Device and method for enriching and recovering rare and precious metal ions through nanometer zero-valent iron
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and rare precious metals, applied in chemical instruments and methods, improvement of process efficiency, water treatment parameter control, etc., can solve the problem of low utilization rate of nano-zero-valent iron and the reaction of heavy metal ions and nano-zero-valent iron Different rates, long residence time and other problems, to achieve the effect of automatic control, enrichment and recovery efficiency improvement, and increase enrichment and recovery efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
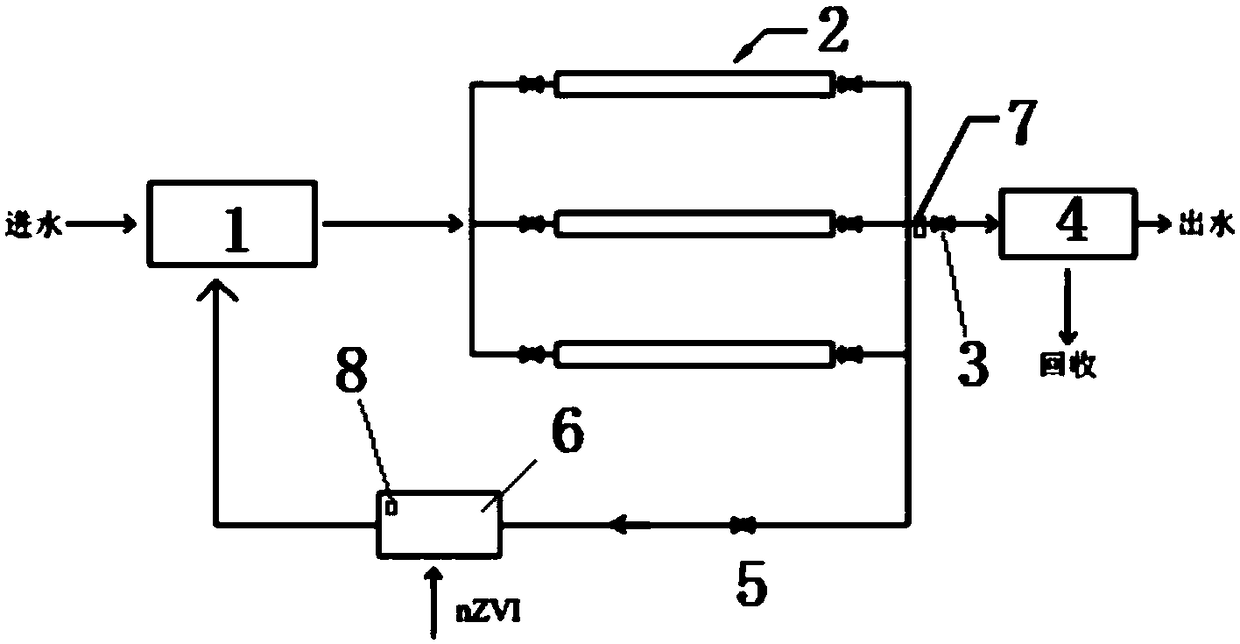
[0038] A device for enriching and recovering rare and precious metal ions by using nanometer zero-valent iron, its structure is as follows figure 1 As shown, it includes a mixer 1 arranged at the end of the sewage pipe and connected in sequence, an electromagnetic separation pipe unit 2 and a settling tank 4, a No. 1 valve 3 is arranged between the electromagnetic separation pipe unit 2 and the settling tank 4, and the device is also provided with There is a dosing pool 6, the outlet of the dosing pool 6 is connected to the mixer 1, one end of the dosing pool 6 is connected to the outlet of the electromagnetic separation pipe unit 2 through a pipeline, and a No. 2 valve 5 is set on the pipeline, and the electromagnetic separation pipe A No. 1 ORP / pH monitor 7 is installed at the outlet of the unit 2, and a No. 2 ORP / pH monitor 8 is installed in the dosing pool 6. The electromagnetic separation tube unit 2 includes three electromagnetic separation tubes arranged side by side.
...
Embodiment 2
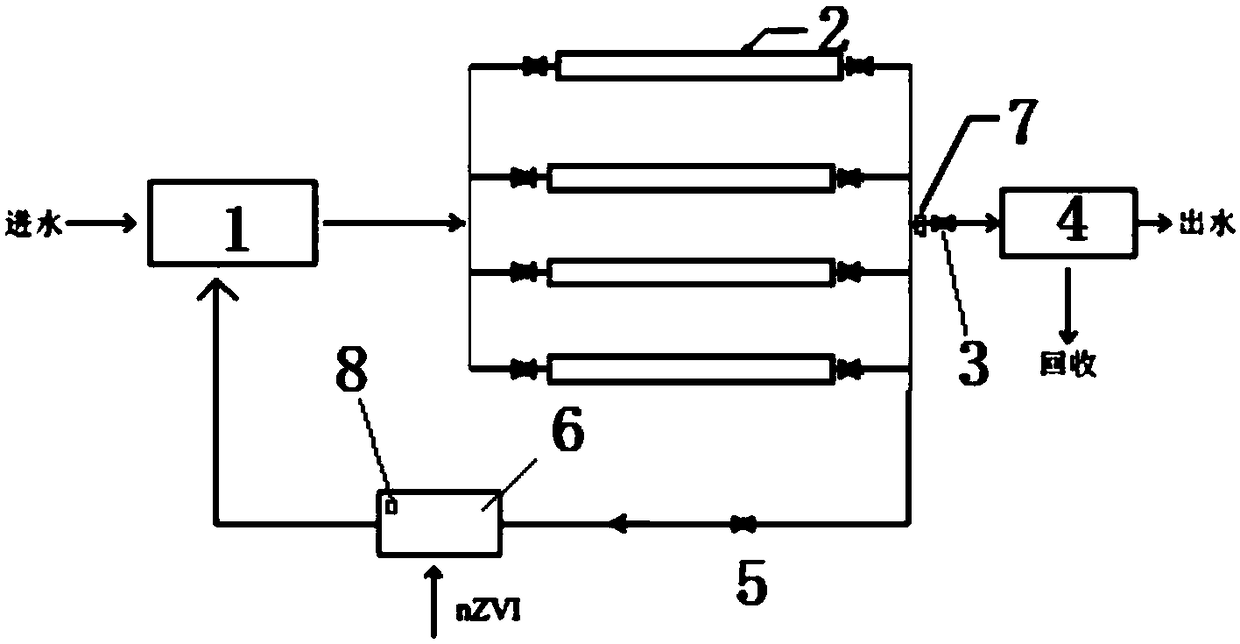
[0043] Using a device similar to Embodiment 1, the difference is that the electromagnetic separation tube unit 2 of the present embodiment includes 4 electromagnetic separation tubes arranged side by side, such as figure 2 shown.
