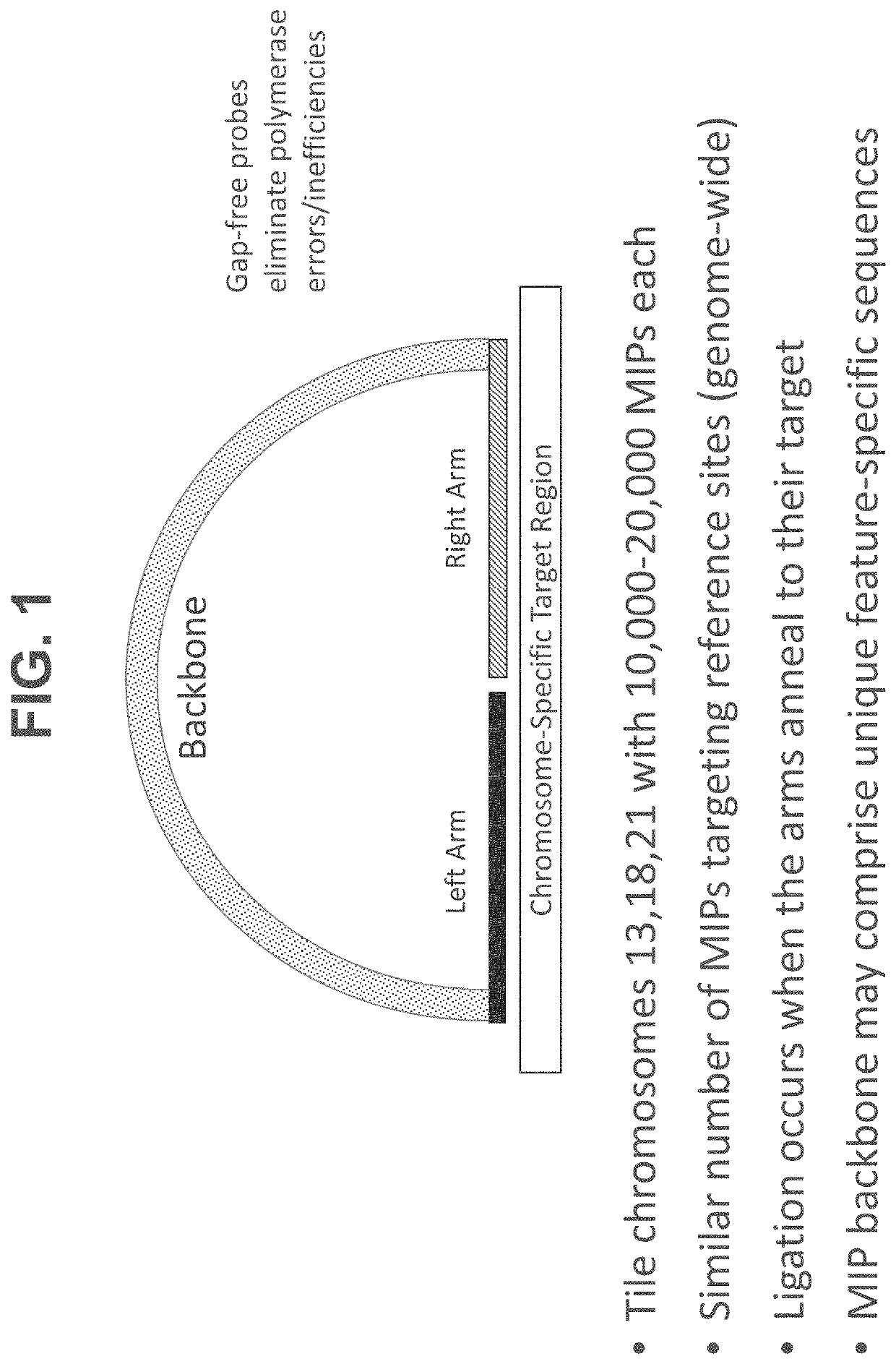
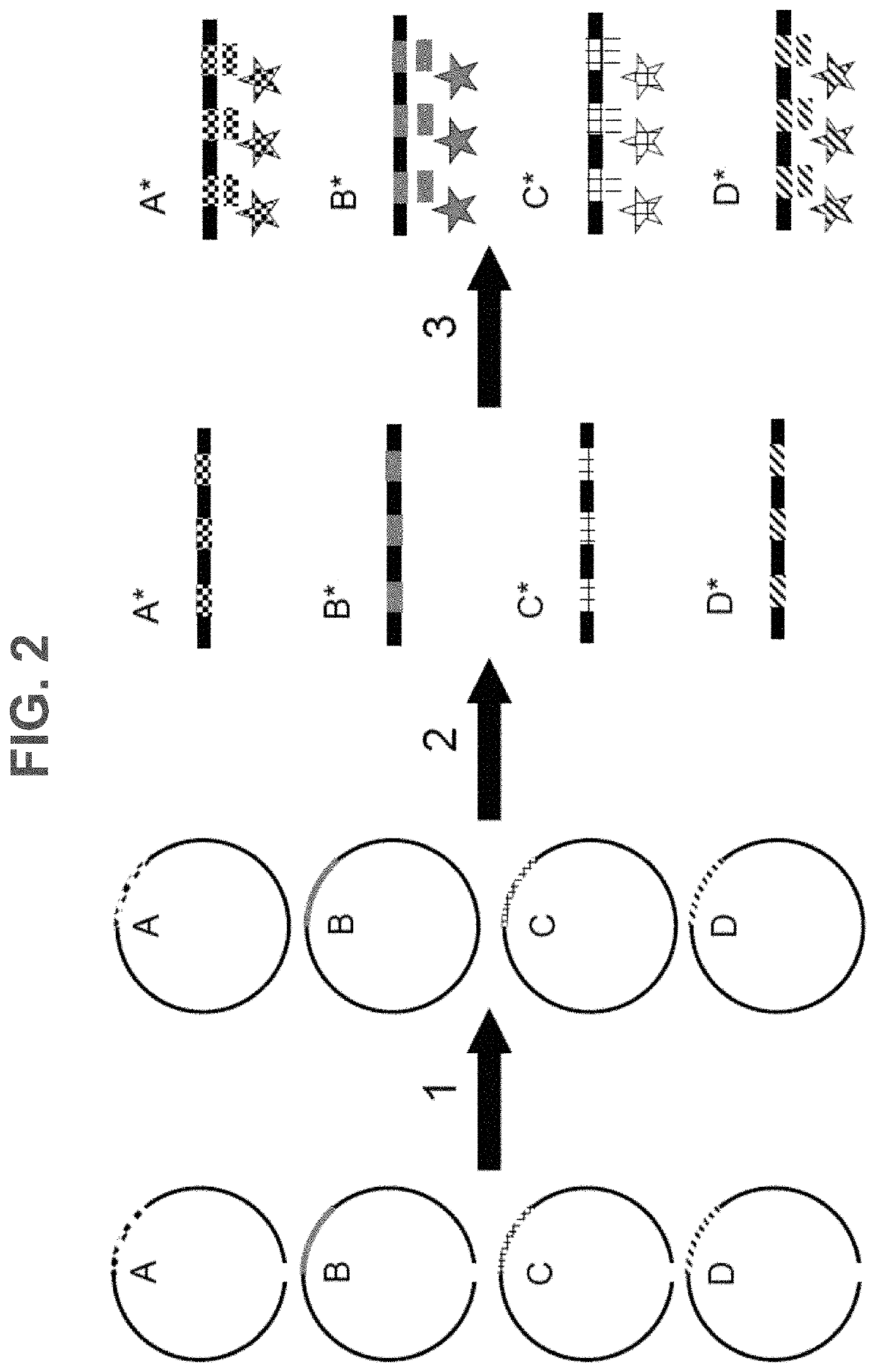
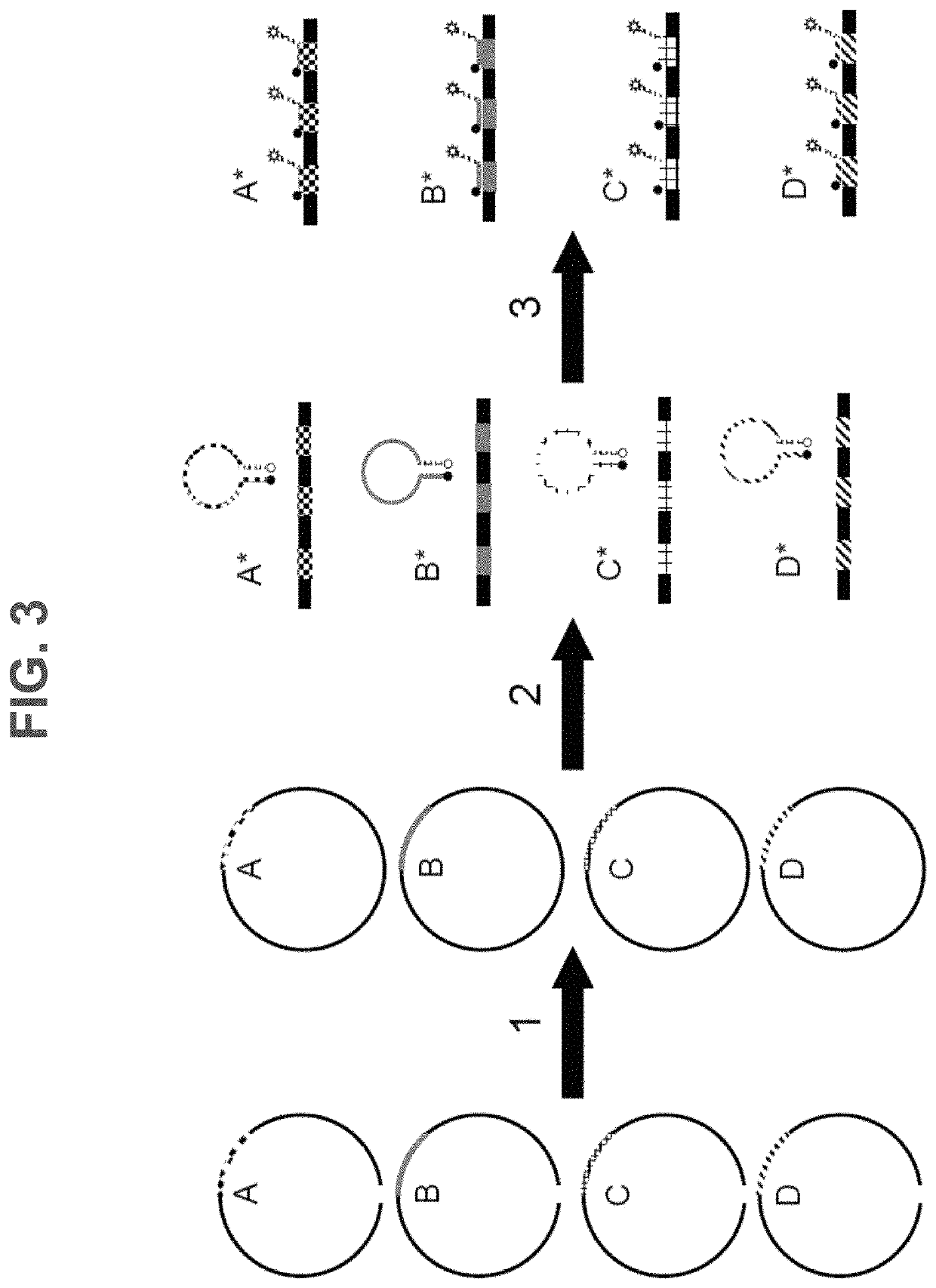
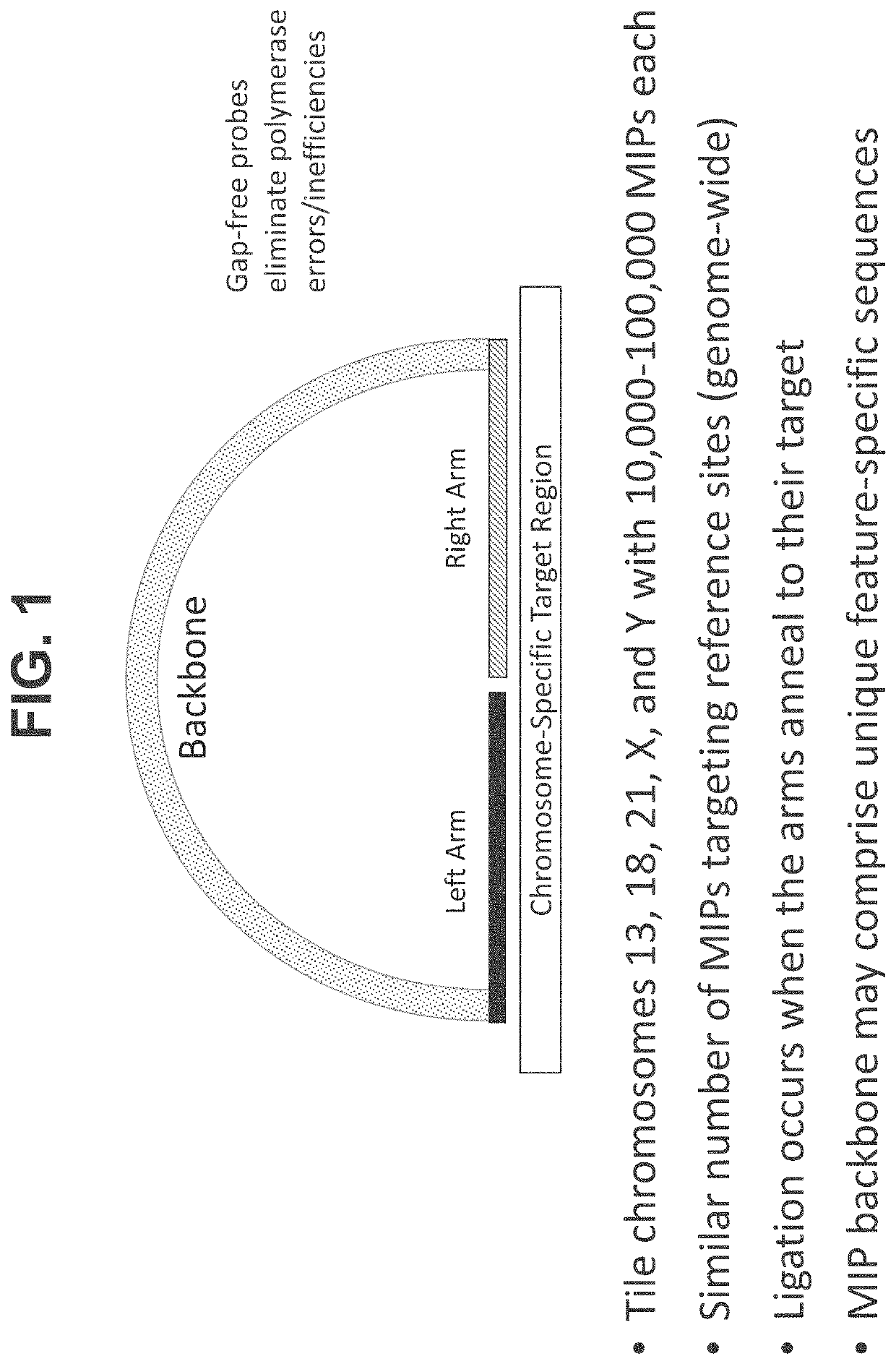
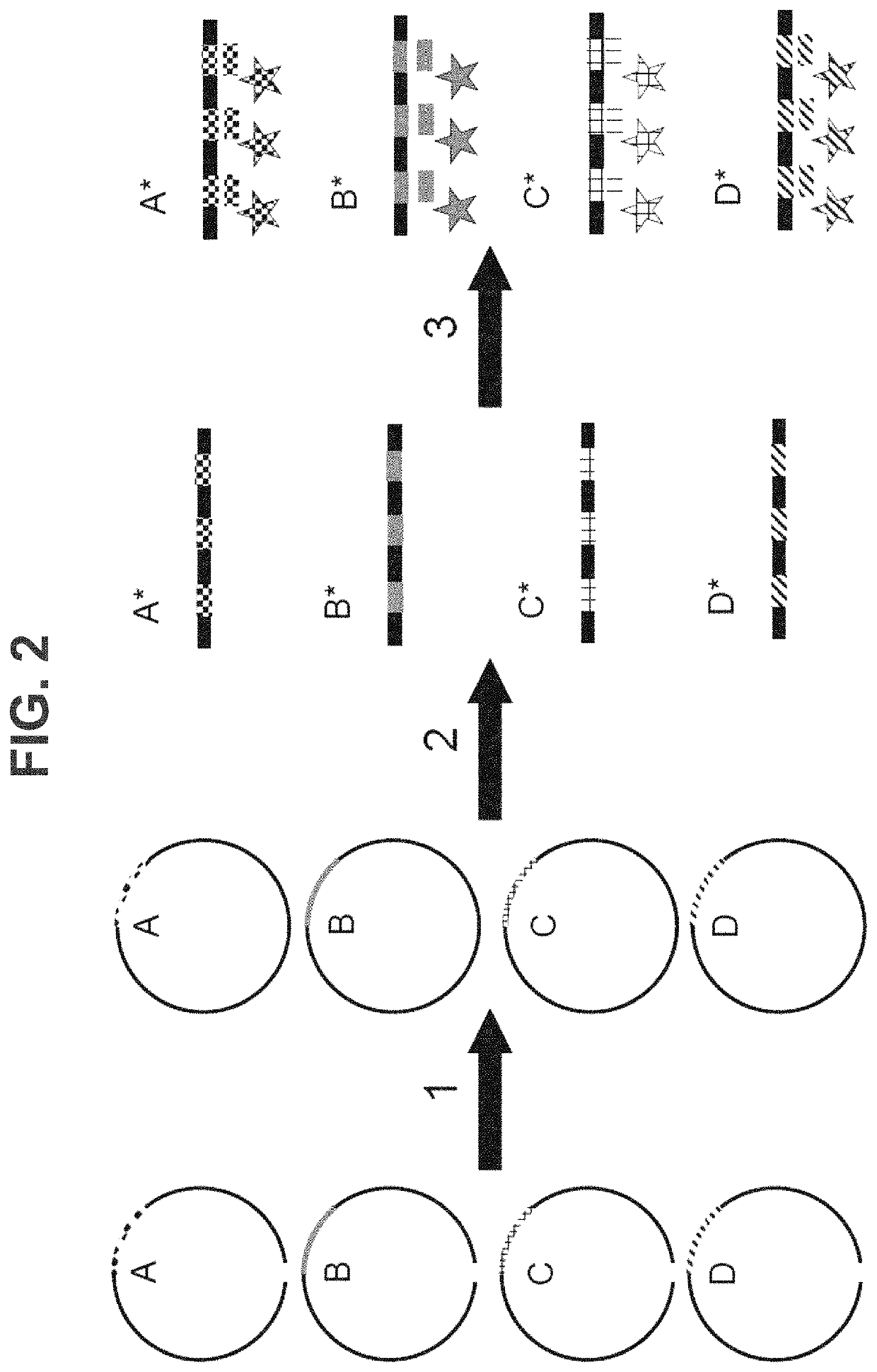
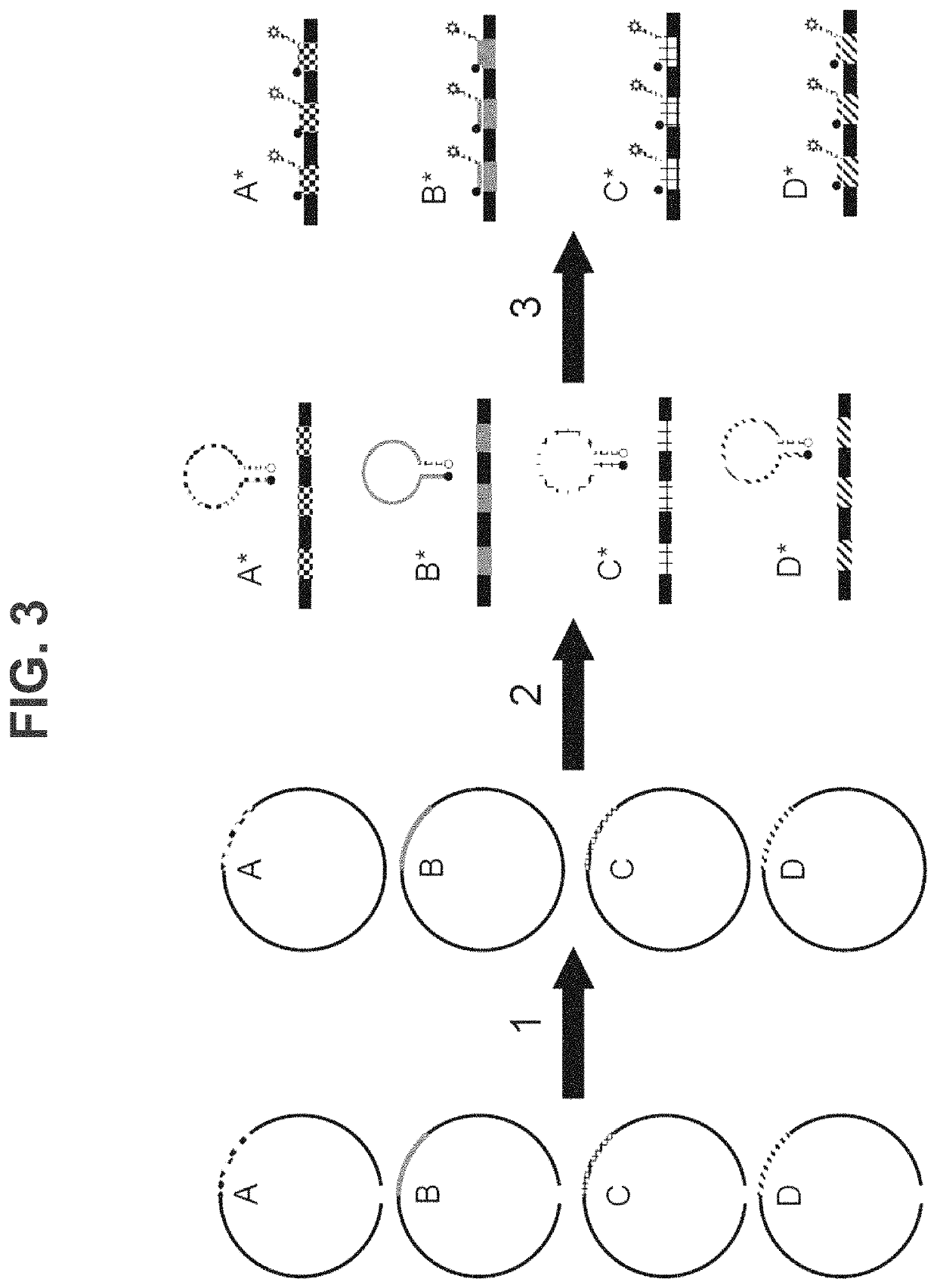
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Gene duplication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. Gene duplications can arise as products of several types of errors in DNA replication and repair machinery as well as through fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements. Common sources of gene duplications include ectopic recombination, retrotransposition event, aneuploidy, polyploidy, and replication slippage.
Amplification based polymorphism detection
InactiveUS7250252B2Improve automationEasy to mergeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementImproved methodPolymorphism Detection
An improved method of amplifying nucleic acids comprising the use of four discrete temperature steps in a thermocyclic amplification reaction, as well as, a method of detecting large nucleic acid insertions or deletions such as those that occur from gene duplication or deletion.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Detection of gene duplications
InactiveUS20050255485A1Easy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsFluorescenceGenetic Anomaly
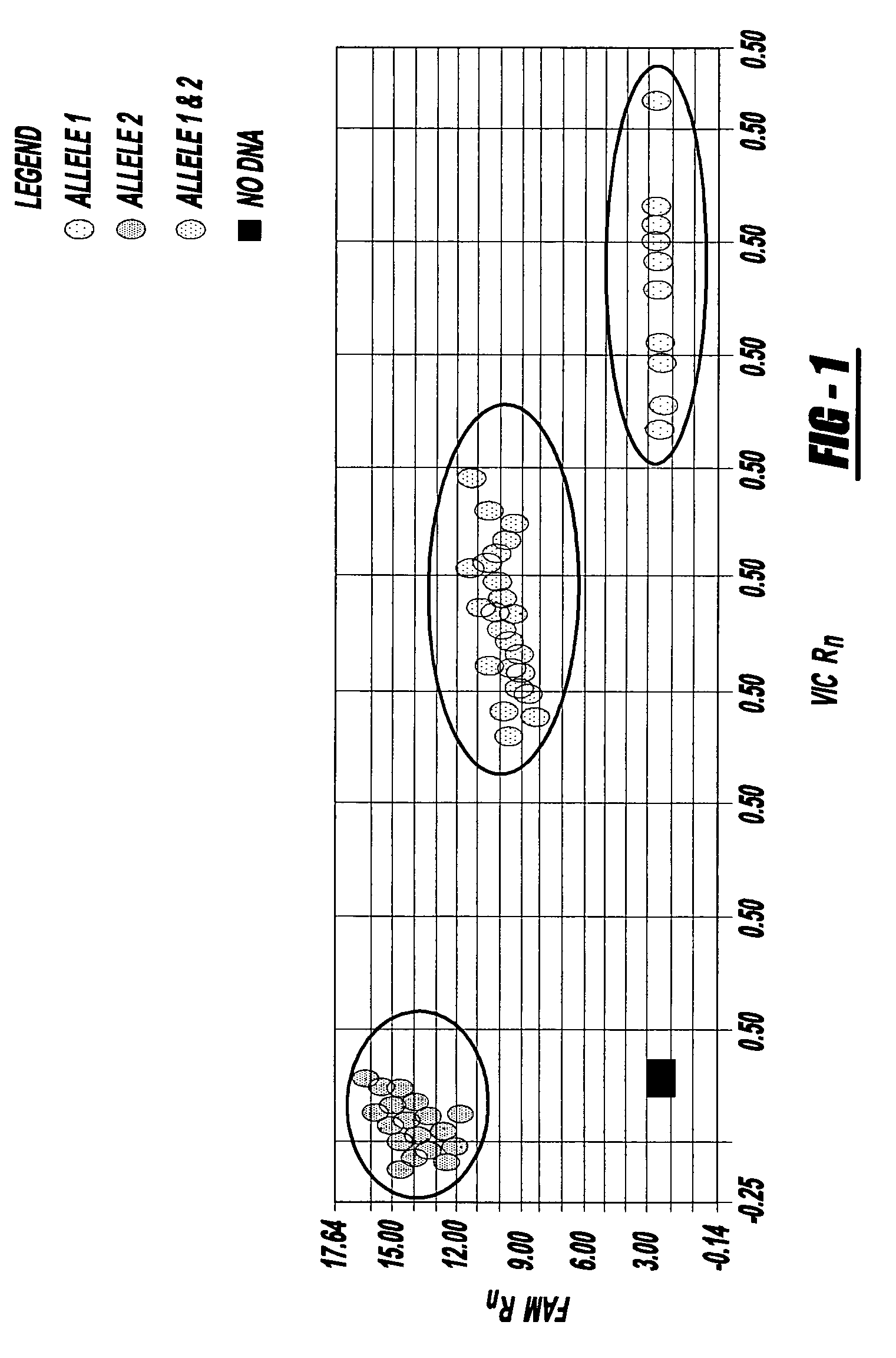
