A low-cost method for removing arsenic from copper smelting high-arsenic soot
A low-cost, copper smelting technology, applied in the improvement of process efficiency, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problems of low comprehensive recovery rate of valuable elements, untreated sodium arsenate, high cost of dearsenic, and achieve high-efficiency selective leaching , the effect of reducing the cost of chemicals and improving the arsenic enrichment rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
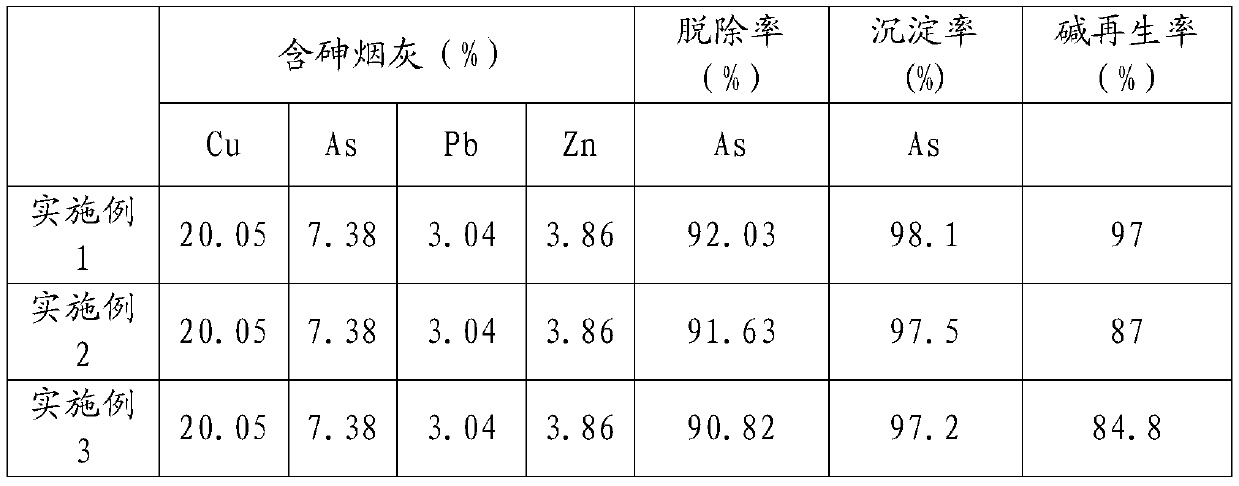
[0035] Cu: 20.05%, As: 7.38%, Pb: 3.04%, Zn: 3.86% in the copper arsenic-containing fume treated in this embodiment. The treatment process and effect are as follows:
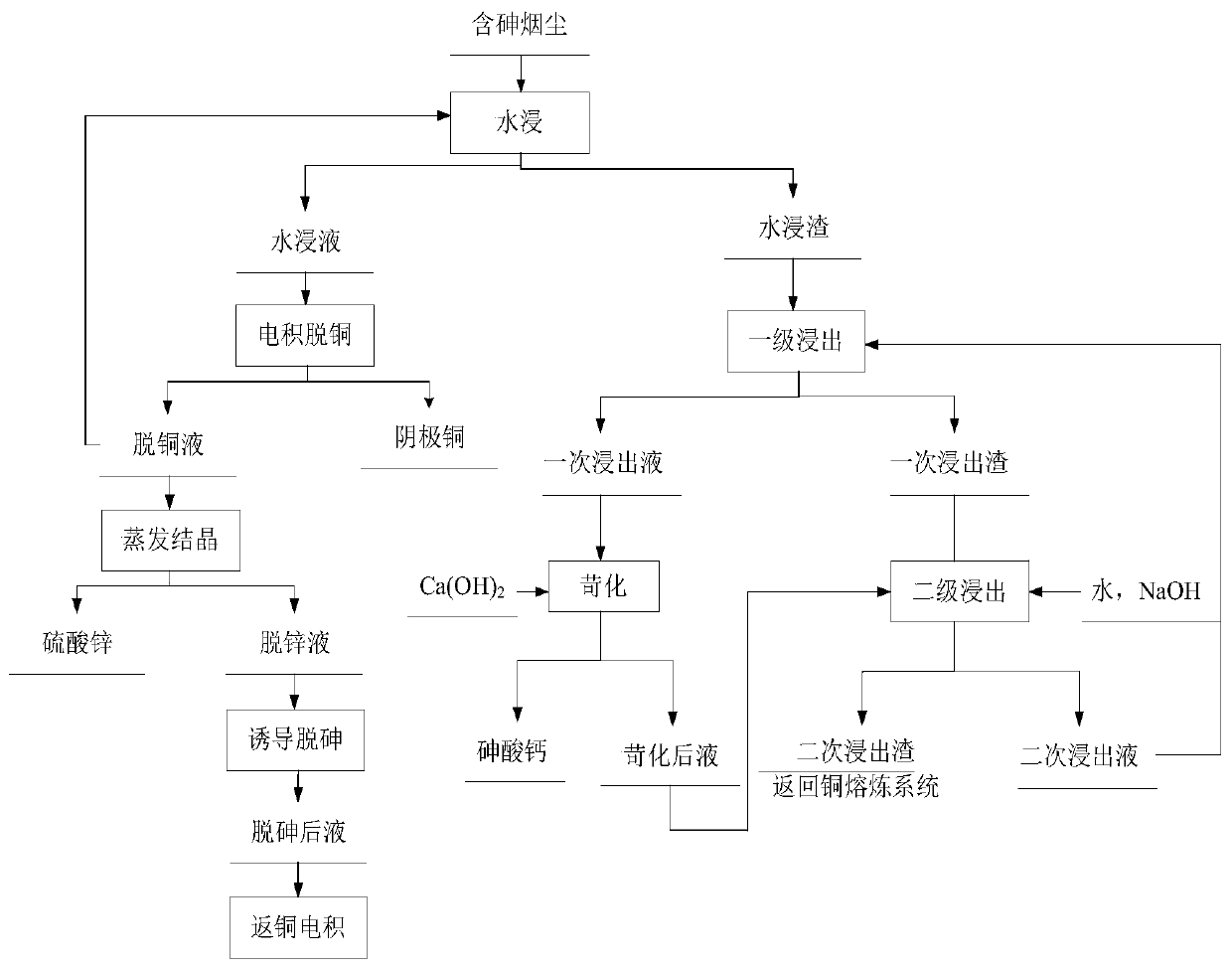
[0036] (1) The arsenic-containing dust is immersed in water, the pH is 6, the liquid-solid ratio is 5, the temperature is 80° C., and the time is 2 hours. In the leaching residue, Cu: 12.76%, As: 7.30%, Pb: 3.45%, Zn: 2.41%; in the leaching solution, Cu: 16.3g / L, As: 1.8g / L, Zn: 3.2g / L.
[0037] (2) The medium leaching residue is subjected to the first-level atmospheric pressure alkaline leaching, the liquid-solid ratio is 5:1, the temperature is 80°C, and the time is 2h. Cu: 14.5%, As: 2.90%, Pb: 3.92%, Zn: 2.74% in primary leaching slag.
[0038] (3) The primary leaching slag was subjected to two-stage atmospheric pressure alkaline leaching, the liquid-solid ratio was 7:1, the NaOH concentration was 90g / L, the temperature was 85°C, and the time was 1h. In the secondary leaching slag, Cu: 20.14%, As: 1.05%, ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Cu: 20.05%, As: 7.38%, Pb: 3.04%, Zn: 3.86% in the copper arsenic-containing fume treated in this example. The treatment process and effect are as follows:
