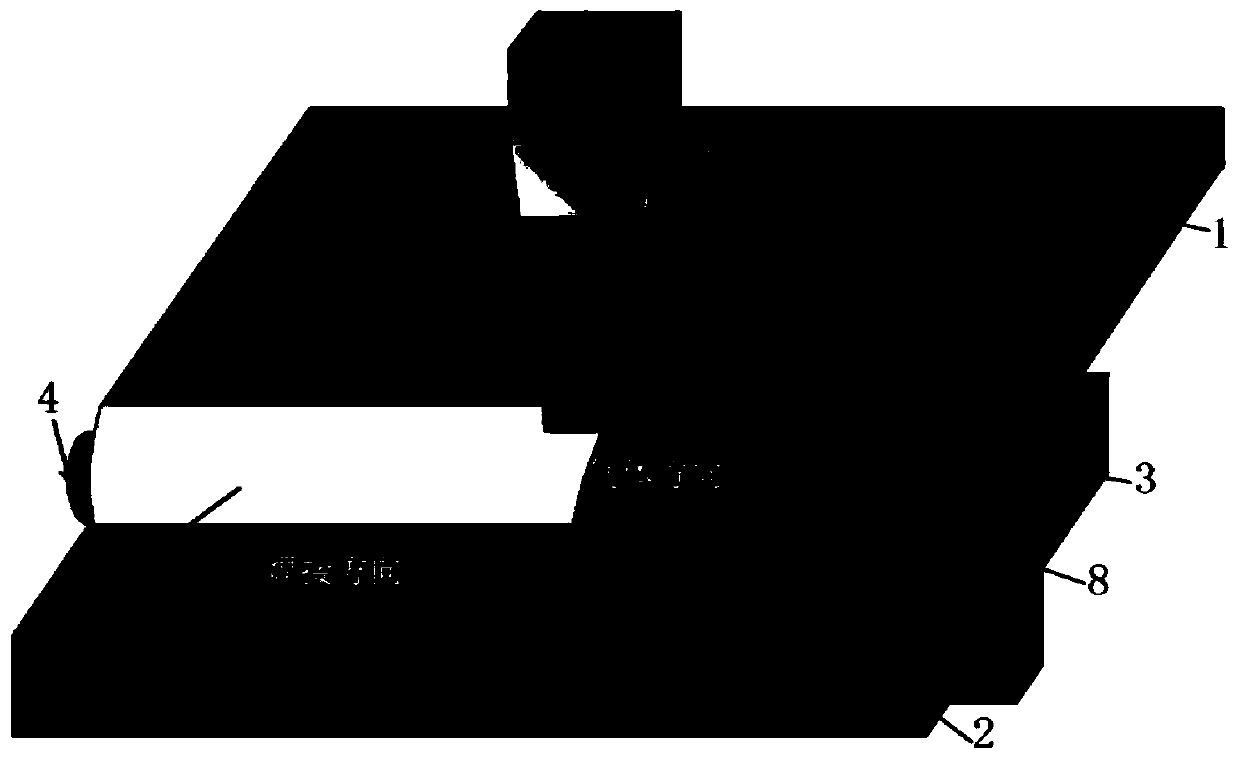
A Laser Filler Welding Process of Magnesium/Al Dissimilar Metals
A dissimilar metal and filler welding technology, which is applied in laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, welding/welding/cutting items, etc., can solve the problems of large heat input, welding deformation, and difficult to control the heating position, and achieve convenient and flexible operation , beautiful weld shape and high welding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1. Selection of welding consumables and intermediate layer
[0032] Magnesium alloy plate (ZEK100): size 60mm×50mm, thickness 1.5mm;
[0033] Aluminum alloy plate (AA5182): size 60mm×50mm, thickness 1.5mm;
[0034] Nickel foil: size 50mm×10mm, thickness 0.2mm, purity 99.9%;
[0035] Zn-Al alloy welding wire: diameter 1.6-2.0mm, the mass percentage of chemical elements in the wire is: Al 21.0%-23.0%, other elements 0.15-0.2%, and the rest is Zn; among them, other elements are Zn- Other components allowed in Al alloy welding wire have no effect on the welding reaction of the main components zinc and aluminum.
[0036]Flux: Superior No.20 (Superior Flux&Mfg.Co.), its composition mass percentage is: LiCl35%~40%, KCl 30%~35%, NaF 10%~21%, NaCl 8%~13%, ZnCl 2 6% to 10%.
[0037] 2. Preparation before welding
[0038] (1) Surface cleaning and flux solution preparation
[0039] Surface cleaning of the aluminum alloy plate: (1) soak the aluminum alloy plate in a 10% to 15%...
Embodiment 2
[0062] 1. Selection of welding consumables and intermediate layer
[0063] Same as Example 1.
[0064] 2. Preparation before welding
[0065] (1) Surface cleaning and flux solution preparation
[0066] The surface cleaning method and the preparation method of the flux solution are the same as in Example 1.