Methods of detecting a candidate genetic anomaly such as a candidate duplication in a genome are disclosed. The methods comprise quantifying fluorogenic assays for alleles of a genetic locus from a plurality of individual genomes, identifying ranges of fluorescent intensities indicative of individual genomes homozygous for a first allele, homozygous for a second allele, or heterozygous for both alleles, and identifying individual genomes in which the fluorescence intensities are outside the range of intensities indicative of homozygosity or heterozygosity for the genetic locus.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Anti-ageing gene oligopeptide-containing preparation and application of preparation to cosmetics
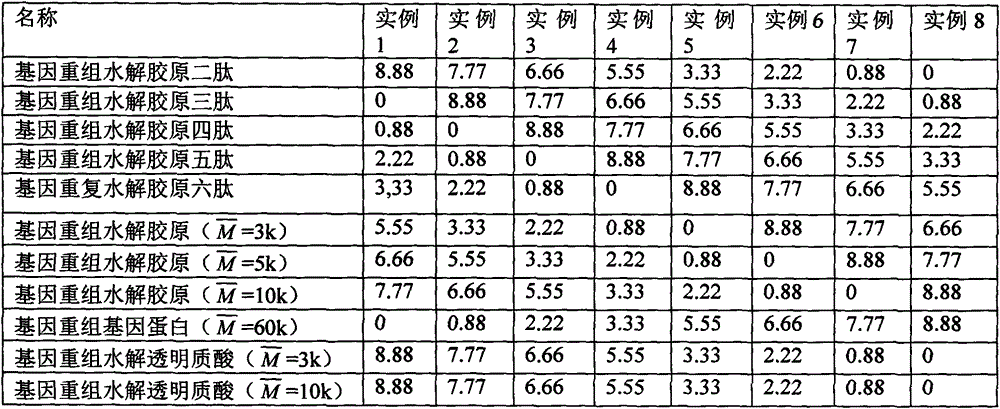
The invention provides an anti-ageing gene oligopeptide-containing preparation and an application of the preparation to cosmetics. The preparation is prepared by compounding gene oligopeptide key components, auxiliary materials and preparation raw materials. Gene oligopeptide is selected from one or a combination of genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen dipeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen tripeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen tetrapeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen pentapeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen hexapeptide, first genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen, second genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen, third genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen, genetic recombination gene protein, first genetic recombination hydrolyzed hyaluronic acid and second genetic recombination hydrolyzed hyaluronic acid.
