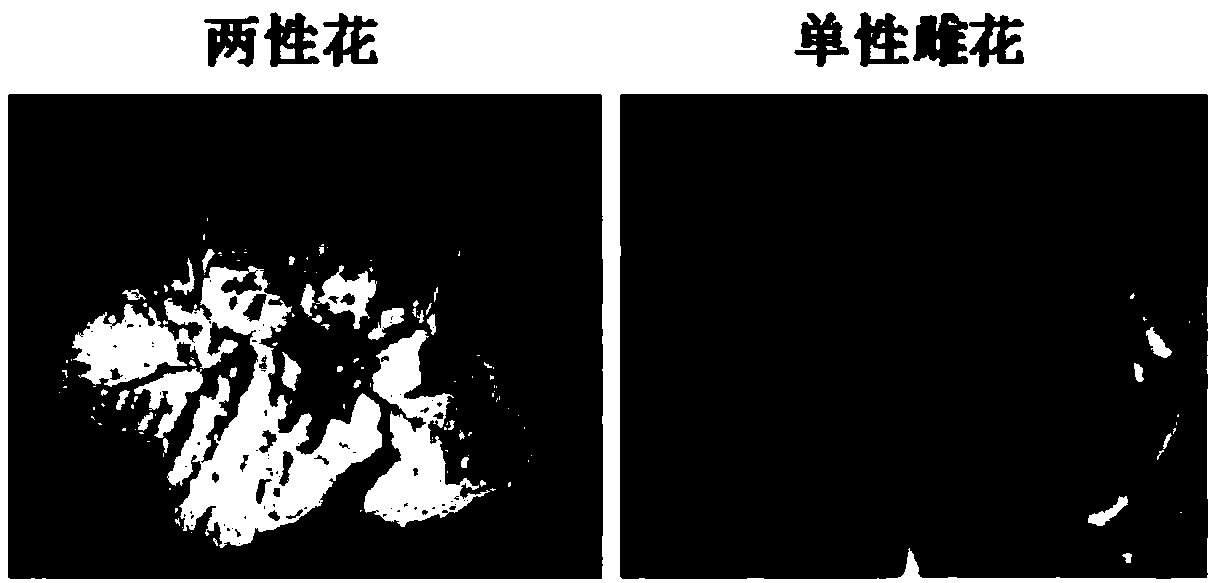
[0035] The melon material Oa831 is the female parent, and Oa808 is the male parent. The F1 generation is obtained by crossing, and the F2 generation melon material is obtained by selfing the F1 generation. Cultivate normally in the field, and observe the flower type of the materials at the flowering stage. According to whether the open flowers contain stamens and pistils, it is determined that Oa831 is a unisexual flower material, Oa808 is a bisexual flower material, F1 generation is a unisexual flower material, 44 plants Among the F2 muskmelon plants, 39 plants showed unisexual female floral material, and 5 plants showed hermaphrodite flower material.
Embodiment 3
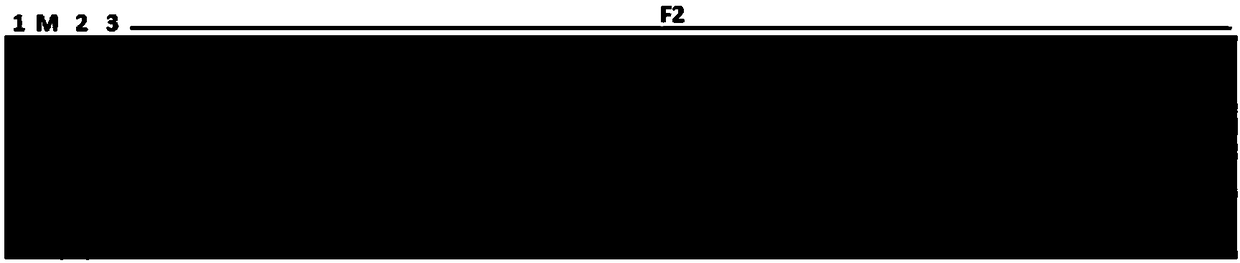
[0036] Example 3, the application of molecular markers in identifying whether the muskmelon is unisexual female flowered melon
[0037]For the melon material in Example 2, use the CTAB method to extract the genomic DNA of the leaves. The specific steps are: take 0.2 g of young melon leaves and put them into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 50 μL of 2% CTAB extraction buffer, grind, and then add Make up to 400 μL, bathe in 65°C water for 30 minutes; add 400 μL of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), and shake gently for 5 minutes. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes; take 200 μL of supernatant, add 200 μL of pre-cooled isopropanol to mix, and place at -20°C for 20 min; centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 min; discard supernatant, add 150 μL of pre-cooled ethanol, mix gently and wash, 10,000 Centrifuge at rpm for 5 min; discard the supernatant, air dry or blow dry; add 100 μL of distilled water to dissolve the DNA, and place at room temperature for 1 h; dilute the DNA to 50 ng / μL with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com