[0043] (1) The arsenic-containing dust is immersed in water, the pH is 2, the liquid-solid ratio is 10, the temperature is 30° C., and the time is 3 hours. In the leaching residue, Cu: 10.67%, As: 6.95%, Pb: 3.58%, Zn: 2.27%; in the leaching solution, Cu: 18.9g / L, As: 2.2g / L, Zn: 3.6g / L.
[0044] (2) The leaching slag is subjected to the first-level atmospheric pressure alkaline leaching, the liquid-solid ratio is 8:1, the temperature is 90°C, and the time is 1h. Cu: 11.86%, As: 3.09%, Pb: 3.96%, Zn: 2.50% in primary leaching slag.
[0045] (3) The primary leaching slag was subjected to secondary atmospheric pressure alkaline leaching, the liquid-solid ratio was 5:1, the NaOH concentration was 150g / L, the temperature was 60°C, and the time was 2h. In the secondary leaching residue, Cu: 16.95%, As: 1.09%, Pb: 5.6...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Cu: 20.05%, As: 7.38%, Pb: 3.04%, Zn: 3.86% in the copper arsenic-containing fume treated in this example. The treatment process and effect are as follows:
[0050] (1) The arsenic-containing dust is immersed in water, the pH is 7, the liquid-solid ratio is 3, the temperature is 95°C, and the time is 1h. In the leaching residue, Cu: 13.38%, As: 7.36%, Pb: 3.38%, Zn: 2.57%; in the leaching solution, Cu: 15.5g / L, As: 1.6g / L, Zn: 3.0g / L.
[0051] (2) The leaching slag is subjected to the first-level atmospheric pressure alkaline leaching, the liquid-solid ratio is 3:1, the temperature is 50°C, and the time is 3h. Cu: 16.73%, As: 3.13%, Pb: 4.21%, Zn: 3.19% in primary leaching slag.
[0052] (3) The primary leaching slag was subjected to two-stage atmospheric pressure alkaline leaching, the liquid-solid ratio was 10:1, the NaOH concentration was 40g / L, the temperature was 90°C, and the time was 0.5h. In the secondary leaching residue, Cu: 21.44%, As: 1.21%, Pb: 5.38%, Zn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com