Owner:SHAANXI HUIKANG BIO TECH CO LTD
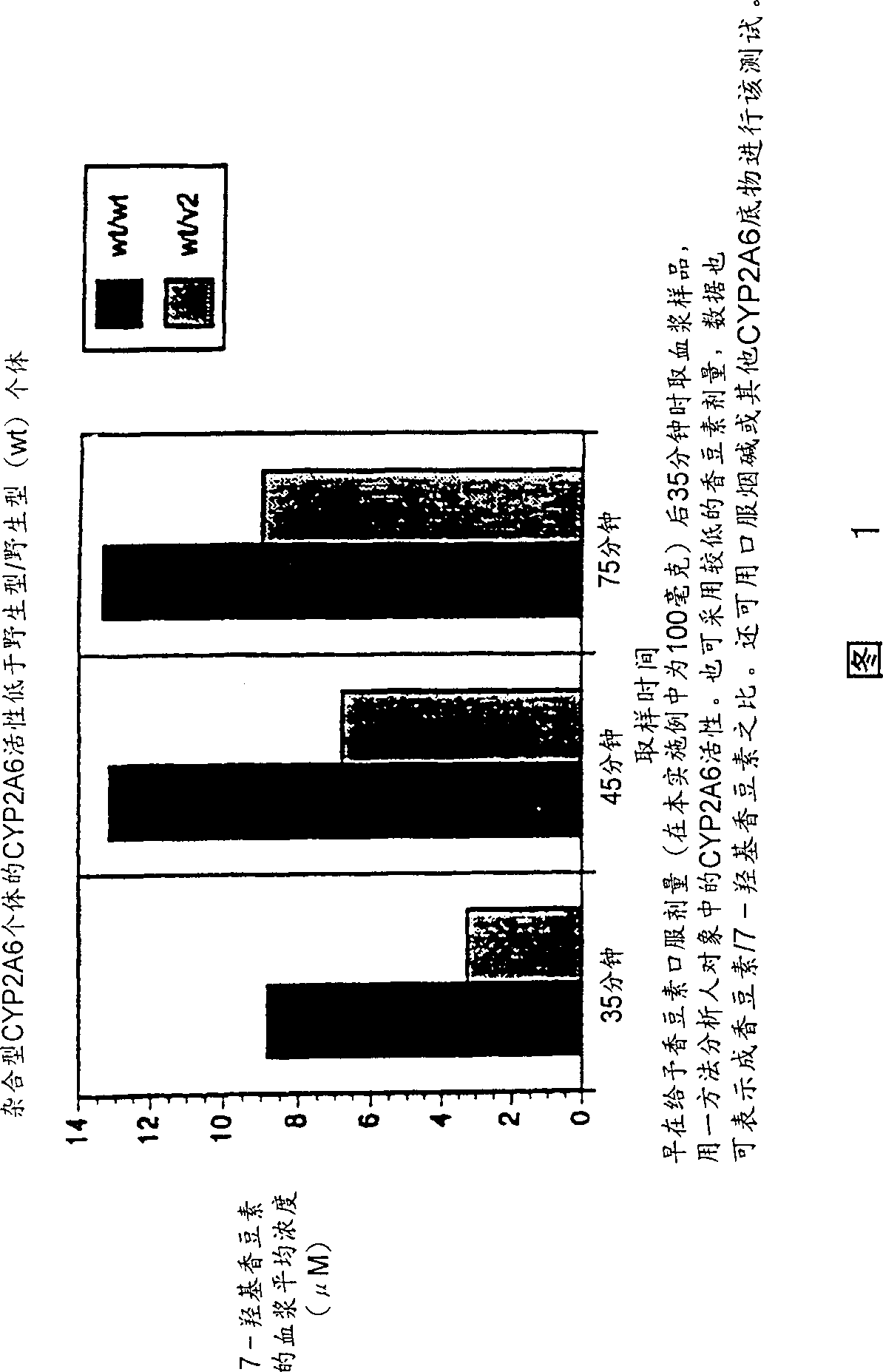
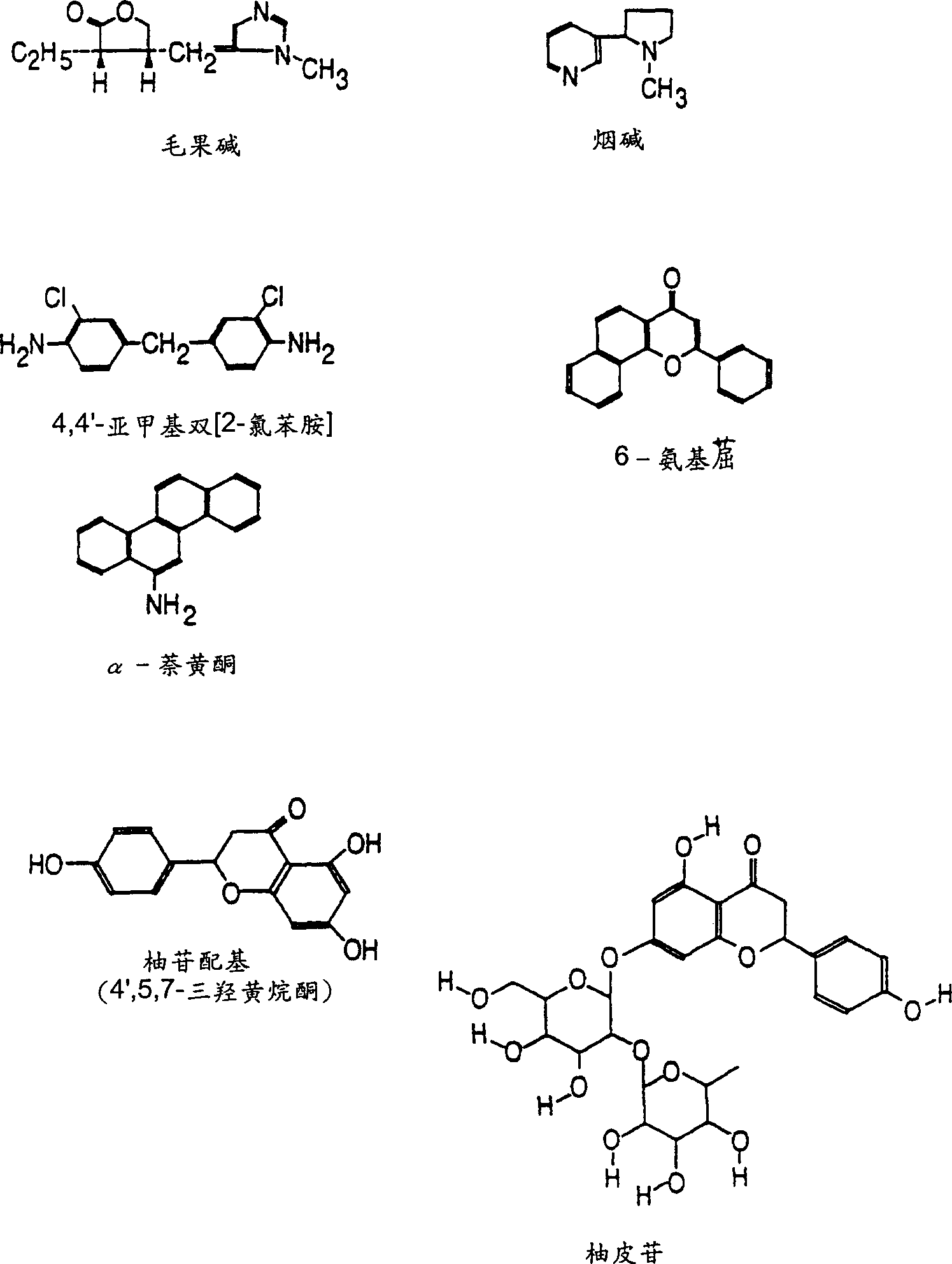
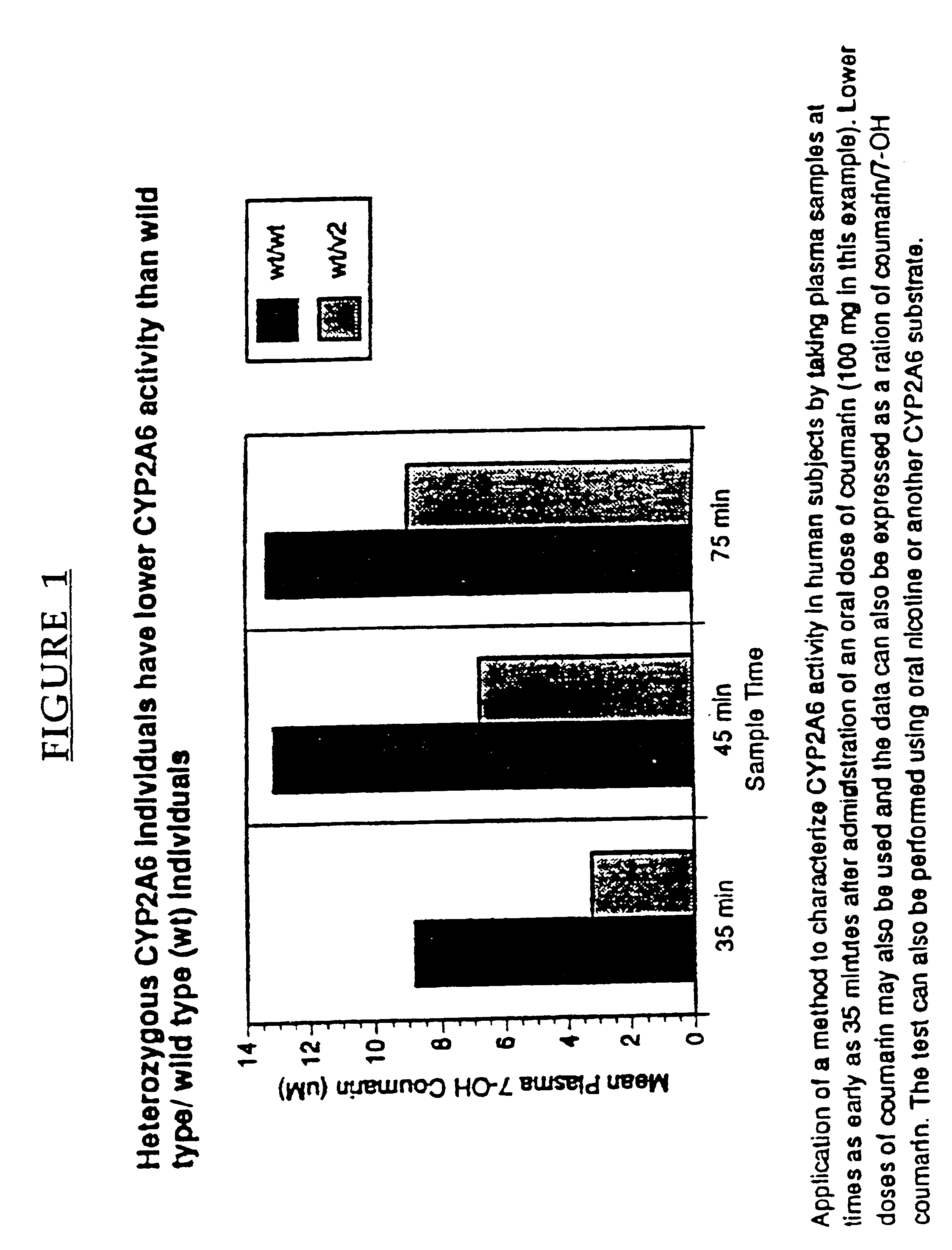
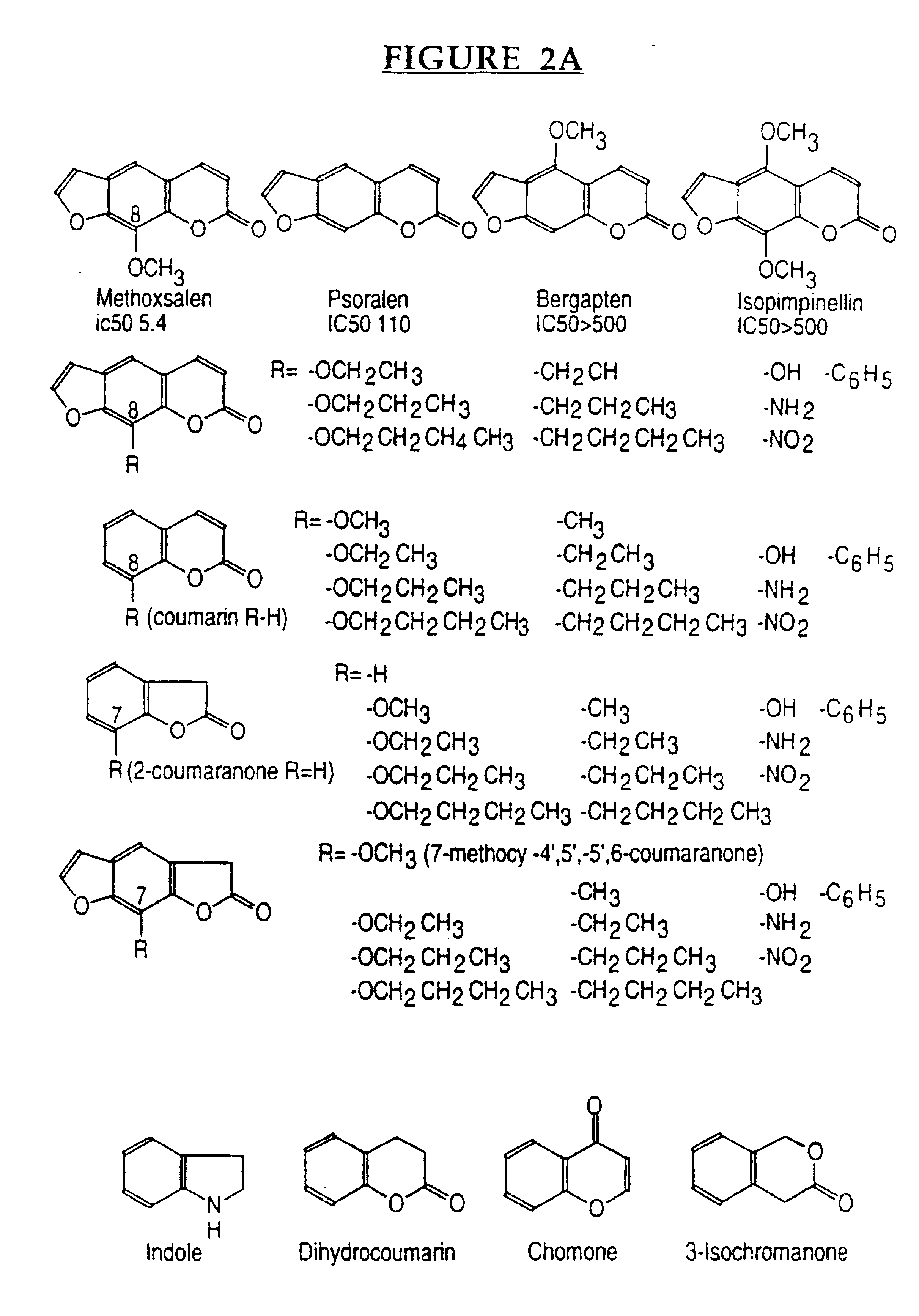
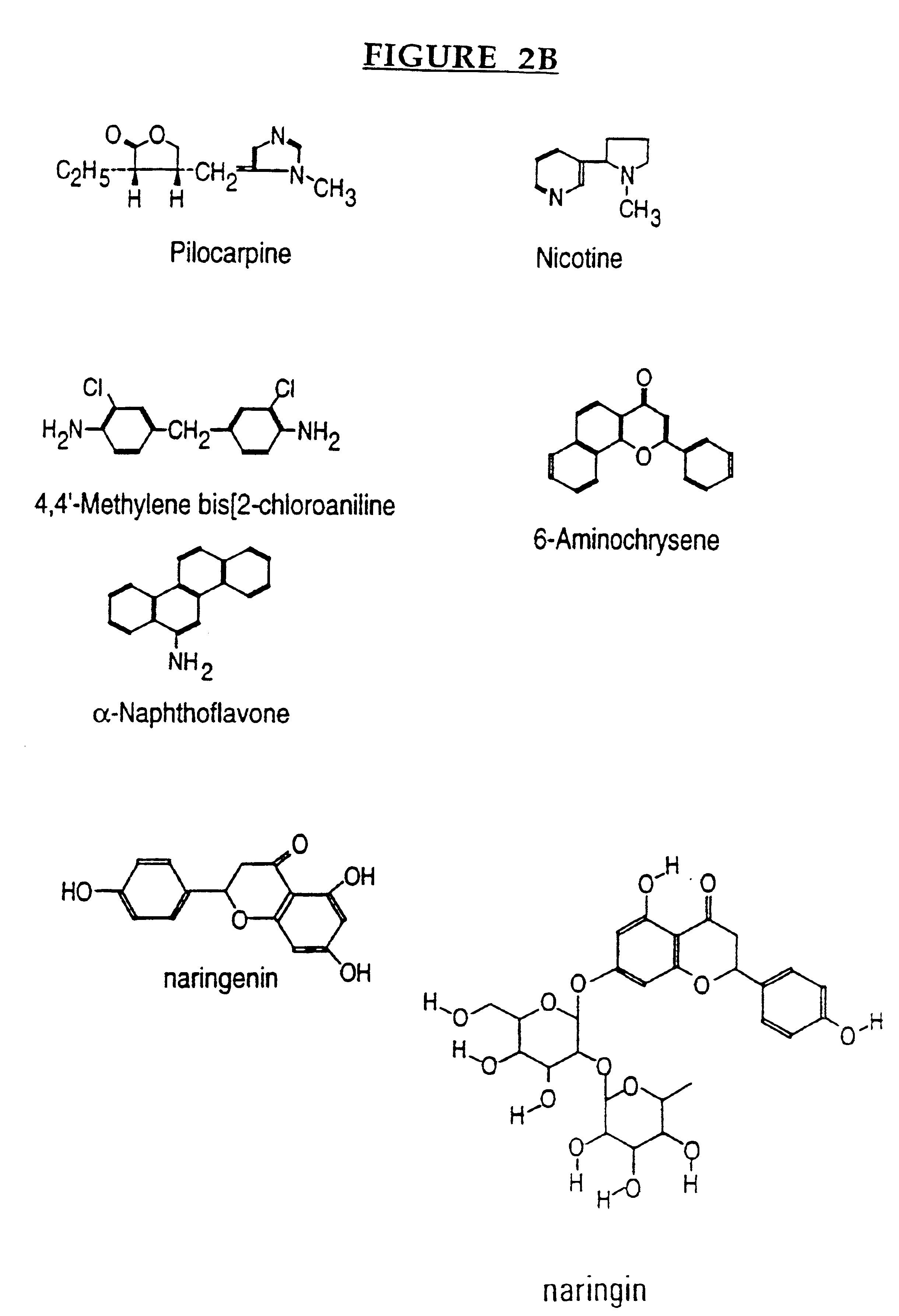
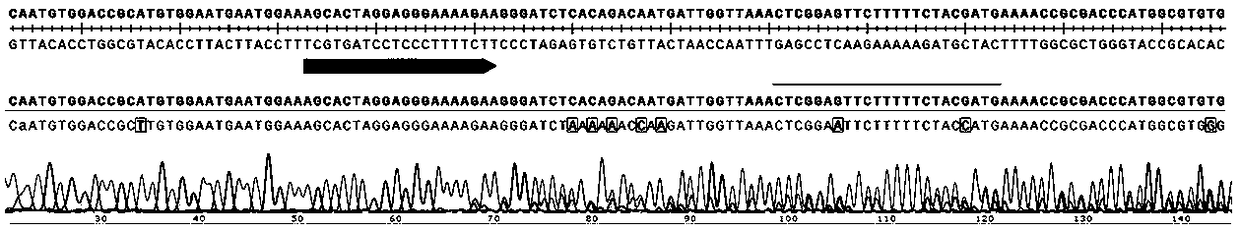
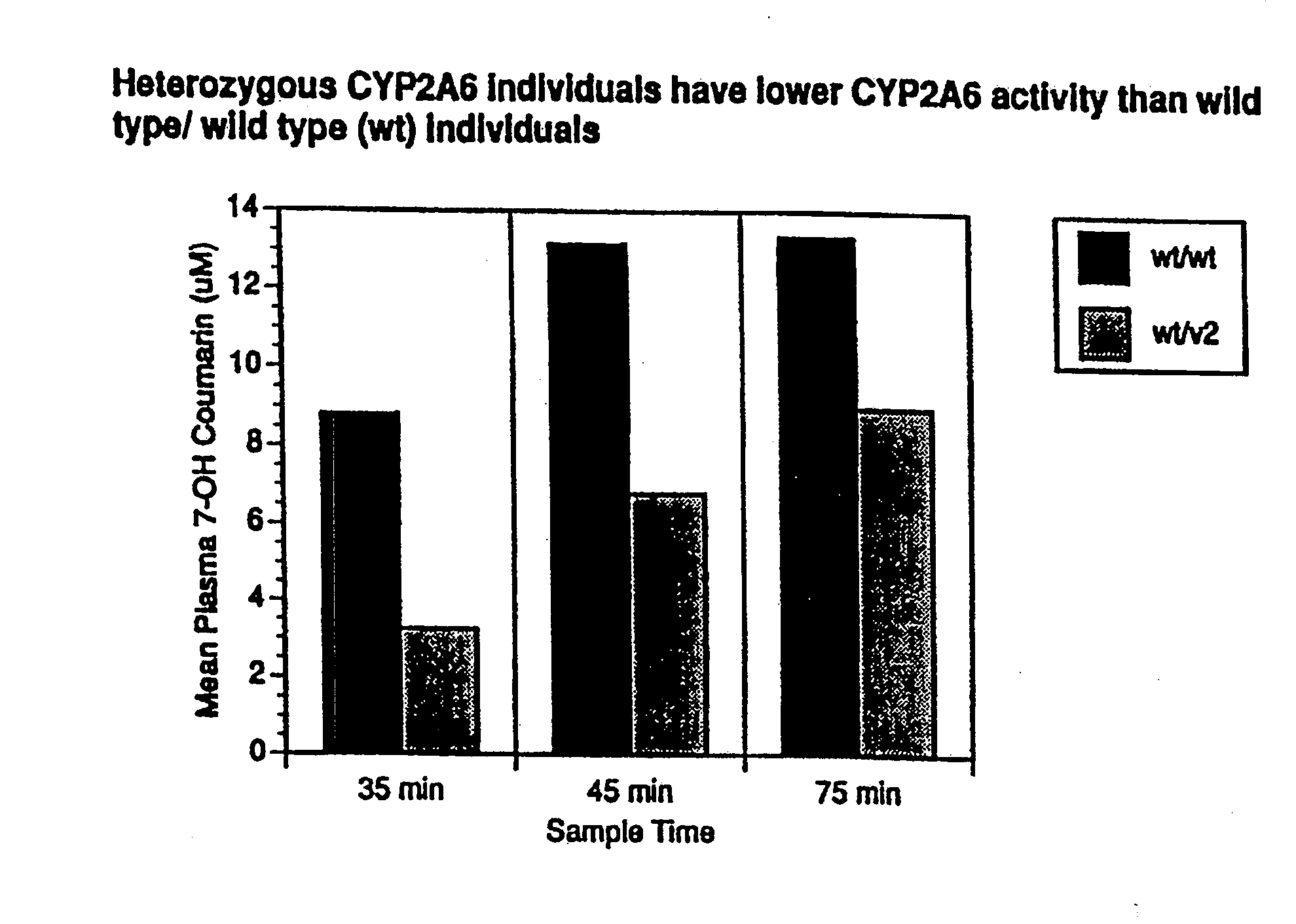
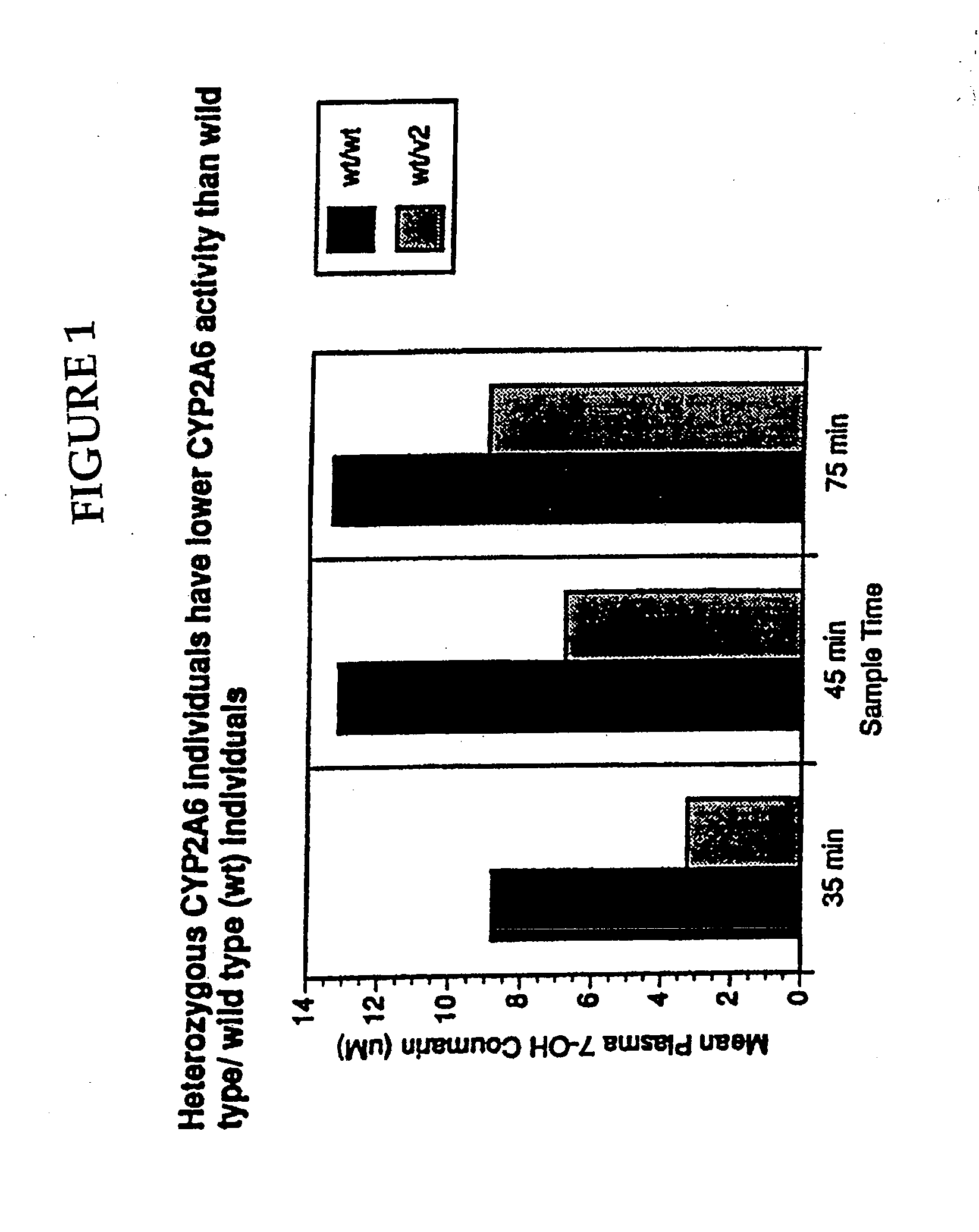
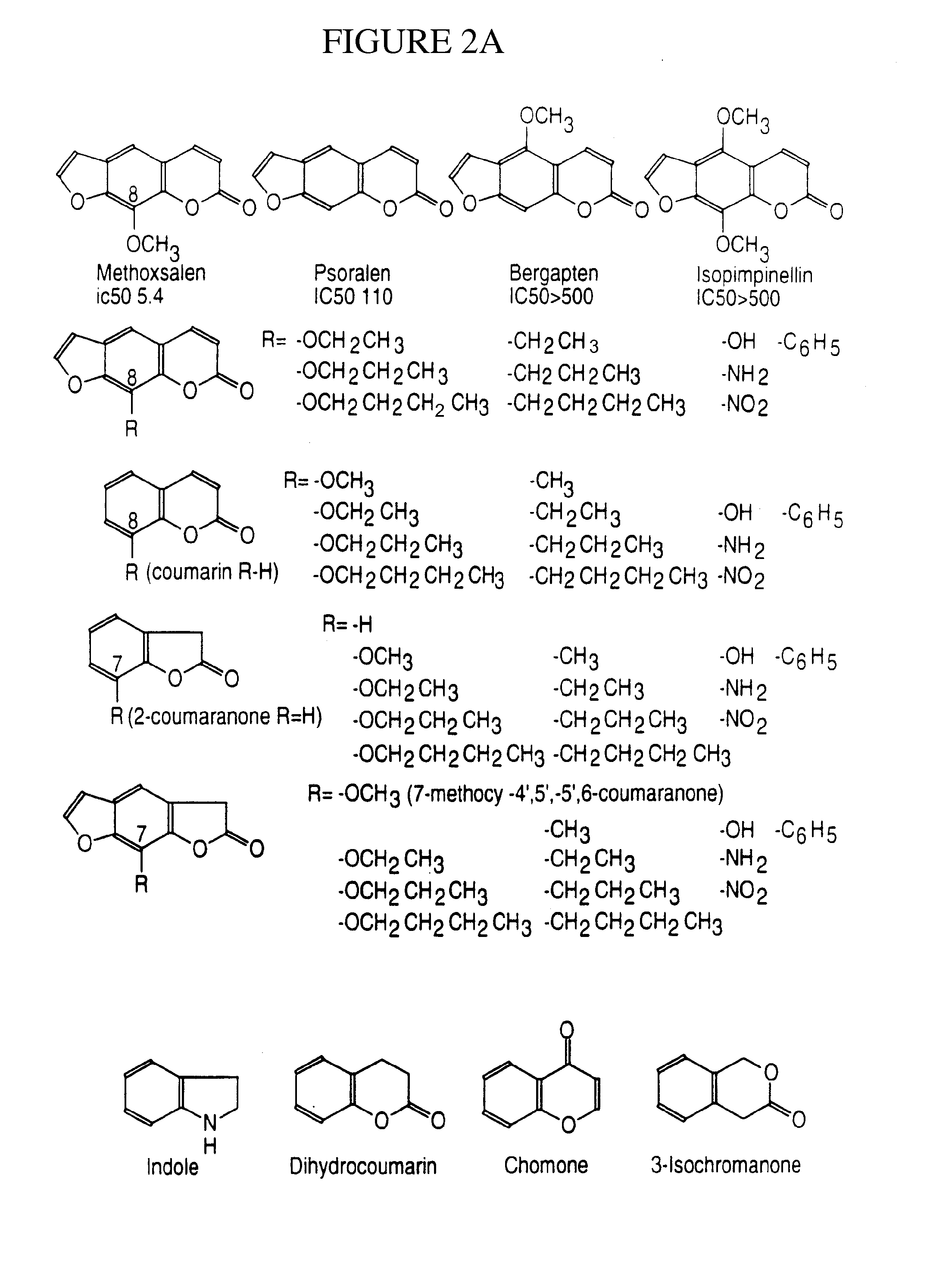
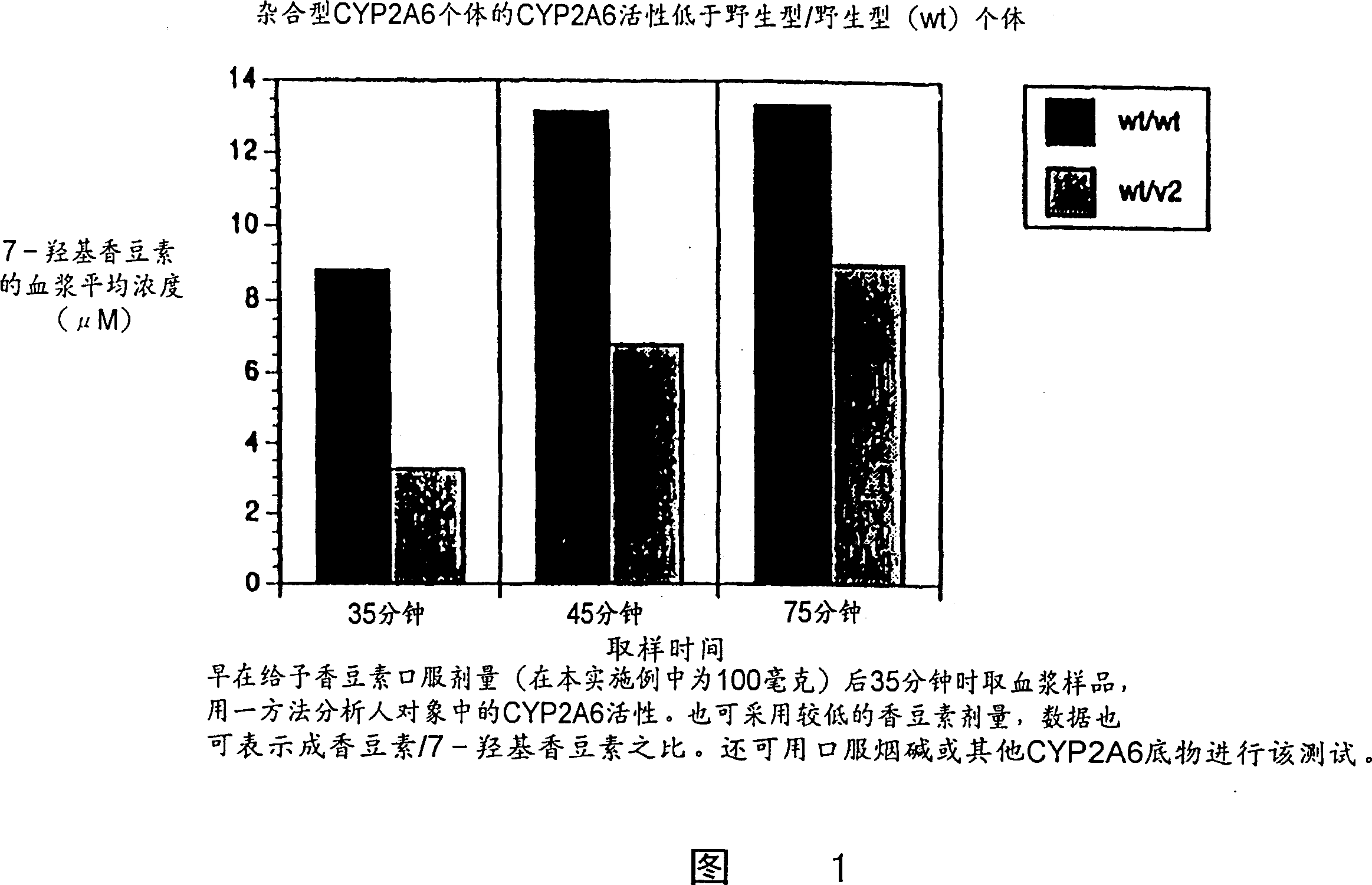
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on cyp2a enzymes
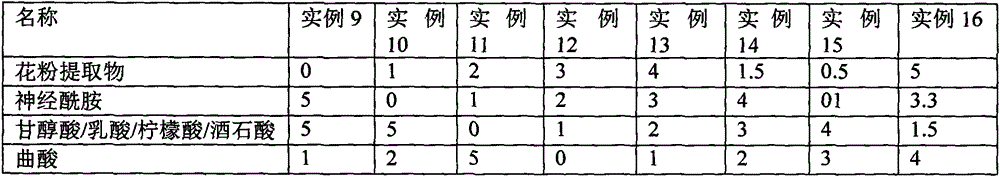
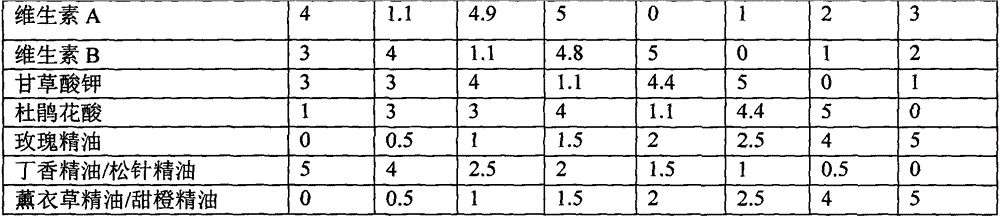
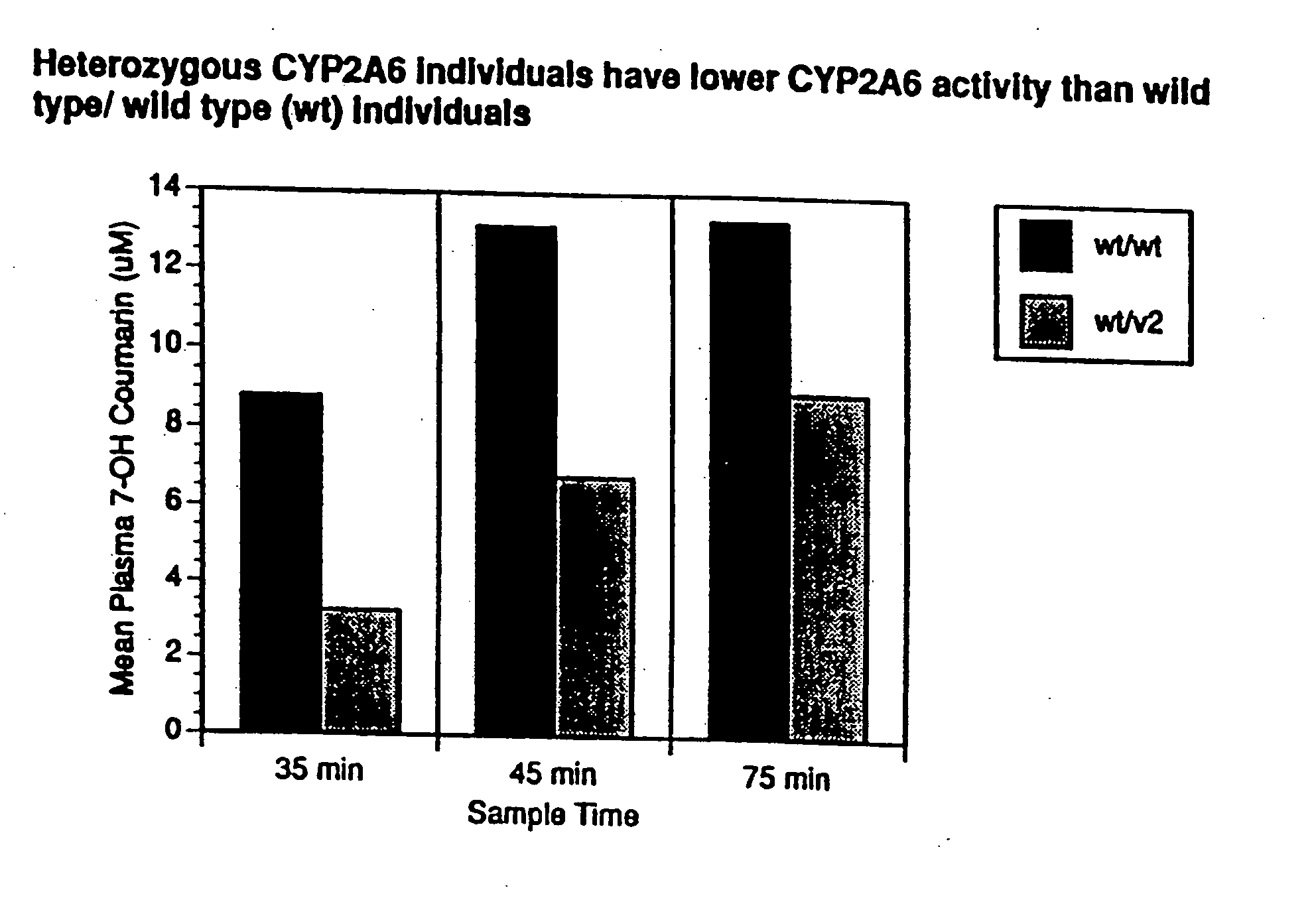
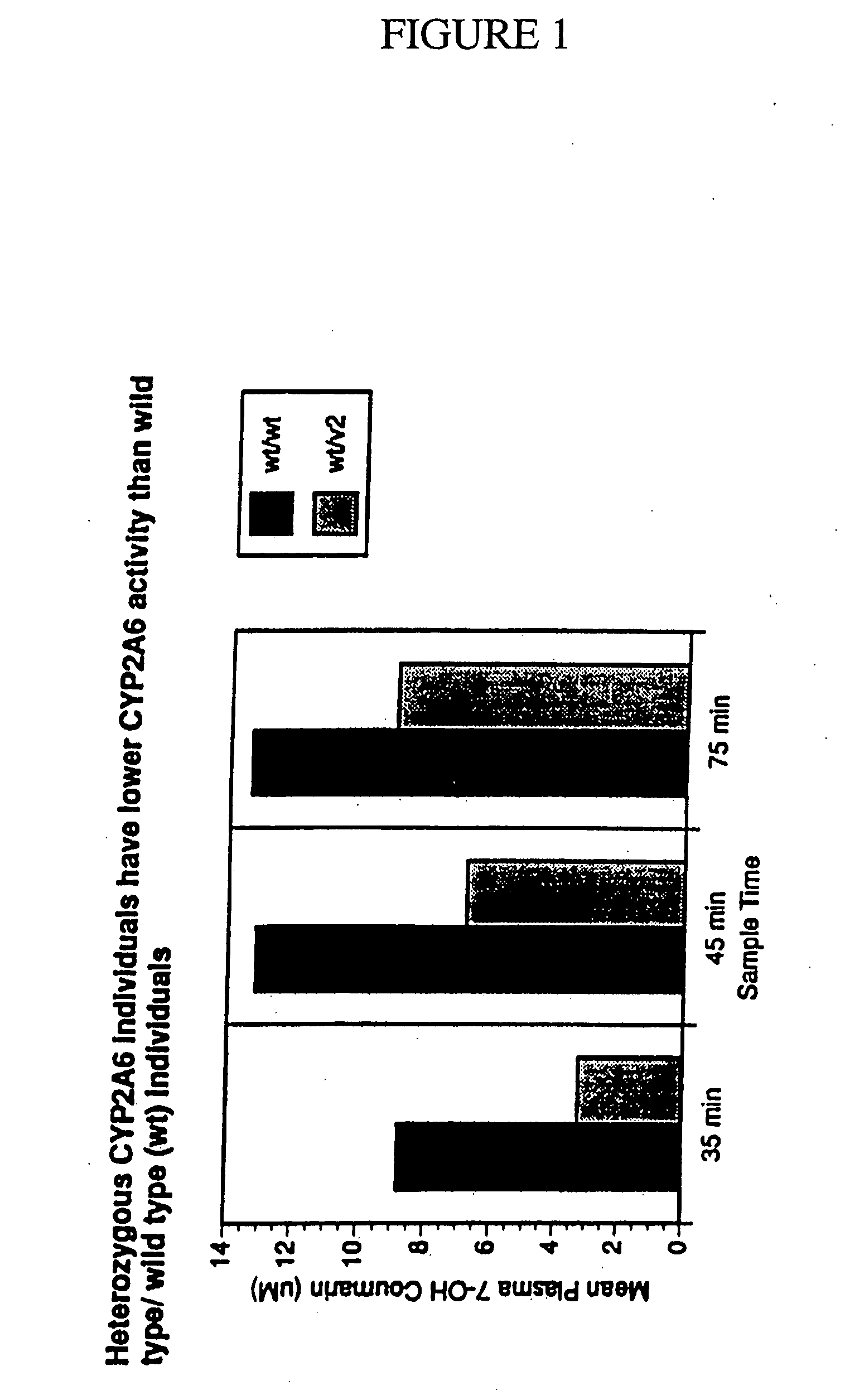
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Genetically stabilized tandem gene duplication
