Preparation method of in-situ polymerization solid-state battery
A solid-state battery and in-situ polymerization technology, applied in the field of green energy storage, can solve problems such as high charging capacity, loss of active materials, and low Coulombic efficiency, and achieve the effects of improving cycle life, improving interface problems, and improving safety performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0022] A method for preparing an in-situ polymerized solid-state battery, comprising the following steps,
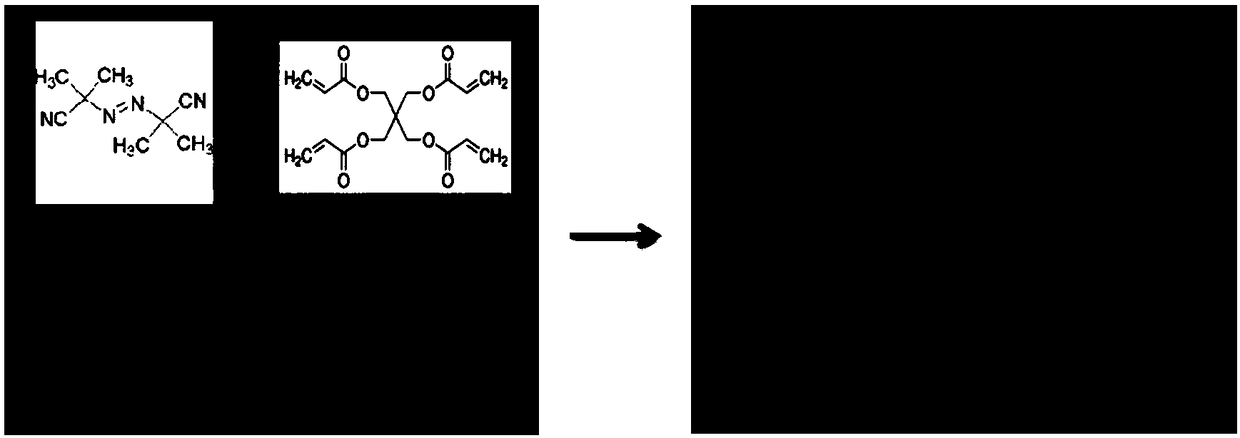
[0023] Step S1: Mix electrolyte salt, organic solvent, 1-10% by mass acrylate and 0.1-1% by mass initiator AIBN to form mixture I; wherein, the acrylate is tetraacrylic acid iso One or more of pentaerythritol triacrylate, allyl hydroxyethyl ether;
[0024] Step S2: Weigh the active material, acetylene black and PVDF at a mass ratio of 6:3:1 to make a positive electrode sheet, use the lithium sheet as the negative electrode, use the mixture I as the electrolyte, and use the polypropylene film as the diaphragm to assemble the battery;
[0025] Step S3: Put the battery in an oven, and after the battery is heated to 40°C-80°C, keep it for 1-30min. Such as figure 2 As shown, the mixture I after baking becomes a gel-state electrolyte, so that the electrode active materials are filled with the cured electrolyte, and the interfacial properties are improved.
[0026] The bene...
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1. Preparation of lithium iron phosphate solid-state battery with isopentyl tetraacrylate and traditional electrolyte:
[0034] The mixture I is prepared by mixing electrolyte salt, organic solvent, isopentyl tetraacrylate with a mass percentage of 1-10% and initiator AIBN with a mass percentage of 0.1-1%. Wherein, the organic solvent is: a mixed solution of dimethoxymethane and dioxolane with a volume ratio of 1:1; the electrolyte salt is 1mol / L LITFSI and 1% LiNO by mass percentage 3 ;
[0035] Weigh lithium iron phosphate, acetylene black and PVDF at a mass ratio of 6:3:1 to make a positive electrode sheet, use the lithium sheet as the negative electrode, use the mixture I as the electrolyte, and use the polypropylene film as the diaphragm in an argon-filled glove Assemble a CR2032 button battery in the box; place the battery in an oven at 70°C, and keep it for 1-30 minutes after the battery is heated to 40°C-80°C.
