A preparation method of high current density stacked high temperature superconducting degaussing cable
A high-current density, high-temperature superconducting technology, applied in the usage of superconducting elements, superconducting devices, cable/conductor manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of large volume, weight and resistance loss, and achieve low power supply, simplified structure, The effect of increasing the current carrying density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
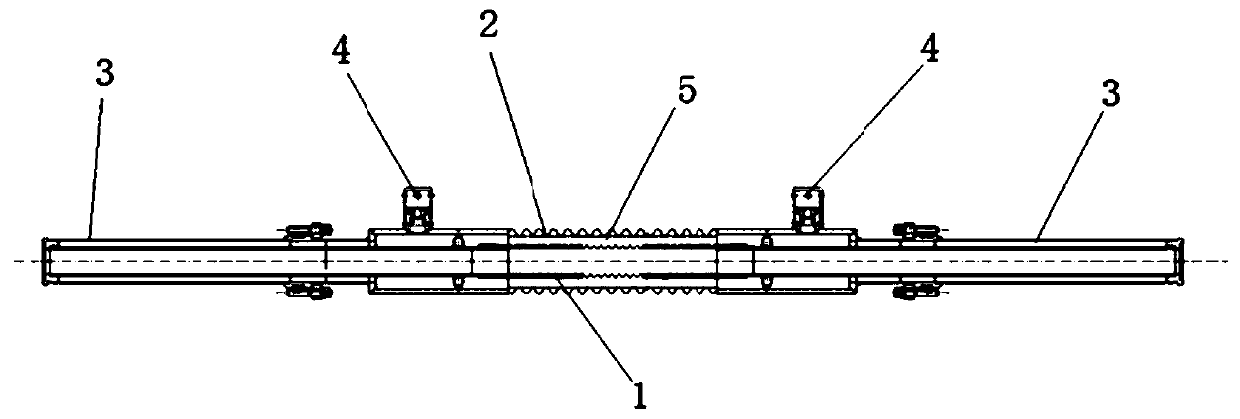
[0044] A method for preparing a high-current-density stacked high-temperature superconducting degaussing cable. The high-temperature superconducting degaussing cable includes a core body 10, an insulating layer 11, an isolation belt, a liquid nitrogen channel 12, and a low-temperature degaussing cable from inside to outside in the radial direction. tile pipe and outer protective cover 13, the preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0045] Step 1, the core body is formed by stacking superconducting tapes; using the characteristics of the critical current Ic of the superconducting tapes changing with the magnetic field, according to the magnitude and direction of the operating current of the core body, the magnitude and magnitude of the magnetic field on the core body of the HTS degaussing cable are determined direction, and then determine the critical current of the core; according to the critical current and operating margin of the core, iteratively calculate the op...
Embodiment 1
[0070] Such as Figure 3a with 3b As shown, the core is obtained by stacking n layers of superconducting strips with a width of w and a thickness of d in parallel to form a stacked superconductor with a rectangular cross section, and then twisting, wherein nd and w are close to or equal in size. The constraint of twisting is to comprehensively consider the twisting stress in the tangential direction of the superconducting strip and the comprehensive experimental value of the bending diameter of the core along the length direction. The twisted stacked superconductor is shaped and fixed by winding the copper wire, and a flexible gasket is used at the joint between the copper wire and the stacked superconductor to disperse the stress generated by the fixing of the copper wire. The copper wire is fixed with multiple turns to shape it. After the core is twisted, it can not only resist part of the electromagnetic wave interference from the outside, but also reduce the mutual inter...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Such as Figure 4a with 4b As shown, the core body is a superconducting conductor block with a combined square cross section formed by stacking four groups of stacked superconductors, and each group of stacked superconductors is composed of n layers of superconducting tapes with a width of w and a thickness of d stacked in parallel. , and the cross-section of each group of stacked superconductors is square, where nd and w are close to or equal in size. The stacking directions of two adjacent stacked superconductors are perpendicular to each other, which can resist part of the electromagnetic wave interference from the outside world, and can also reduce the mutual interference between the superconducting strips. The stacked cores are fixed in the isolation belt.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com