[0044] The device of this embodiment is used to recover rare and precious metal ions in a certain electroplating wastewater, wherein the content of rare and precious metal ions is shown in Table 2. The device for enriching and recovering rare and precious metal ions in nanometer zero-valent iron in this embodiment is as follows: figure 2 Shown: The residence time of wastewater in the pipeline mixer is 1 minute; the dosage of nano-zero-valent iron in each ton of wastewater is 0.7kg, and fresh nano-iron is added every 5 hours; four electromagnetic separation tubes are set, and the normal When working, the magnetic induction intensity is 0.02 Tesla, the residence time of waste water in the electromagnetic separation pipe is 5 minutes, and the electr...
Embodiment 3
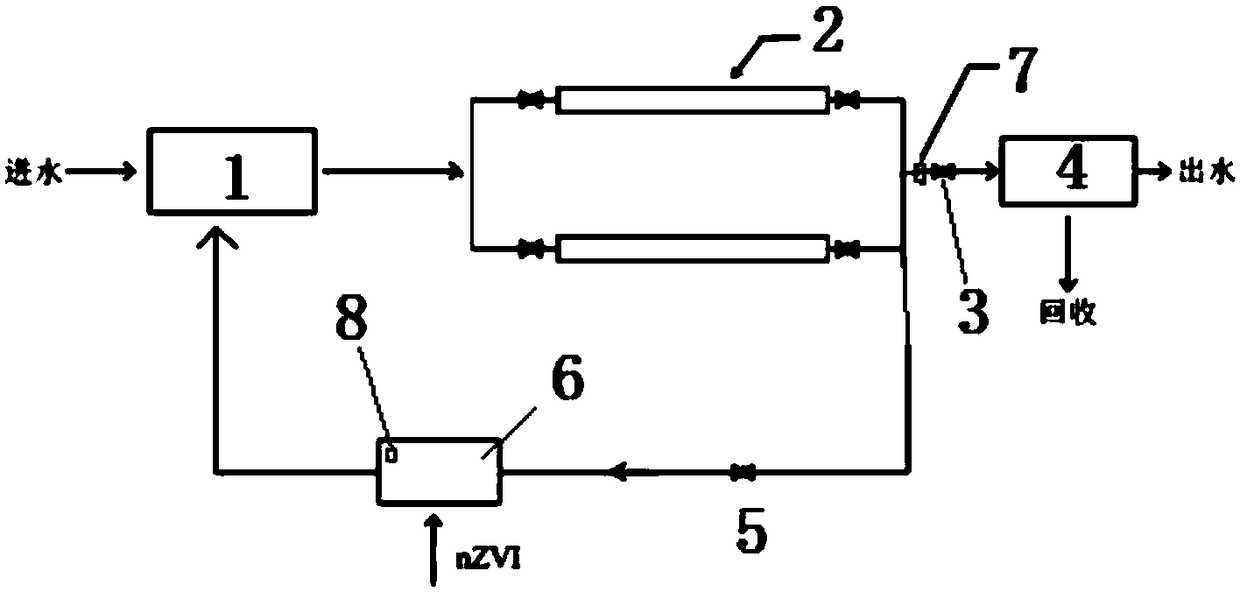
[0048] A device similar to Embodiment 1 is adopted, except that the electromagnetic separation tube unit 2 of the present embodiment includes two electromagnetic separation tubes arranged side by side, such as image 3 shown.
[0049] The device of this embodiment is used to recover rare and precious metal ions in a certain electroplating wastewater, wherein the content of rare and precious metal ions is shown in Table 3. The device for enriching and recovering rare and precious metal ions in nanometer zero-valent iron in this embodiment is as follows: image 3 Shown: The residence time of wastewater in the pipeline mixer is 5 minutes; the dosage of nano-zero-valent iron in each ton of wastewater is 0.1kg, and fresh nano-iron is added every 4 hours; two electromagnetic separation tubes are set, and the normal When working, the magnetic induction intensity is 0.04 Tesla, the residence time of waste water in the electromagnetic separation pipe is 4 minutes, and the electromagne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com