Decellularized tilapia skin biomimetic substrate for soft tissue restoration as well as preparation method and application thereof
A tilapia and decellularization technology, applied in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as difficult quality control or risk monitoring, safety in clinical use, sensitization or immune rejection, etc. cost, good industrialization market potential, and the effect of reducing the risk of immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
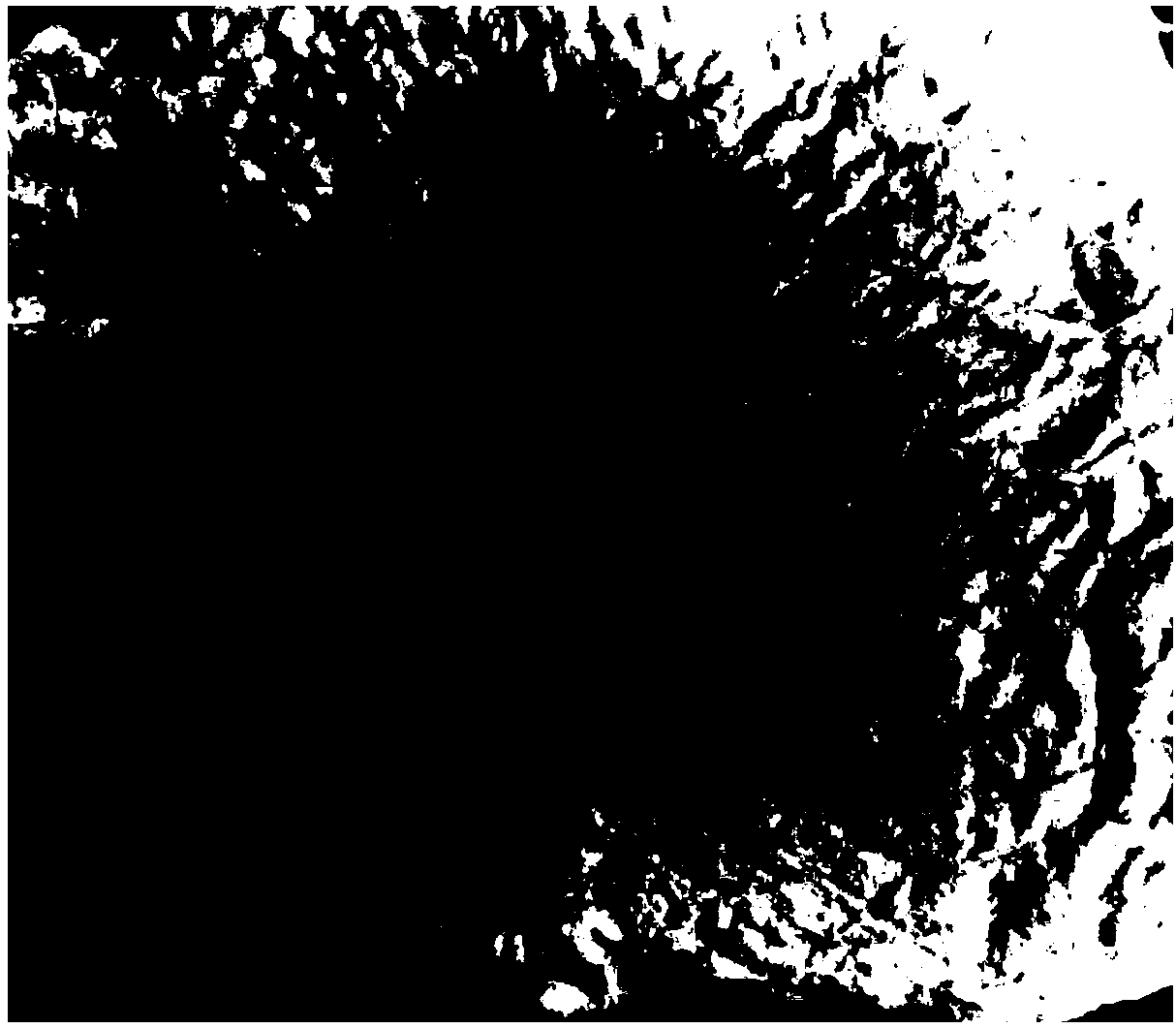
[0041] Example 1 Preparation of acellular tilapia skin biomimetic matrix for soft tissue repair
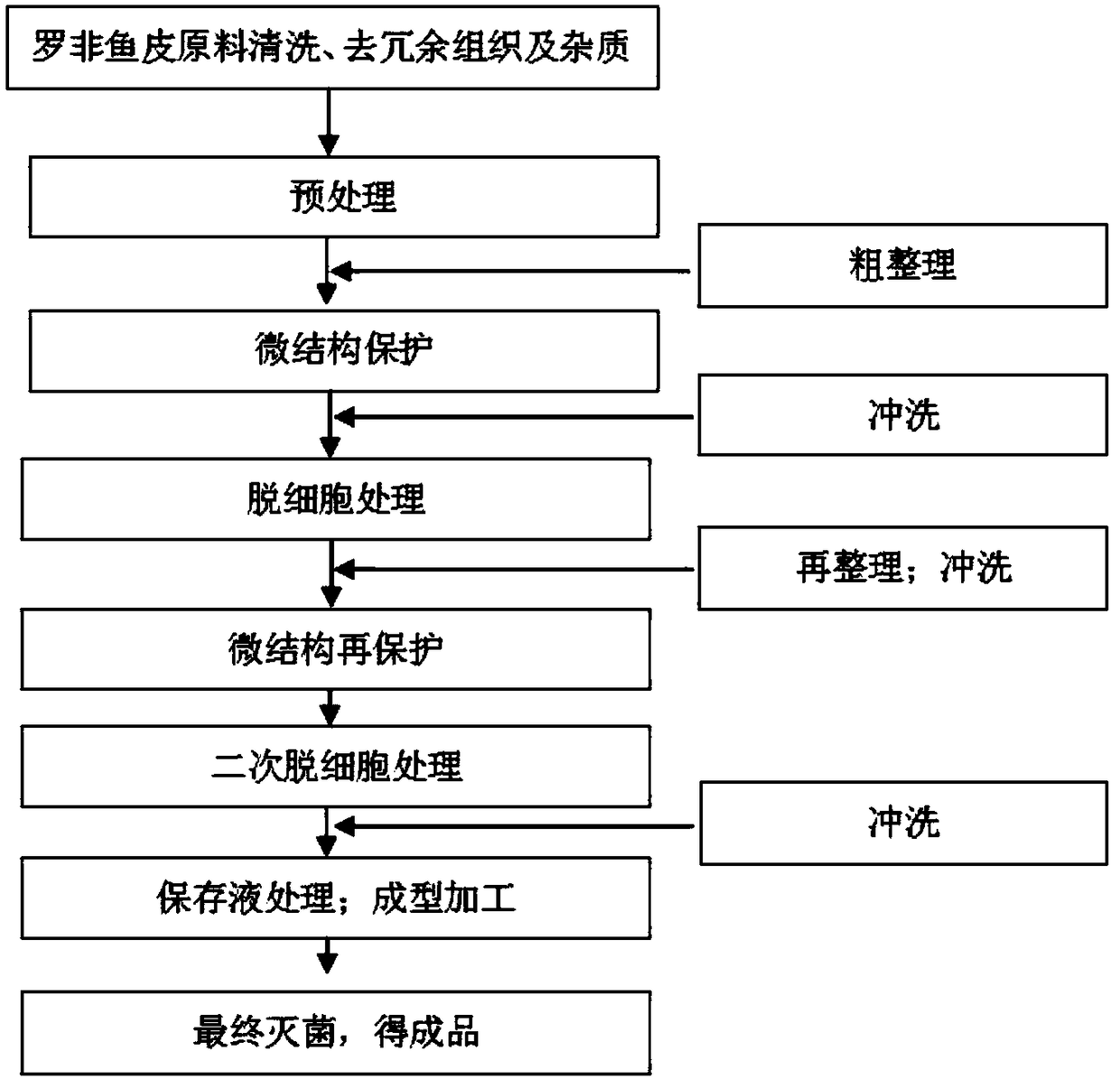
[0042] 1) Tilapia skin pretreatment: fresh tilapia skin is scraped off residual scales and redundant muscle tissues, rinsed with deionized water at 4°C several times to remove residual blood; cut into appropriate sizes according to different anatomical parts, and placed quickly Freeze at -40°C, take out and thaw under running water at room temperature before use;
[0043] 2) Pretreatment: at 4°C, stir with a 3.5% NaCl solution with a solid-liquid ratio of 1:20 (w / w) for 1 hour and then remove the waste liquid, repeating twice; Citric acid solution (0.005mol / L) was treated for 2 hours; the tilapia skin was roughly sorted to remove some redundancy;
[0044] 3) Microstructure protection: at 4°C, stir with PBS buffer solution (0.1M, pH7.4) with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20 (w / w) for 2 hours and then remove the waste liquid; repeat the above steps twice;
[0045] 4) Cleaning: at 4...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 Preparation of acellular tilapia skin biomimetic matrix for soft tissue repair
[0053] 1) tilapia skin pretreatment: with embodiment 1;