InactiveUS20110236927A1Stable and tunable and high-level expression of proteinIncrease in lycopene yieldFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGene duplication
The invention provides constructs and methods for producing genetically stabilized tandem gene duplications.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multiplex PCR rapid identification method for salmonella and listeria monocytogenes
InactiveCN1603422AEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses a kind of appraisal bacterium, specially appraises the monk fungus (Salmonella), produces the uninuclear cell Liszt fungus (Listeria monocytogenes) the examination method. First (YAU_DSL1) separately uses the monk fungus and the backwoods coli the thermal crack solution to withdraw respective DNA template, produces the uninuclear cell Liszt fungus to use the enzyme solution to withdraw the DNA template, then carries on disposable PCR to expand increases the specific many genes, finally passes through the electricity to swim the appraisal. The invention through sample DNA, disposable at the same time to the monk fungus histidine transportation operon gene which possibly has, produces the uninuclear cell hemolysin gene to expand increases (YZU_DSL1) the material particle carries on with the certain existence backwoods coli expands increases, forms the massive genes duplication fragment, quite is convenient, can appraise whether for the monk fungus, produces the uninuclear cell Liszt fungus, and makes the judgement to the negative result reacting system accuracy. The invention more classical method bacterium separation, the appraisal and the blood serum school grades testing method fast, is accurate.