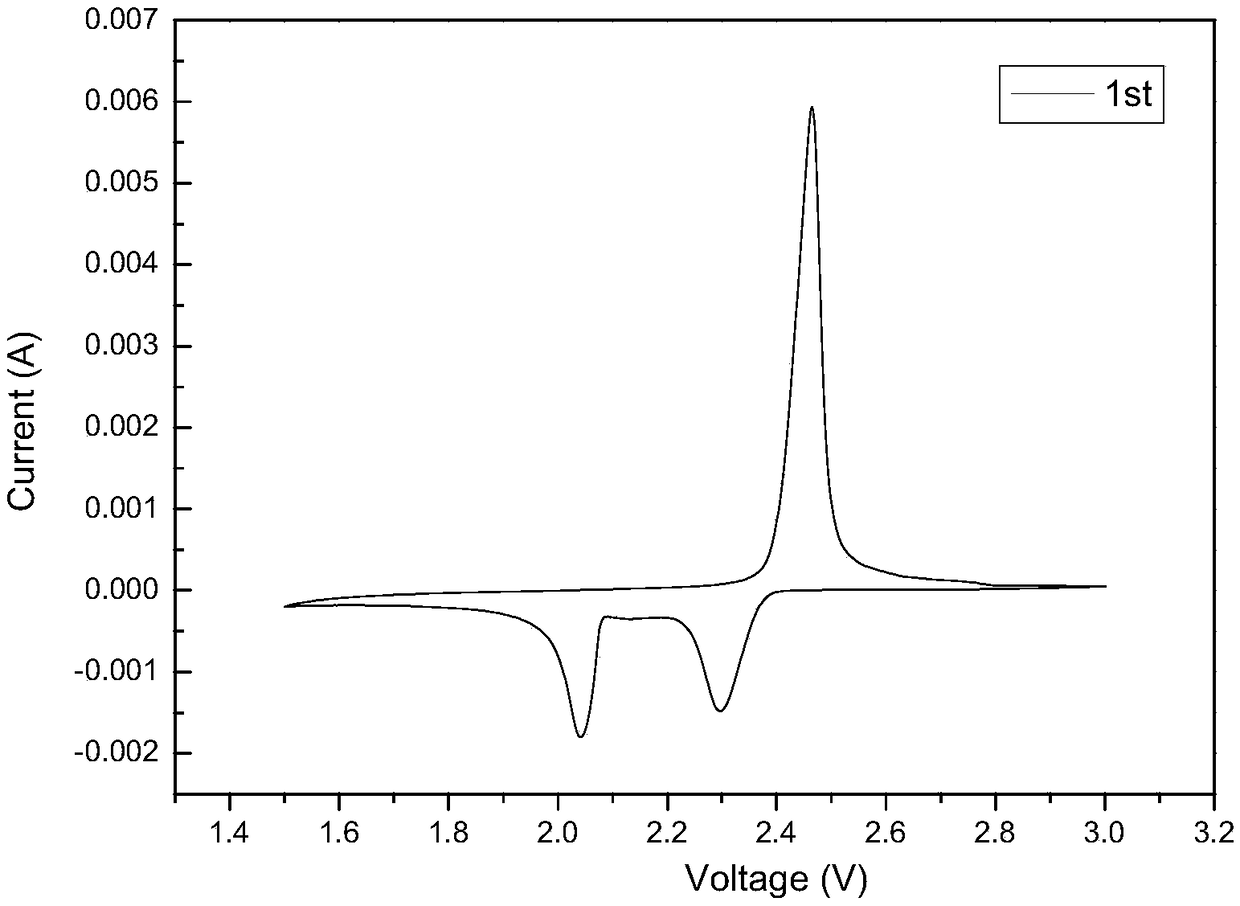
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, th...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2. Preparation of ternary positive electrode (NCA1:1:1) battery with pentaerythritol triacrylate and traditional electrolyte:
[0040] The mixture I is prepared by mixing electrolyte salt, organic solvent, pentaerythritol triacrylate with a mass percentage of 1-10% and initiator AIBN with a mass percentage of 0.1-1%. Wherein, the organic solvent is: a mixed solution of dimethoxymethane and dioxolane with a volume ratio of 1:1; the electrolyte salt is 1mol / L LITFSI and 1% LiNO by mass percentage 3 ;
[0041] Weigh the ternary positive electrode material, acetylene black and PVDF with a mass ratio of 6:3:1 to make the positive electrode sheet, use the lithium sheet as the negative electrode, use the mixture I as the electrolyte, and use the polypropylene film as the diaphragm in an argon-filled environment. A CR2032 button battery is assembled in a glove box; the battery is placed in an oven at 70° C., and the battery is heated to 40° C.-80° C. and maintained ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com