Culture medium suitable for improvement of tolerance of glucose and xylose co-fermentation saccharomyces cerevisiae for multiple kinds of pretreatment inhibitors and application
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and pretreatment, applied in the field of microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Preparation of Screening Medium Containing Various Pretreatment Inhibitors
[0030] Specific steps are as follows:
[0031] (1) Pretreatment of corn stalk with dilute acid to prepare corn stalk pretreatment solution: prepare a dilute sulfuric acid solution with a sulfuric acid mass fraction of 1.0%, as a cooking solution for dilute acid pretreatment, mix corn stalk (pulverized to 20-80 mesh) with The cooking liquid is mixed evenly in a 1.5L small steel tank at a material-liquid ratio of 1:10. After sealing, the small tank is placed in the cooking pot. At the upper end of the small pot in the middle, seal the cooking pot and set the required reaction temperature to 170°C and start heating, and keep the reaction for 25 minutes after reaching the temperature. Immediately after the reaction, the canister was taken out and put into cold water so that the temperature of the canister was lowered to room temperature. The pretreatment liquid in the small tank is sep...
Embodiment 2
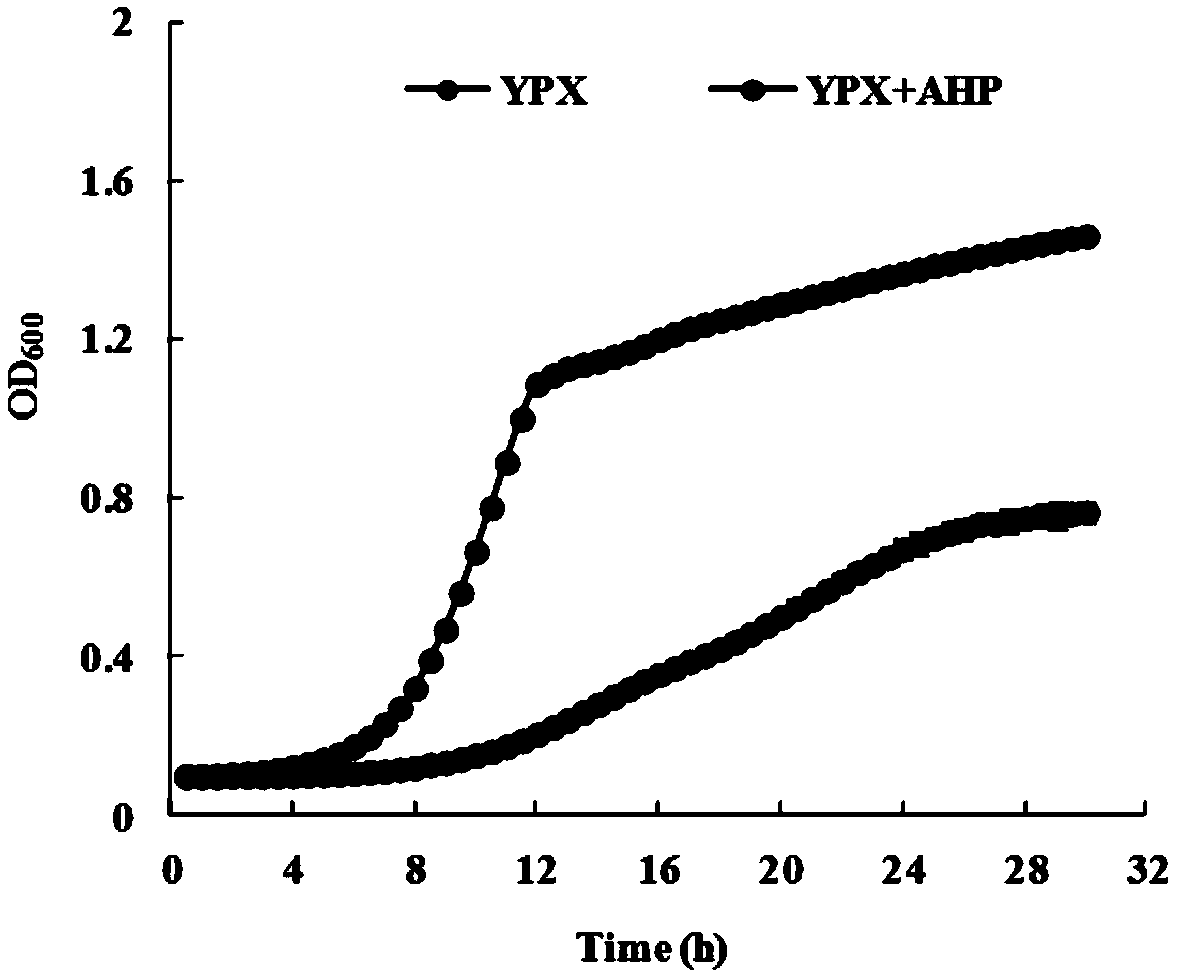
[0034] Example 2: Effect of medium containing dilute acid and AHP pretreatment hydrolyzate inhibitor on yeast growth
[0035] Specific steps are as follows:
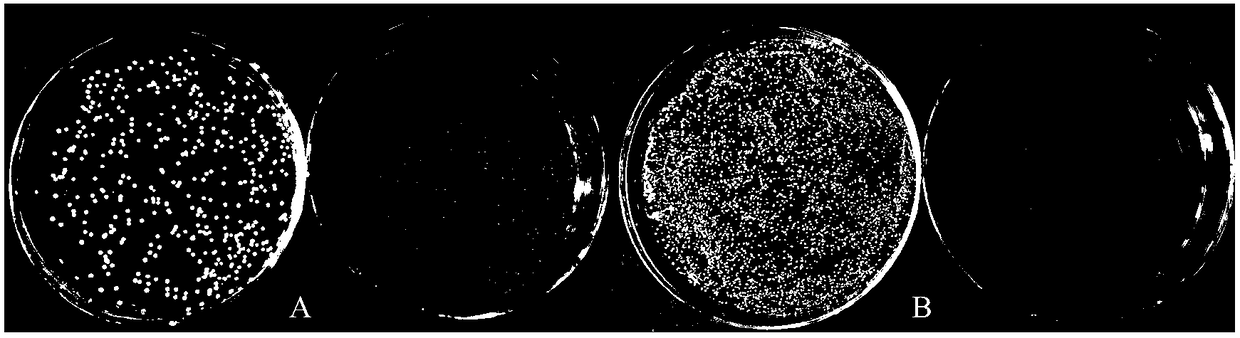
[0036] (1) Dilution coating experiment: The industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (deposit number: CGMCC No. 11331), which has undergone metabolic engineering and can efficiently co-metabolize glucose and xylose, was used as the starting strain for this experiment, and 5 mL of YPD was added to it. (YPD medium formula: yeast powder 10g / L, peptone 20g / L, glucose 20g / L.), culture overnight, take 1ml of bacterial suspension, centrifuge at 8000r / min, remove the supernatant, wash and suspend with 1mL sterile water Bacteria, centrifuge, remove supernatant, adjust OD 600 = about 1.0, diluted 1000 times, take 100 μL and apply it to YPX plate, (YPX + dilute acid pretreatment) plate and (YPX + AHP) plate, cultivate at 30 ° C for 3 to 4 days, observe the growth of the strain, take pictures, the results show ( like figure ...