Owner:江苏瑞邦生物科技有限公司
Saccharopolyspora spinosa rhamnose biosynthesis gene duplication engineering strain
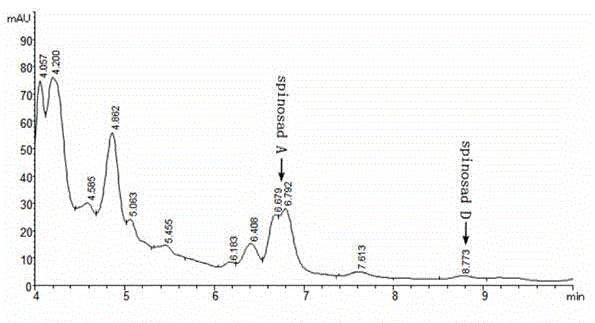
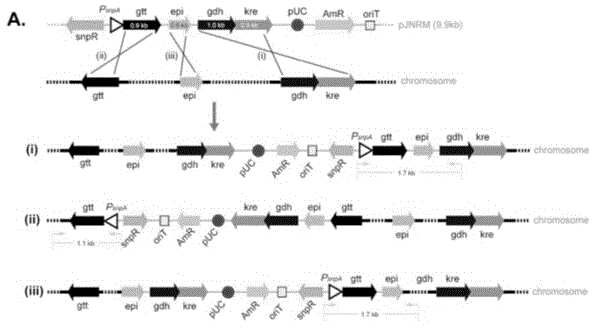
The invention relates to a Saccharopolyspora spinosa rhamnose biosynthesis gene duplication engineering strain (S. sp-RM, Saccharopolyspora spinosa) which is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection on June 8th, 2015, and the culture collection number is CCTCC NO:M2015363. The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) identification result indicates that the plasmid is successfully integrated to the Saccharopolyspora pogona genome. The real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR result indicates that the transcription levels of genes gdh, kre, epi and gtt in the engineering strain are respectively enhanced by 80.3 times, 30.8 times, 23.8 times and 18.3 times as compared with the initial strain. The HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) detection result indicates that the pleocidin yield of the engineering bacterium S. sp-RM is enhanced by 73% as compared with the initial strain.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
CYP2A enzymes and their use in therapeutic and diagnostic method
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as 'CYP2A6' for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on CYP2A enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Detection of gene duplications
InactiveUS20100203525A1Easy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenetic AnomalyAllele
Methods of detecting a candidate genetic anomaly such as a candidate duplication in a genome are disclosed. The methods comprise quantifying fluorogenic assays for alleles of a genetic locus from a plurality of individual genomes, identifying ranges of fluorescent intensities indicative of individual genomes homozygous for a first allele, homozygous for a second allele, or heterozygous for both alleles, and identifying individual genomes in which the fluorescence intensities are outside the range of intensities indicative of homozygosity or heterozygosity for the genetic locus.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Carcinoma-related genes and polypeptides and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7348418B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSquamous CarcinomasNovel gene
