Synthetic gene as well as method and application for establishing tobacco multi-gene site-directed mutation vector
A technology for gene synthesis and site-directed mutagenesis, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as time-consuming and labor-intensive, inability to obtain multiple mutants, and achieve the effects of simplifying intermediate steps, good application and promotion prospects, and ensuring mutation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
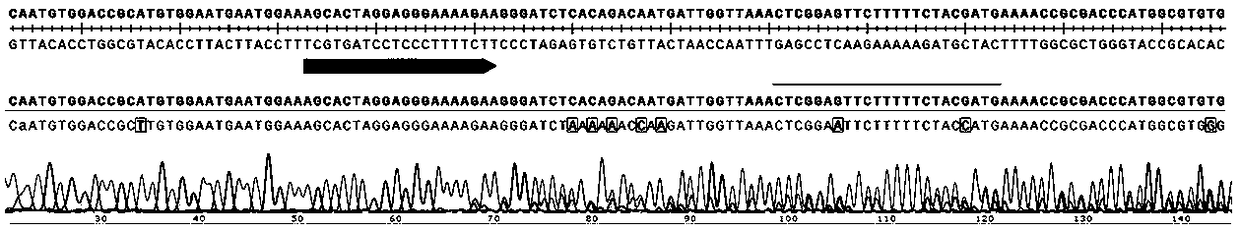
[0102]Two sgRNA sequences were designed for Ntab1 and Ntab2 genes, sgRNA1: agcactaggagggaaaagaa; sgRNA2: gggatctcacagacaatgat. then follow figure 1 Target site gene sequences for synthetic mutations of these 2 genes are shown. By extracting the amplified pUC57-Kan Escherichia coli plasmid (the plasmid contains multiple gene knockout target site sequences), such as figure 2 As shown, after digestion with Bsa I, the DNA band marked by the white arrow shows the band of the synthetic gene. After cutting the gel to recover the synthetic gene, use T4 ligase to digest the pORE-CRISPR / Cas9 ( figure 2 The position marked by the black arrow) was ligated with the plant expression vector, and the ligated product was transformed into Escherichia coli, and after verification by screening and sequencing, a knockout multi-gene CRISPR / Cas9 vector was obtained. The constructed vector was transformed into tobacco, and the Ntab1 and Ntab2 genes were detected by sequencing (such as image 3 ...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Two sgRNA sequences were designed for Ntab3, 4, and 5 genes, sgRNA1: agtgtttggaaaaccctagg; sgRNA2: tggagtgtttggaaaaccct: sgRNA3: gcacttgaaaccctagccct. then follow Figure 5 Target site gene sequences for synthetic mutations of these 2 genes are shown. Using M13 as a primer, the pUC57-Kan plasmid containing the synthetic gene was used as a template to amplify the synthetic gene fragment by PCR under the action of high-fidelity DNA polymerase ( Image 6 left arrow). After the amplified gene fragment was digested with Bsa I, it was subjected to electrophoresis ( Image 6 Arrow on the right), and the recovery after cutting the gel is the synthetic gene sequence with linker. Then the pORE-CRISPR / Cas9 vector is also digested with Bsa I (such as figure 2 Black arrow), linearized cohesive ends were obtained after electrophoresis and gel recovery. The knockout vector for knocking out these two genes is constructed by ligating the synthetic gene sequence and the linearized ...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Two sgRNA sequences were designed for Ntab6 and 7 genes, sgRNA1: aacattaggaggaaaacgca; sgRNA2: gacattagggaaaacgca. then follow Figure 10 Target site gene sequences for synthetic mutations of these 2 genes are shown. Using M13 as a primer, the pUC57-Kan plasmid containing the synthetic gene was used as a template to amplify the synthetic gene fragment by PCR under the action of high-fidelity DNA polymerase ( Figure 11 left arrow). The amplified gene fragments were digested with Bsa I, electrophoresed and gel-cut, and recovered as synthetic gene sequences with adapters ( Figure 11 right arrow). Then the pORE-CRISPR / Cas9 vector is also digested with Bsa I (such as figure 2 .Black arrow), the linearized cohesive ends were obtained after electrophoresis and gel cutting recovery. The knockout vector for knocking out these two genes is constructed by ligating the synthetic gene sequence and the linearized vector using T4 ligase. After the vector is transformed into A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com