[0067] (2) Overlap
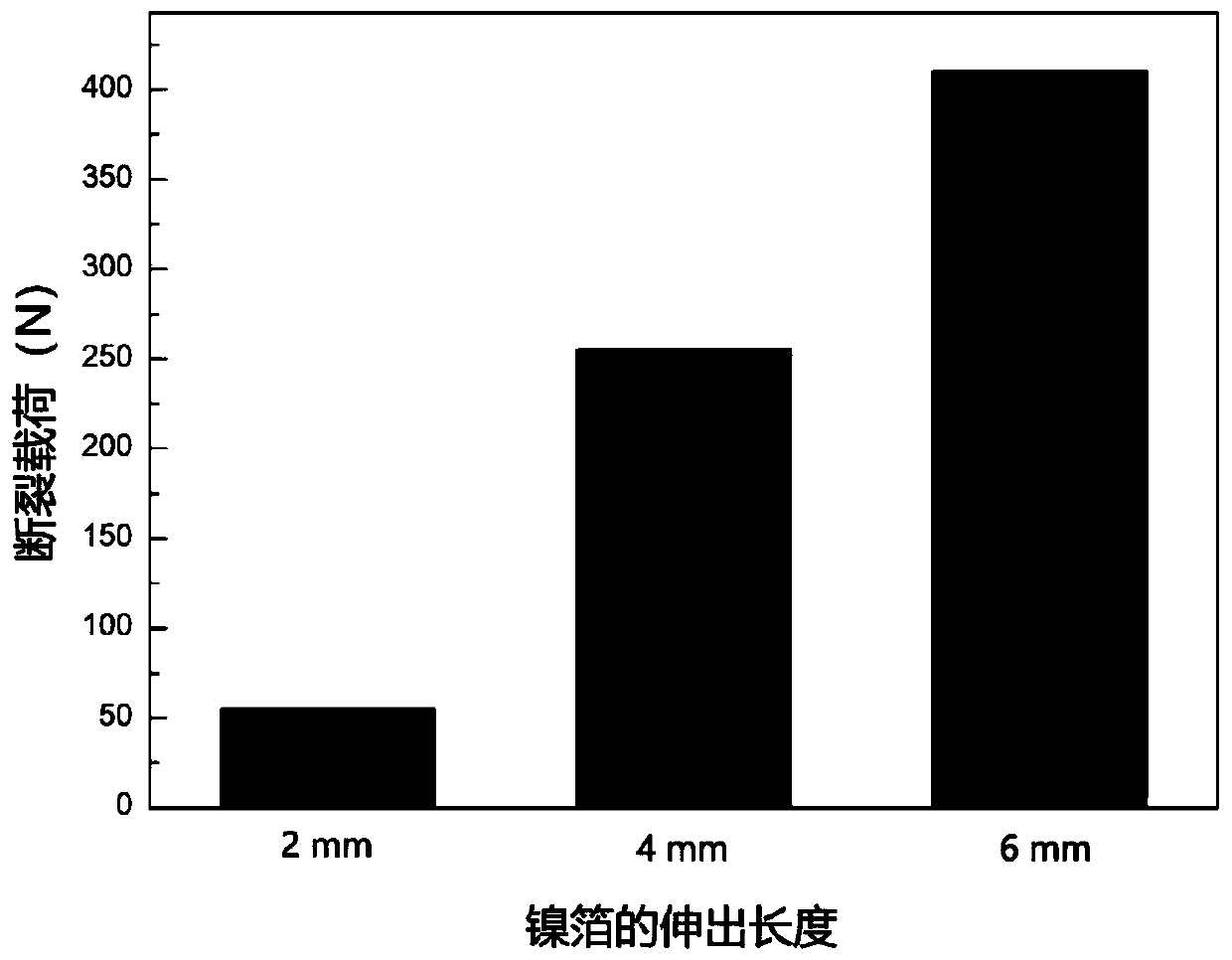
[0068] The overlapping method is the same as in Example 1, except that the difference from Example 1 is that the length of the overlapped joint between the nickel foil inserted into the magnesium alloy plate and the aluminum alloy plate is 6 mm, and the remaining 4 mm extends out of the magnesium alloy plate and the aluminum alloy plate. Overlapped joints.
[0069] 3. Welding
[0070] The welding method is the same as in Example 1, except that the laser parameters are: laser power 2.4kW, welding speed 0.24m / min.
[0071] 4. Post-welding treatment
[0072] (1) Cooling after welding: the method is the same as in Example 1.
[0073] (2) Clean up a...
Embodiment 3
[0080] 1. Selection of welding consumables and intermediate layer: the same as in Example 1.
[0081] 2. Preparation before welding
[0082] (1) Surface cleaning and flux solution preparation: the surface cleaning method and flux solution preparation method are the same as in Example 1.
[0083] (2) Overlap
[0084] The lapping method is the same as in Example 1, except that the difference from Example 1 is that the length of the overlapping overlapping parts of the nickel foil inserted into the magnesium alloy plate and the aluminum alloy plate is 4 mm, and the remaining 6 mm extends out of the magnesium alloy plate and the aluminum alloy plate. Overlapped joints.
[0085] 3. Welding
[0086] The welding method is the same as in Example 1, except that the laser parameters are: laser power 2.0kW, welding speed 0.28m / min.
[0087] 4. Post-welding treatment
[0088] (1) Cooling after welding: the method is the same as in Example 1.
[0089] (2) Clean up after welding: the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com