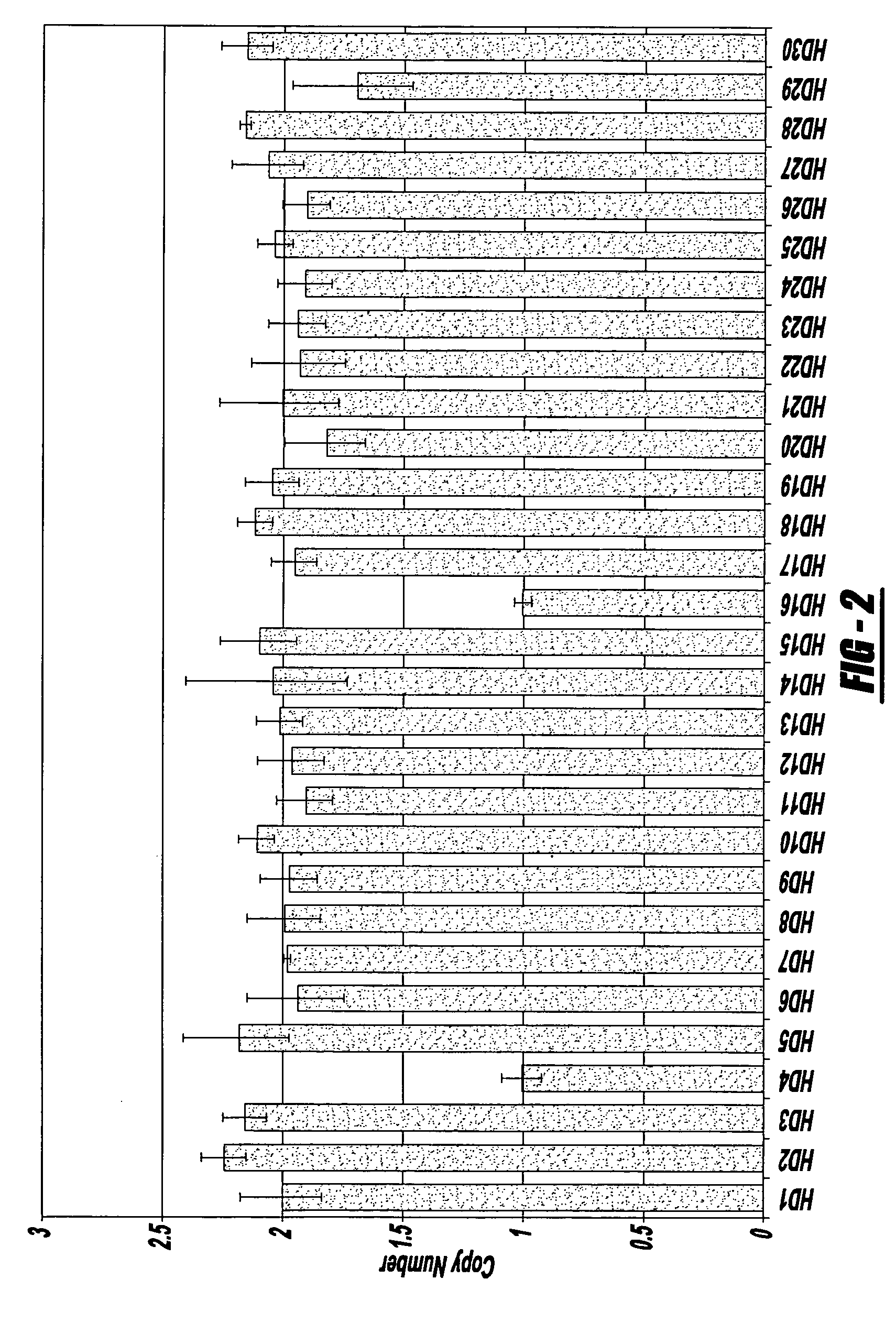
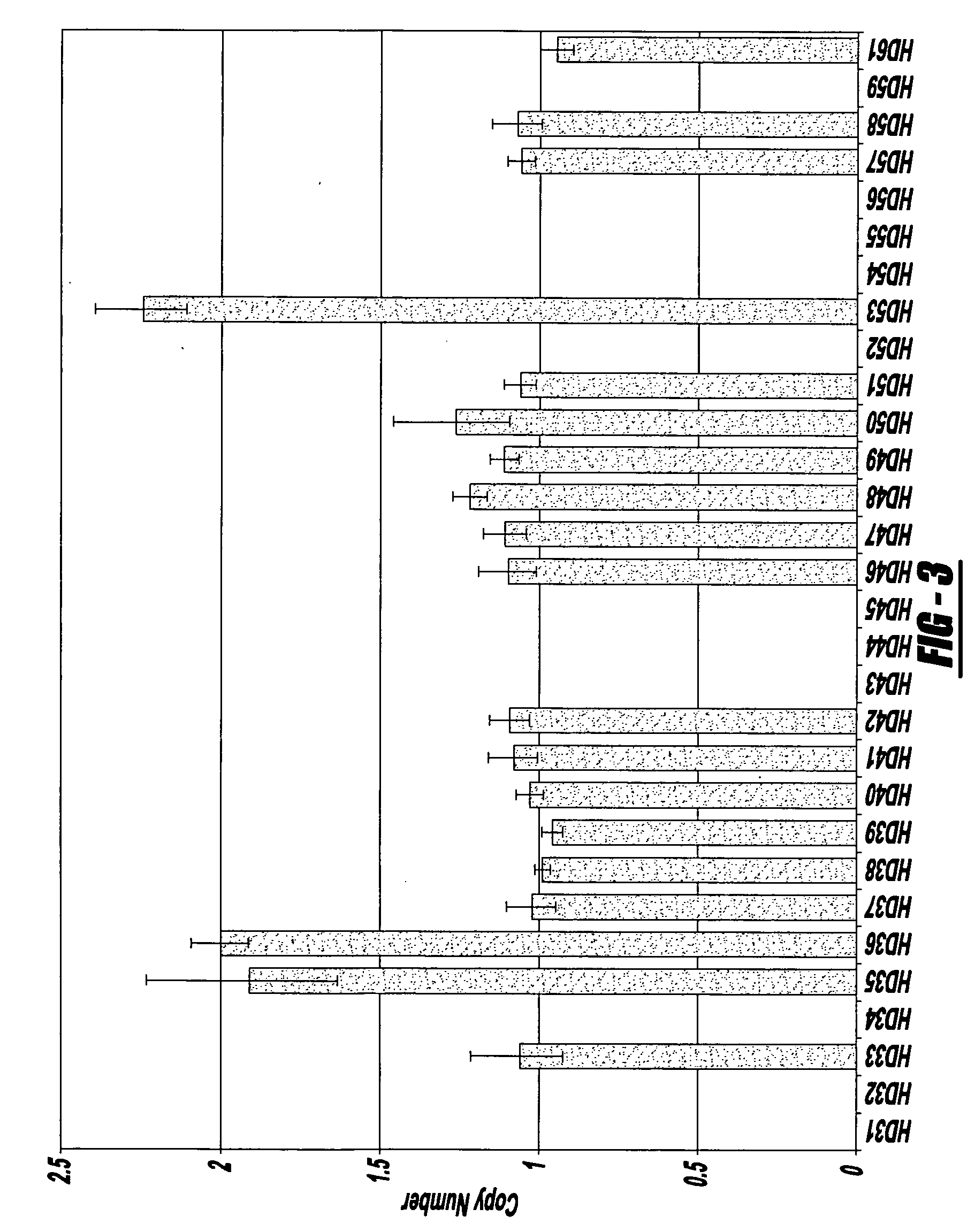
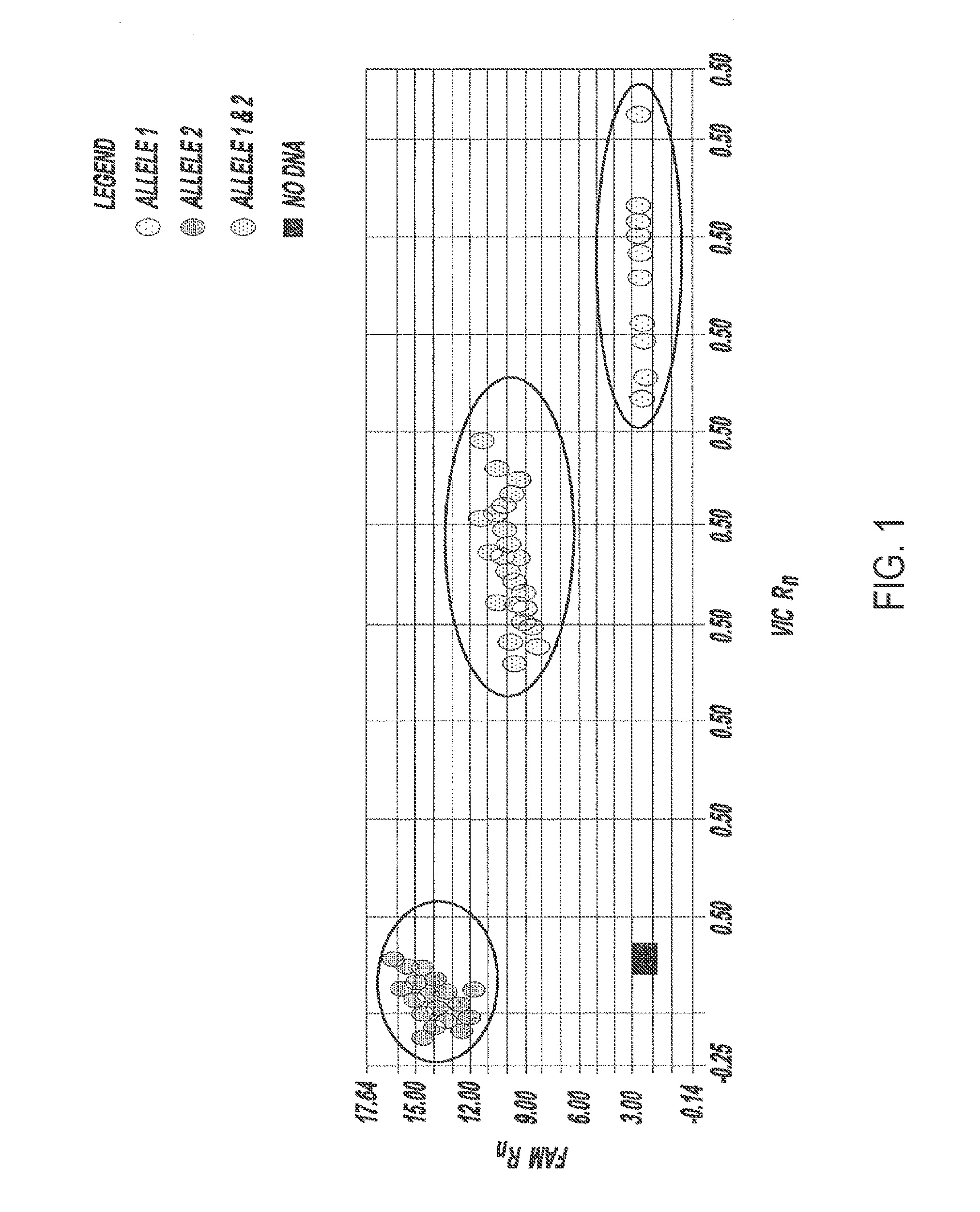
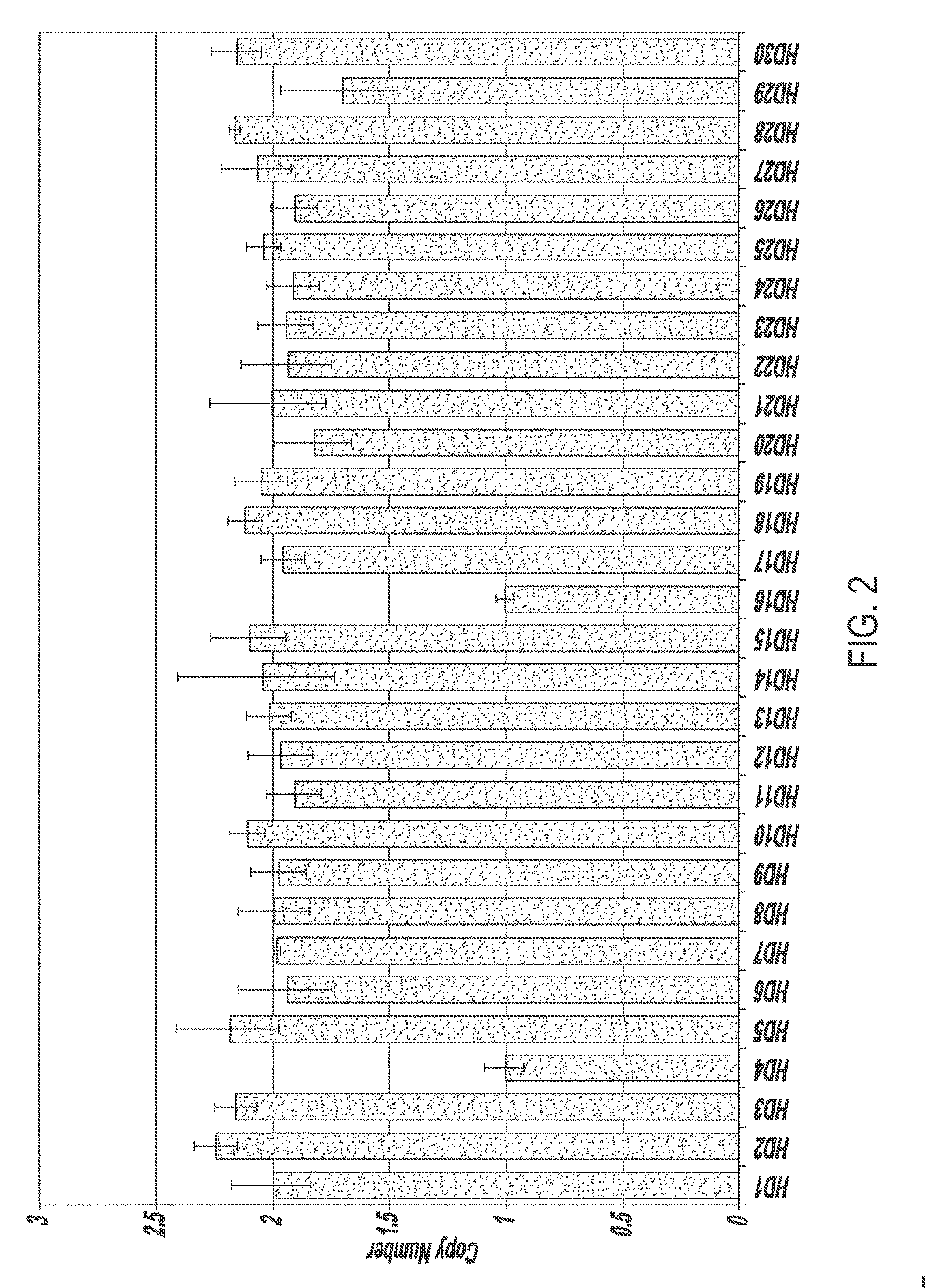
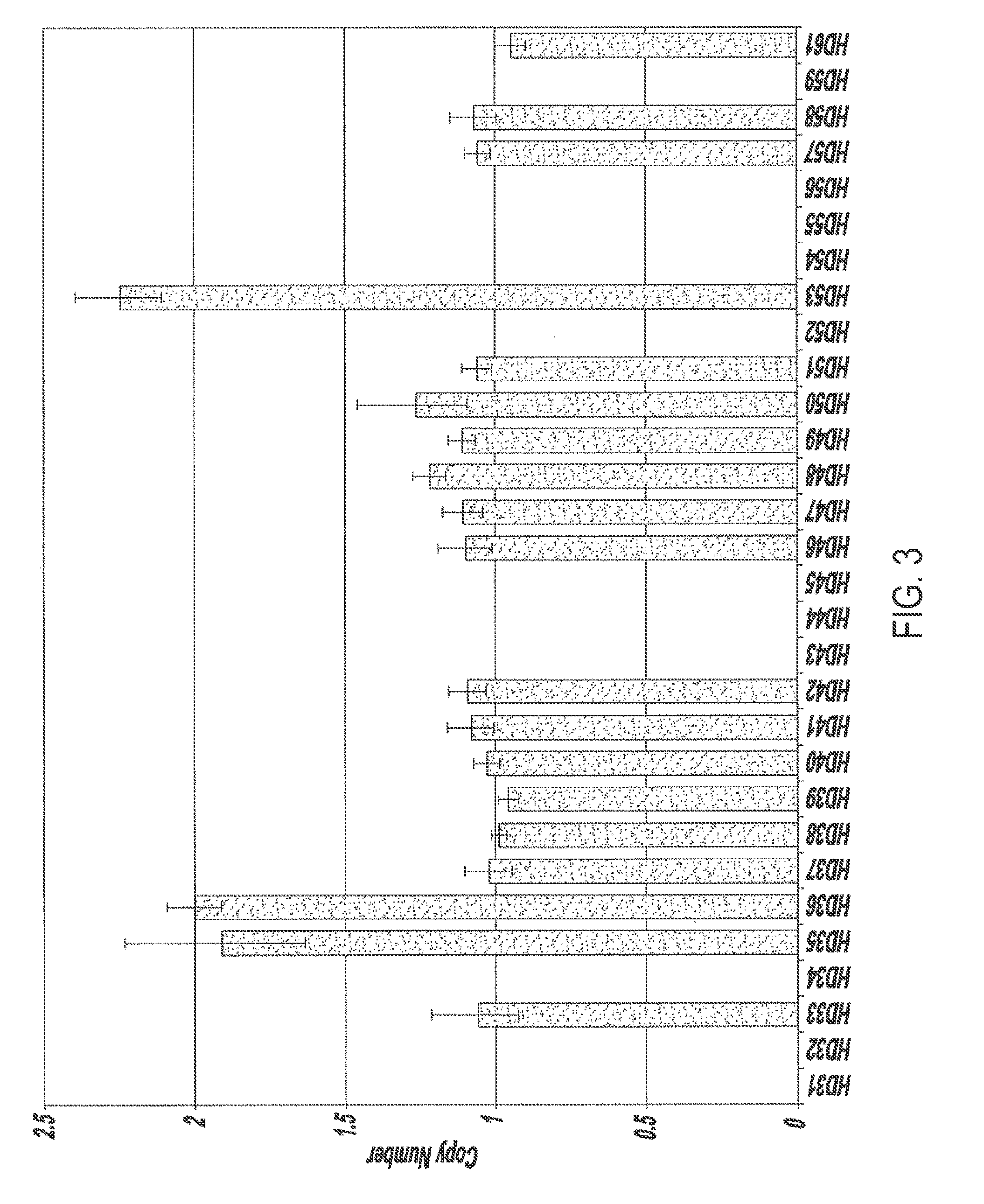
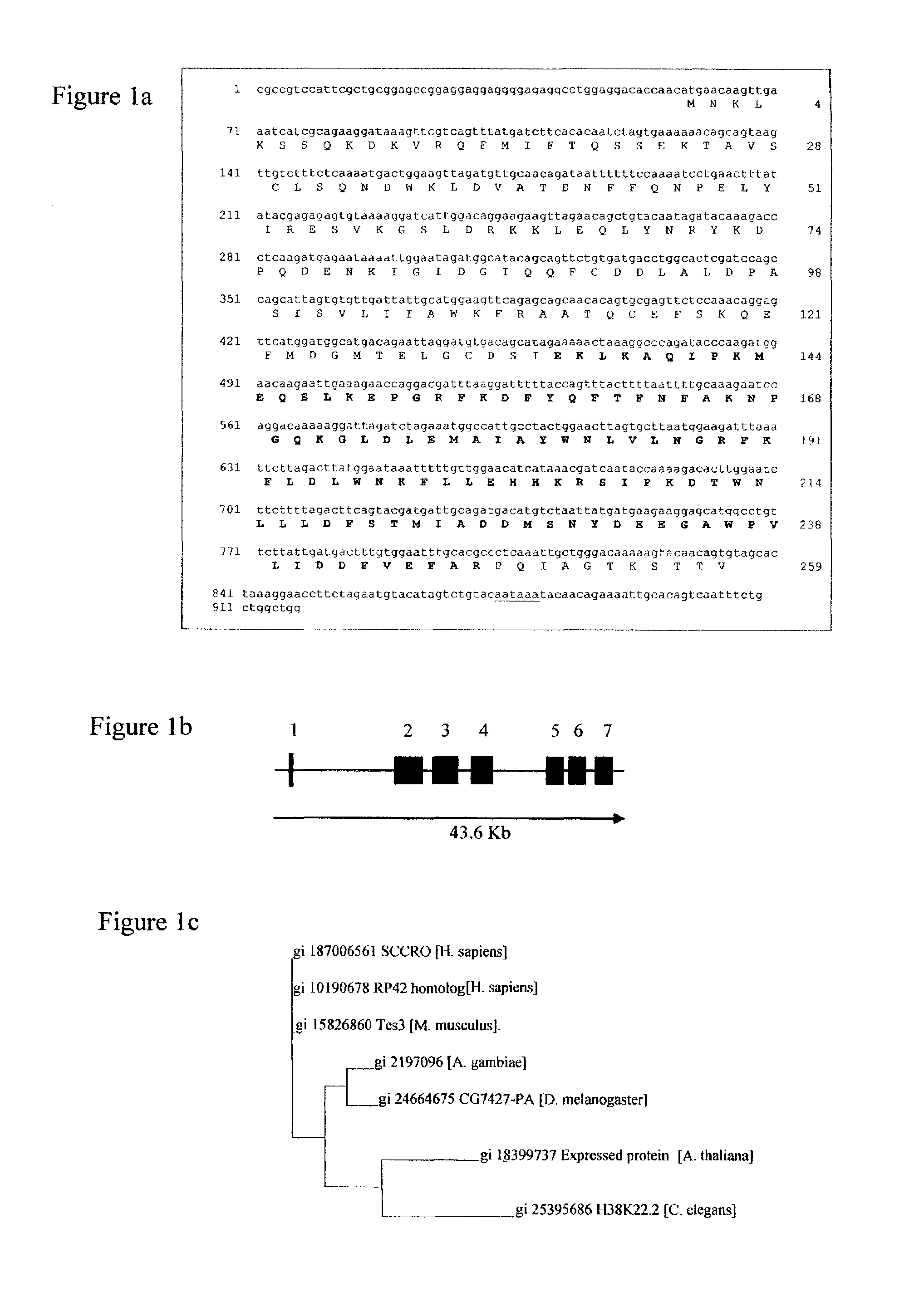
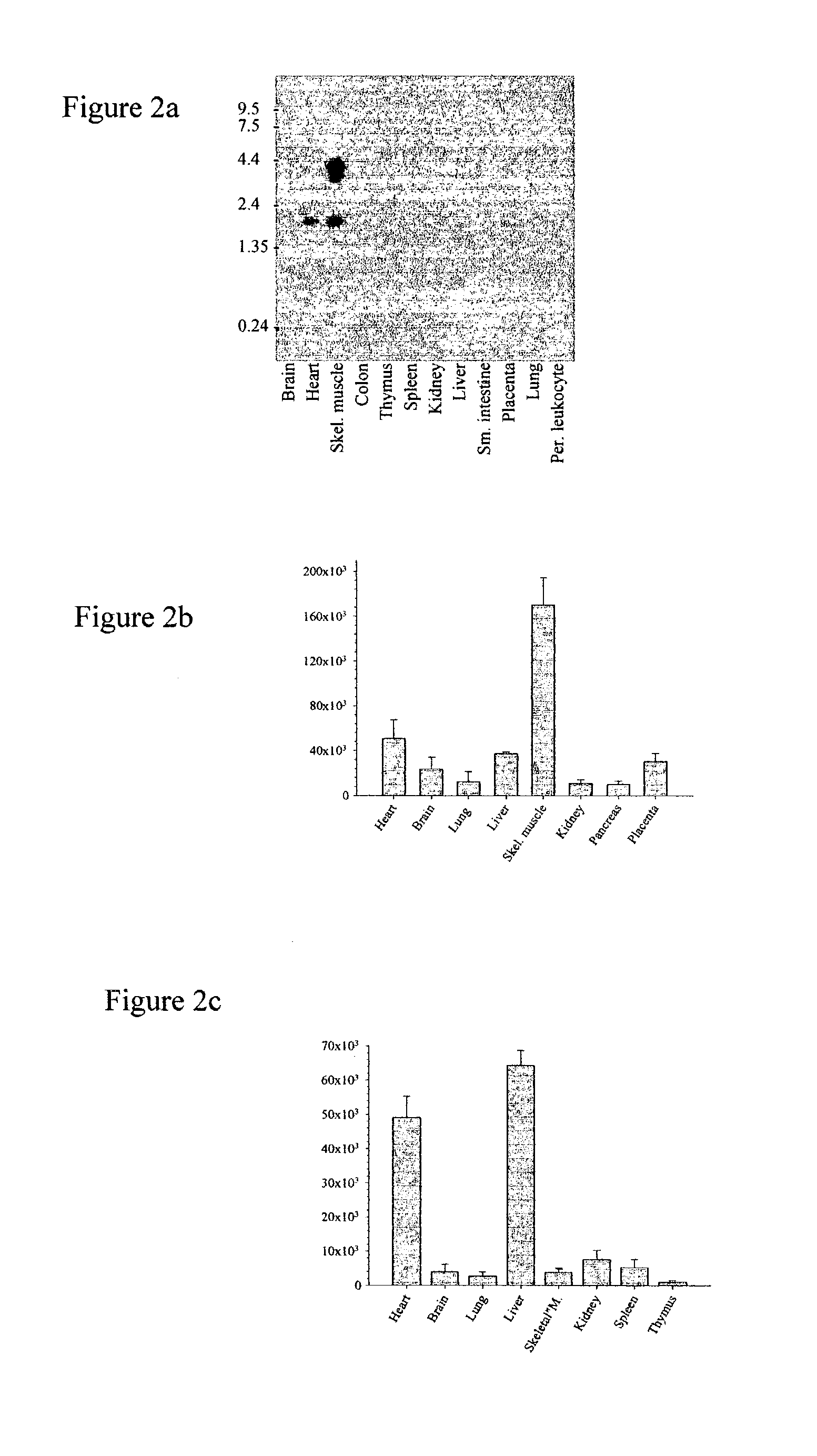
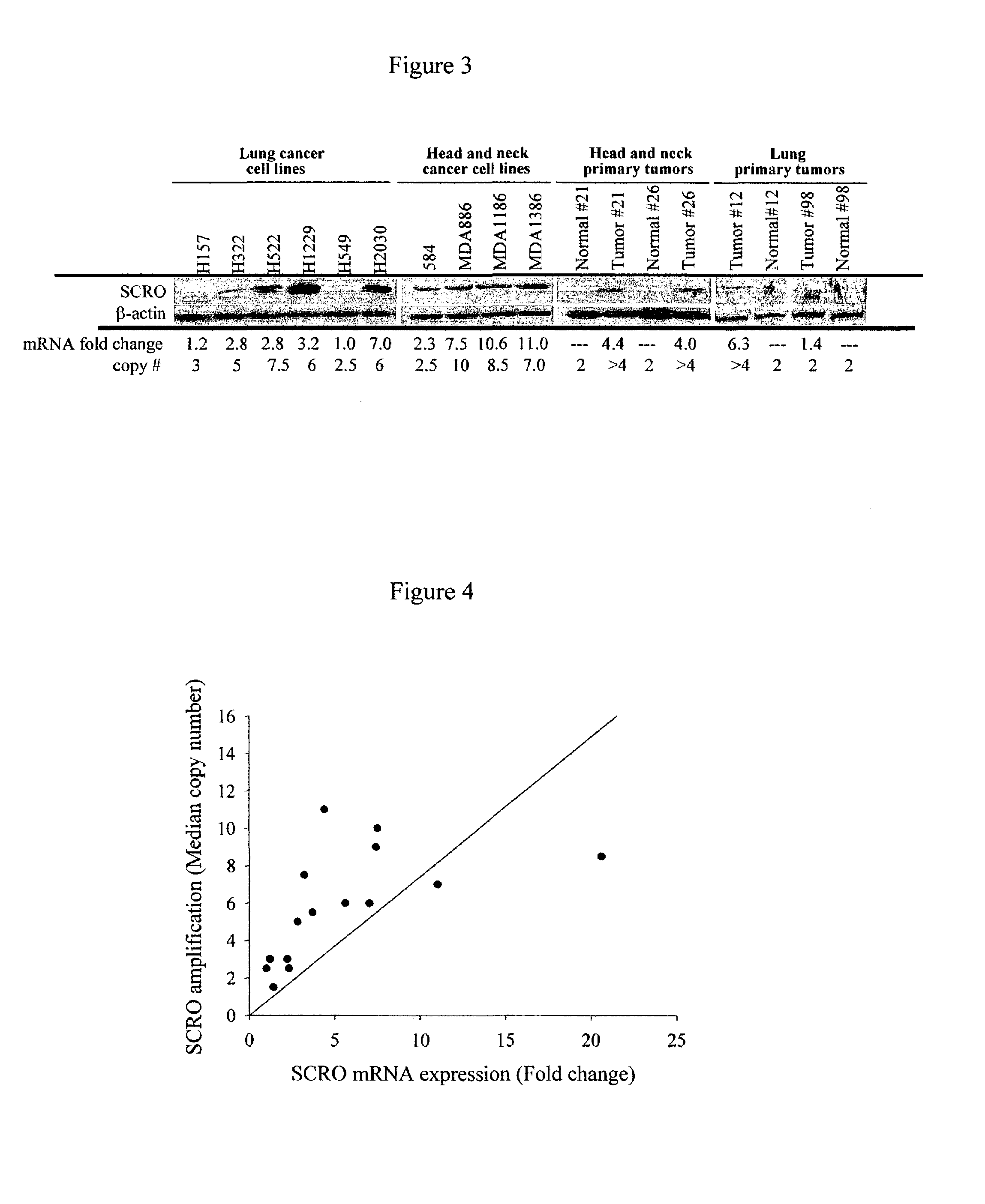
Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides encoded thereby are provided that are highly duplicated and overexpressed in squamous cell carcinomas of a variety of tissues. Antibodies specific for binding the novel polypeptides are also provided. The invention further discloses several assays for gene duplication and overexpression of the novel gene and excessive production of the novel polypeptide in a sample. These assays permit assessing copy number in a sample from a subject, and contribute to the diagnosis, prognosis and development of therapeutic strategy for a pathology such as squamous cell carcinoma in a subject.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Probe and method for carrying out hybrid capturing on gene duplication area
InactiveCN109777858AImprove capture efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExtension theoryComplementary pair
The invention discloses a probe and method for carrying out hybrid capturing on a gene duplication area. The probe is a primer probe with a conserved area beside a target gene duplication area or a specific position in the duplication area as a 3'terminal and with a detecting mark. According to the technical scheme, based on the primer amplification and extension theory, the specificity requirement of primer extension on a sequence, especially a 3' terminal sequence is larger than the specificity requirement of base complementary pairing in hybrid capturing for the sequence, the conserved areabeside the gene duplication area or a relatively specific position in the duplication area is adopted as the 3'terminal with the highest requirement for the specificity of the primer, the primer probe with the detecting mark is designed as the capturing probe, and in combination with a traditional liquid phase hybrid capturing system, the capturing efficiency of the gene duplication area is specifically improved.