[0054] 2) Pretreatment: at 4°C, stir 5% NaCl solution with a solid-liquid ratio of 1:10 (w / w) for 2 hours, then remove the waste liquid, and repeat twice; Citric acid solution (0.01mol / L) was treated for 2 hours; the tilapia skin was roughly sorted to remove some redundancy;
[0055] 3) Microstructure protection: at 4°C, stir with PBS buffer solution (0.2M, pH7.0) with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (w / w) for 2 hours and then remove the waste liquid; repeat the above steps twice;
[0056] 4) Cleaning: at 4°C, stir with a 5% NaCl solution with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (w / w) for 4 hours and then remove the waste liquid;
[0057] 5) Initial decellularization treatment: spread the above-mentioned tilapia skin on a dry-baked and sterilized tray, quickly freeze it at -40°C for 4 hours, and thaw it under clean conditions...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3 Preparation of acellular tilapia skin biomimetic matrix for soft tissue repair
[0064] 1) tilapia skin pretreatment: with embodiment 1;
[0065] 2) pretreatment: with embodiment 2;
[0066] 3) Microstructure protection: at 4°C, stir for 2 hours with D-Hank’s buffer solution (pH7.2) with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (w / w) and then remove the waste liquid; repeat the above steps twice;
[0067] 4) Cleaning: at 4°C, stir with a 4% NaCl solution with a material-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (w / w) for 4 hours and then remove the waste liquid;
[0068] 5) Initial decellularization treatment: same as in Example 1;
[0069] 6) Microstructure re-protection: at 4°C, stir with D-Hank’s buffer solution (pH7.2) with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (w / w) for 2 hours and then remove the waste liquid; repeat the above steps twice;
[0070] 7) Secondary decellularization treatment: at 4°C, stir for 18 hours with 1% sodium deoxycholate (containing gentamicin sulfate 50 μg / ml) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com