Embodiment 3
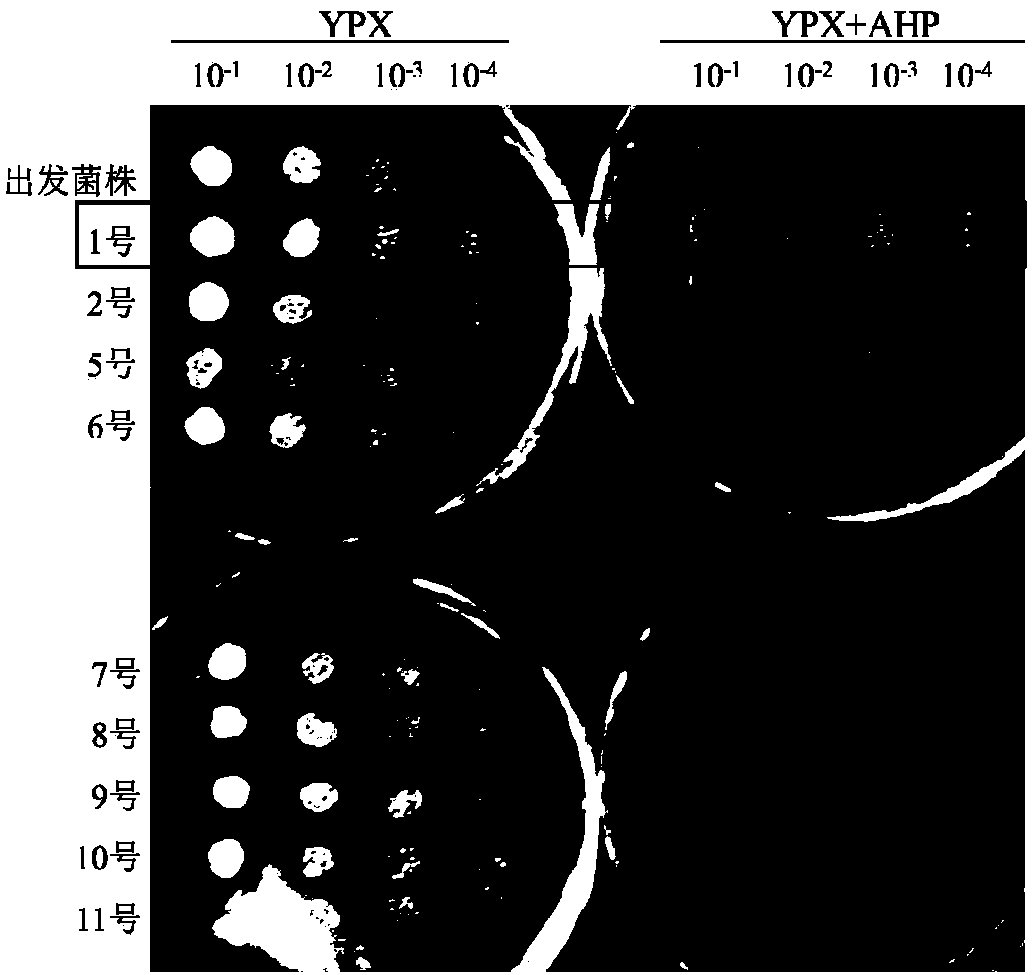
[0038] Example 3: Using ARTP mutagenesis technology to improve the ability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to tolerate AHP pretreatment corn stover hydrolyzate inhibitor
[0039] Specific steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) Activation of the starting strain: Inoculate the starting strain on the YPD plate, inoculate it upside down at 30°C for 2 to 3 days, then inoculate it into the YPD liquid, shake it for 12h to 24 hours, and transfer the bacterial liquid to fresh YPD to control the bacteria. Concentration OD 600 = 0.1, incubate at 30°C with shaking for several hours, and control the final concentration of bacteria OD 600 = within 1.0, as the ARTP mutagenesis starting strain.
[0041] (2) ARTP mutagenesis: take 1 mL of bacterial solution, suspend it in a 1.5 mL EP tube, centrifuge at 8000 r / min for 2 min, and discard the supernatant. After washing twice with normal saline, diluted to make the bacterial concentration at 10 6 ~10 7 Between the bacterial suspension, take 10 μL of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com