Method for recovering valuable metals from waste chips of copper indium gallium selenide solar thin film batteries
A solar thin film, copper indium gallium selenide technology, applied in the field of secondary utilization of resources, can solve the problems of high production cost, dangerous operation process, intense reaction process, etc., achieve high-efficiency selective leaching, no operation risk, simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
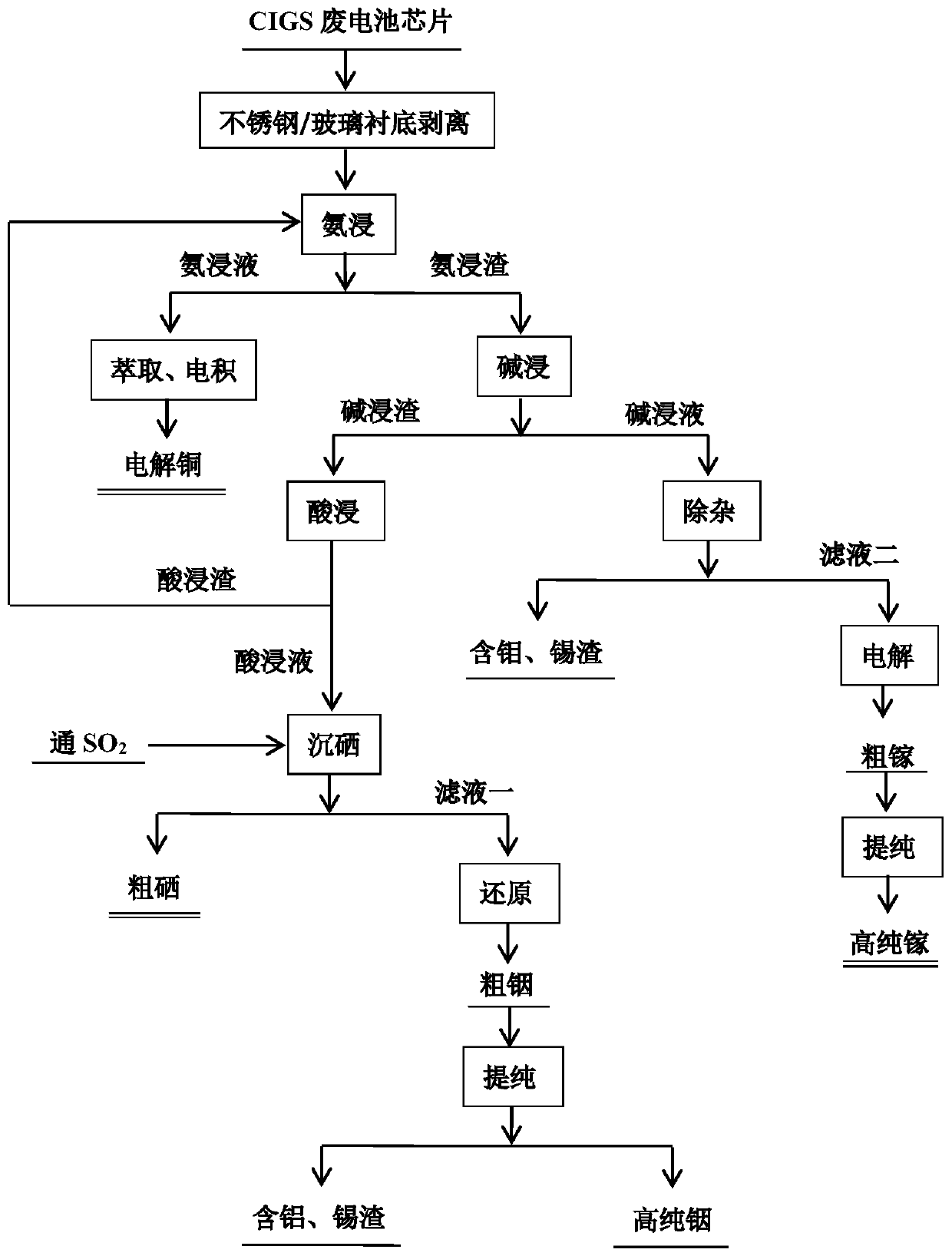
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, the implementation steps of this embodiment include: taking 50g of CIGS waste battery chips to peel off the substrate, using a mixture solution of ammonia and ammonium salt with a certain mass concentration as the leaching agent to carry out ammonia leaching on the peeled valuable metal layer, the leaching agent concentration in NH 3 The total concentration is 200g / L, the solid-liquid ratio before leaching is 1:5g / mL, the leaching temperature is 30°C, and the leaching time is 5h. After the leaching is completed, ammonia leaching solution and ammonia leaching residue are obtained through liquid-solid separation; ammonia leaching solution extraction , Electrolytic copper can be obtained after electrowinning; the ammonia leaching residue uses NaOH solution with a mass concentration of 80% as the leaching agent for alkaline leaching under normal pressure conditions. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:10g / mL, and after leaching, the alkali leaching so...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The implementation steps of this embodiment include: taking 100g of CIGS waste battery chips and peeling off the substrate, using a solution containing ammonia at a certain mass concentration as the leaching agent to carry out ammonia leaching on the peeled valuable metal layer, the concentration of the leaching agent is expressed as NH 3 The total value is 350g / L, the solid-liquid ratio before leaching is 1:10g / mL, the leaching temperature is 60°C, and the leaching time is 3h. After the leaching is completed, ammonia leaching liquid and ammonia leaching residue are obtained through liquid-solid separation; ammonia leaching liquid extraction , Electrolytic copper can be obtained after electrowinning; ammonia leaching slag uses KOH solution with a mass concentration of 60% as the leaching agent to perform alkaline leaching under pressure. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:5g / mL. After leaching, the alkali leaching solution and alkali leaching residue are obtained through liq...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The implementation steps of this embodiment include: taking 50g of CIGS waste battery chips to peel off the substrate, using a mixture solution of ammonia and ammonium salt with a certain mass concentration as the leaching agent to carry out ammonia leaching on the peeled valuable metal layer, the concentration of the leaching agent is expressed as NH 3 The total concentration is 50g / L, the solid-liquid ratio before leaching is 1:10g / mL, the leaching temperature is 60°C, and the leaching time is 3h. After the leaching is completed, ammonia leaching liquid and ammonia leaching residue are obtained through liquid-solid separation; ammonia leaching liquid extraction , Electrolytic copper can be obtained after electrowinning; the ammonia leaching slag uses NaOH solution with a mass concentration of 50% as the leaching agent to perform alkaline leaching under normal pressure conditions. The liquid ratio is 1:5g / mL, and the alkali leaching liquid and alkali leaching residue ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com