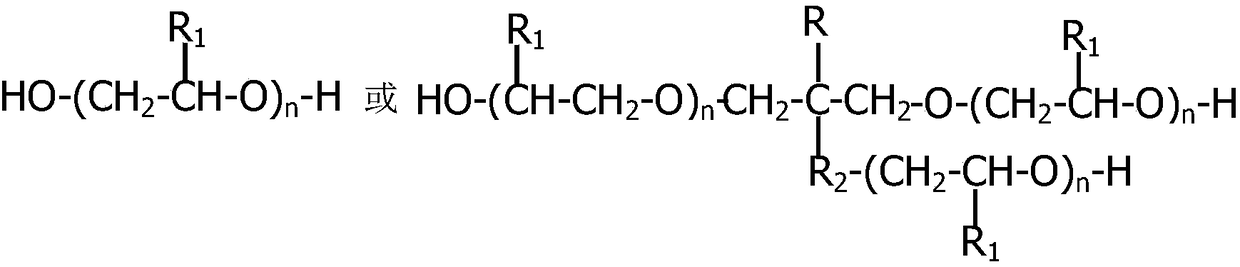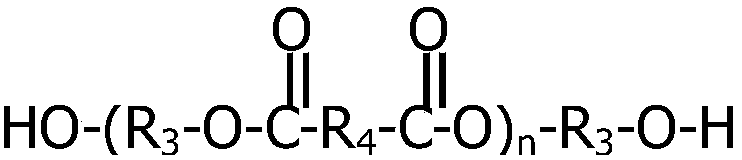Polymer building material for 3D printing
A building material, 3D printing technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, etc., to achieve the effect of shortening the construction period, fast curing, and reducing construction costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
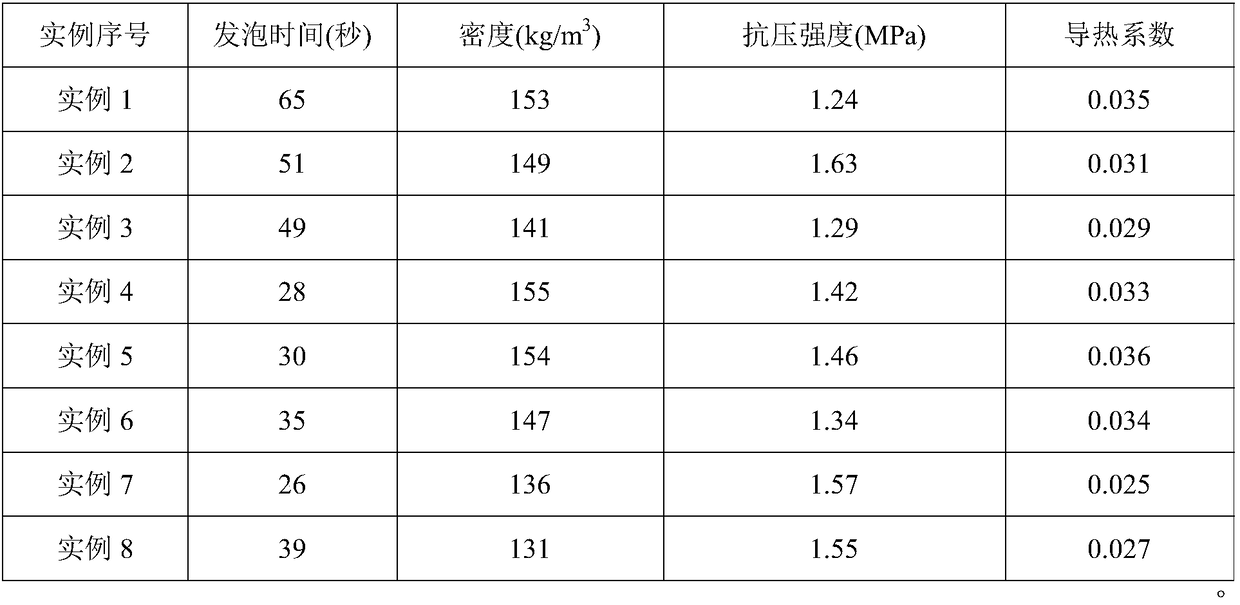
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Component A: Liquefied diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI). Component B: 27 parts of trimethylolpropane, 18 parts of glycerin, 300 parts of polypropylene glycol (500), 20 parts of polyethylene glycol (200), 2 parts of water, 5 parts of OP-10, dibutyltin dilaurate ( DBTDL) 4 parts, phosphate tris (2-ethylhexyl) ester 2 parts. Mix components A and B evenly at a mass ratio of 1:1.5 to obtain a uniform and fine rigid foam.
Embodiment 2
[0047]Component A: Liquefied diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI). Component B: 27 parts of trimethylolpropane, 12 parts of diethylene glycol, 300 parts of polypropylene glycol (500), 20 parts of polyethylene glycol (200), 3 parts of water, 4 parts of OP-10, dichlorodiphenyl 6 parts of methane diamine (MOCA), 4 parts of diethylene triamine (DABCO), 3 parts of (2-ethylhexyl)-diphenyl phosphate. Mix components A and B evenly at a mass ratio of 1:1.2 to obtain a uniform and fine rigid foam.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Component A: Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate (PAPI). Component B: 24 parts of trimethylolpropane, 10 parts of glycerin, 280 parts of polypropylene glycol (500), 1 part of water, 2 parts of OP-10, 2 parts of polysiloxane, 4 parts of diphenylmethanediamine (DDM) 3 parts, 3 parts of diethylenetriamine (DABCO), 2 parts of tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) phosphate. Mix components A and B evenly at a mass ratio of 1:1.3 to obtain a uniform and fine rigid foam.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com