Owner:天津诺禾医学检验所有限公司
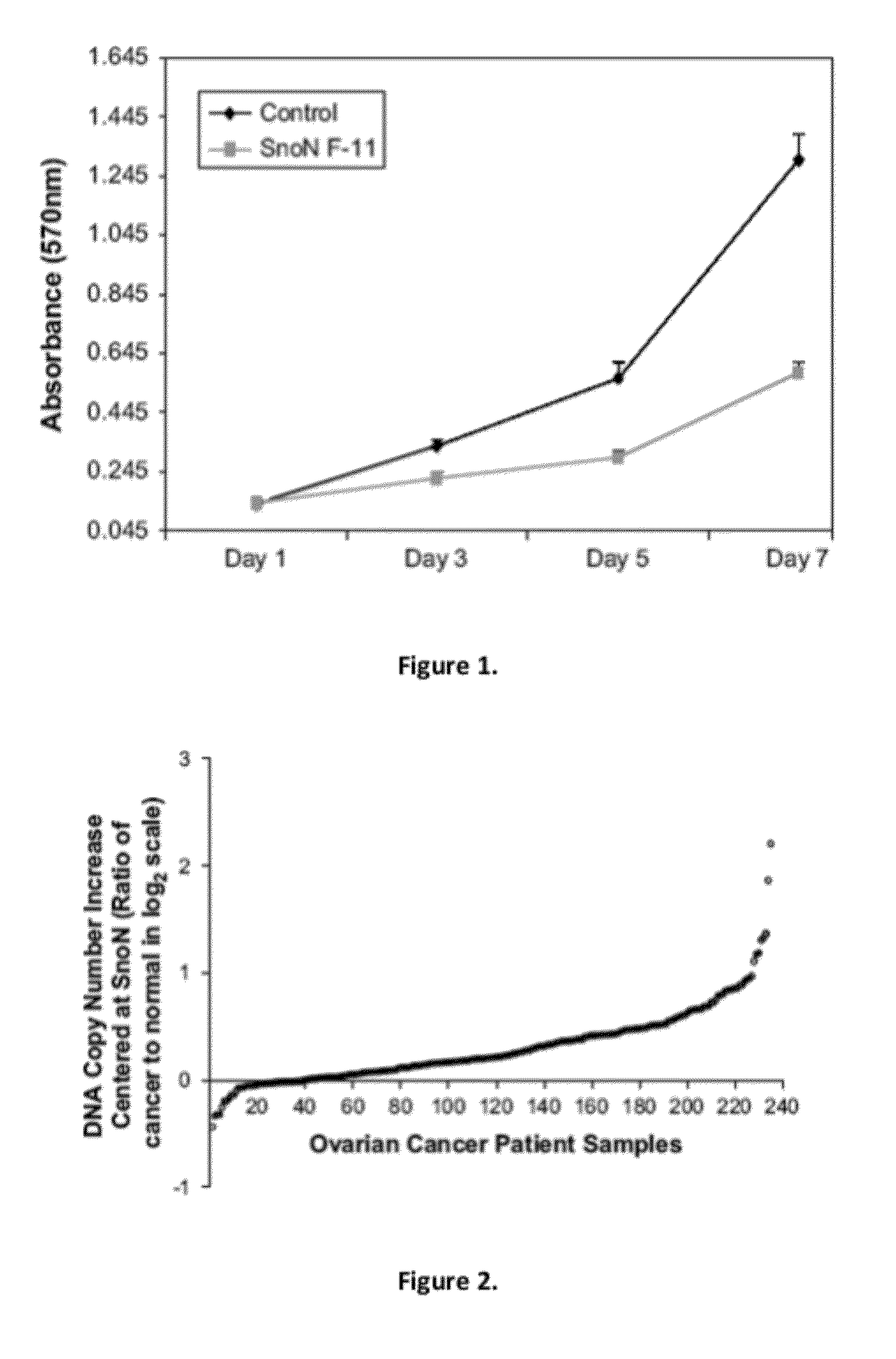
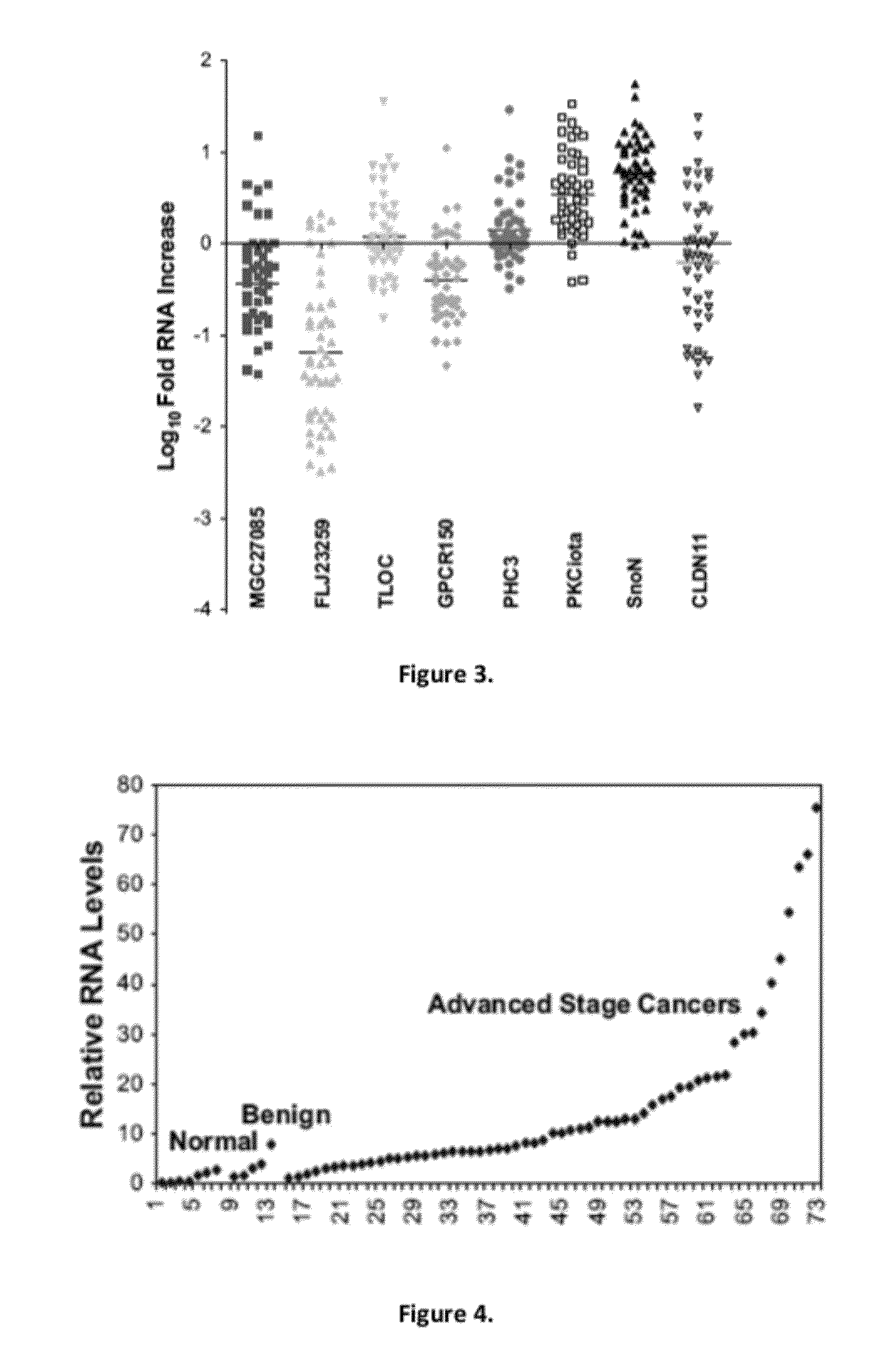
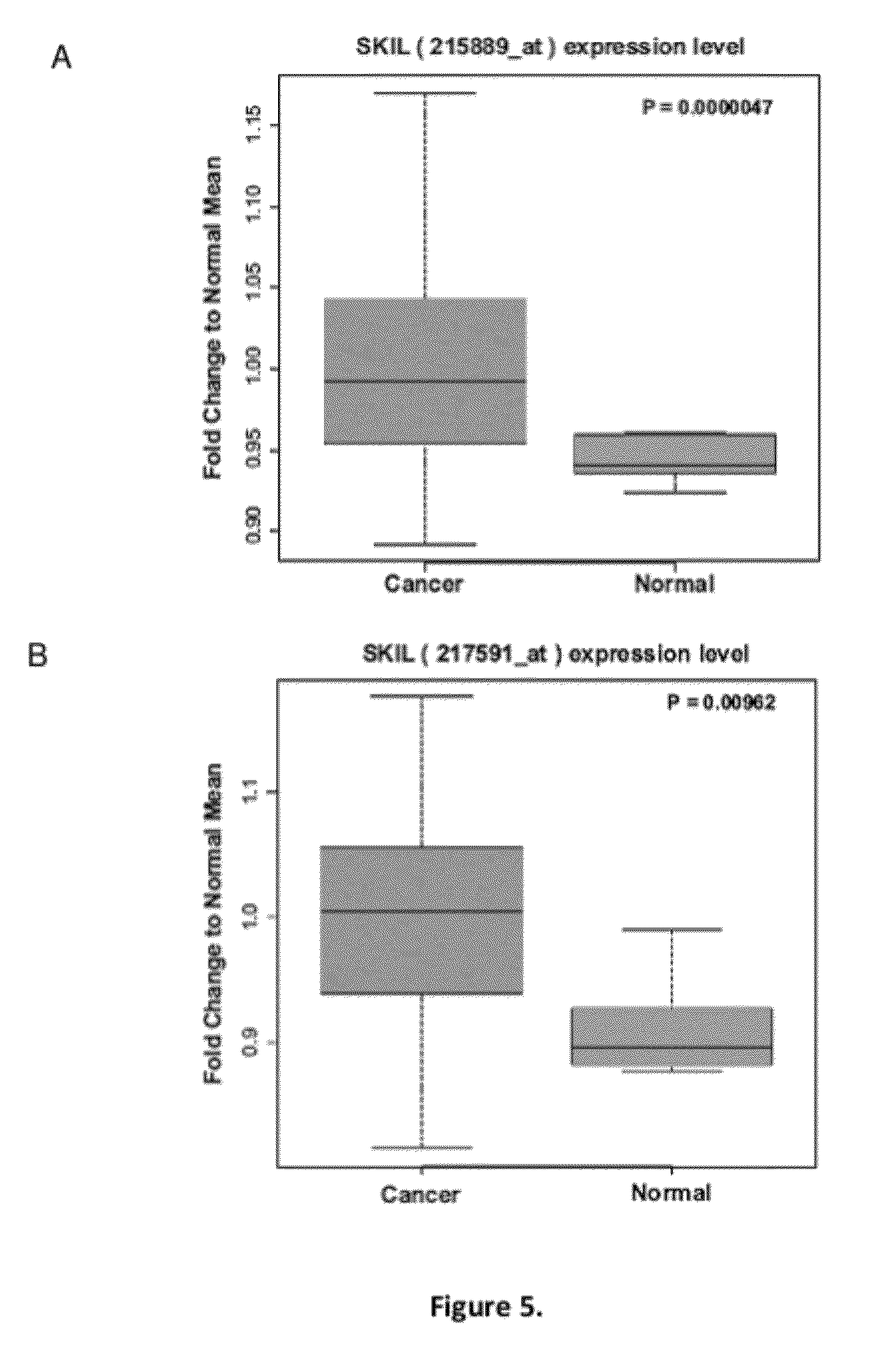
Methods of treating ovarian cancer by modulating SnoN
Genomic analysis of ovarian cancers demonstrated a regional chromosomal increase in expression and gene duplication. TGF-β stimulation indicated a link between SnoN RNA and TGF-β. In TIOSE, SnoN protein levels were reduced 15 min post TGF-β-stimulation, likely by proteosome-mediated degradation. SnoN inhibition decreased cell growth between 20 and 50% concurrent with increased p21 levels. Stable expression of SnoN led to growth arrest through induction of senescence. Collectively, these results implicate SnoN levels in multiple roles during ovarian carcinogenesis: promoting cellular proliferation in ovarian cancer cells and as a positive mediator of cell cycle arrest and senescence in non-transformed ovarian epithelial cells.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
Synthetic gene as well as method and application for establishing tobacco multi-gene site-directed mutation vector
InactiveCN108531481AEasy constructionEasy to build intermediate processVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a synthetic gene as well as a method and application for establishing a tobacco multi-gene site-directed mutation vector. A sequence of the synthetic gene is one or multiple gene repeated sequence synthesized in a nucleotide sequence of tRNA+sgRNA+gRNA. The synthesized gene is connected into a pUC57-Kan escherichia coli clone antibody. The synthetic gene sequence is obtained by augmentation in two ways. The established vector is used for transforming the tobacco, and a transgenic tobacco plant with the multi-gene being successively knocked out is selected by virtue of sequencing. The synthetic gene is suitable for simultaneously causing the site-directed mutation and application of multiple target genes in one transgenic tobacco, so that a rapid and simple method isprovided for researching the interaction of multiple genes in the tobacco.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Therapeutic and Diagnostic Methods Dependent on CYP2A Enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme.Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Methods, systems, and compositions for counting nucleic acid molecules
Owner:ENUMERA MOLECULAR INC
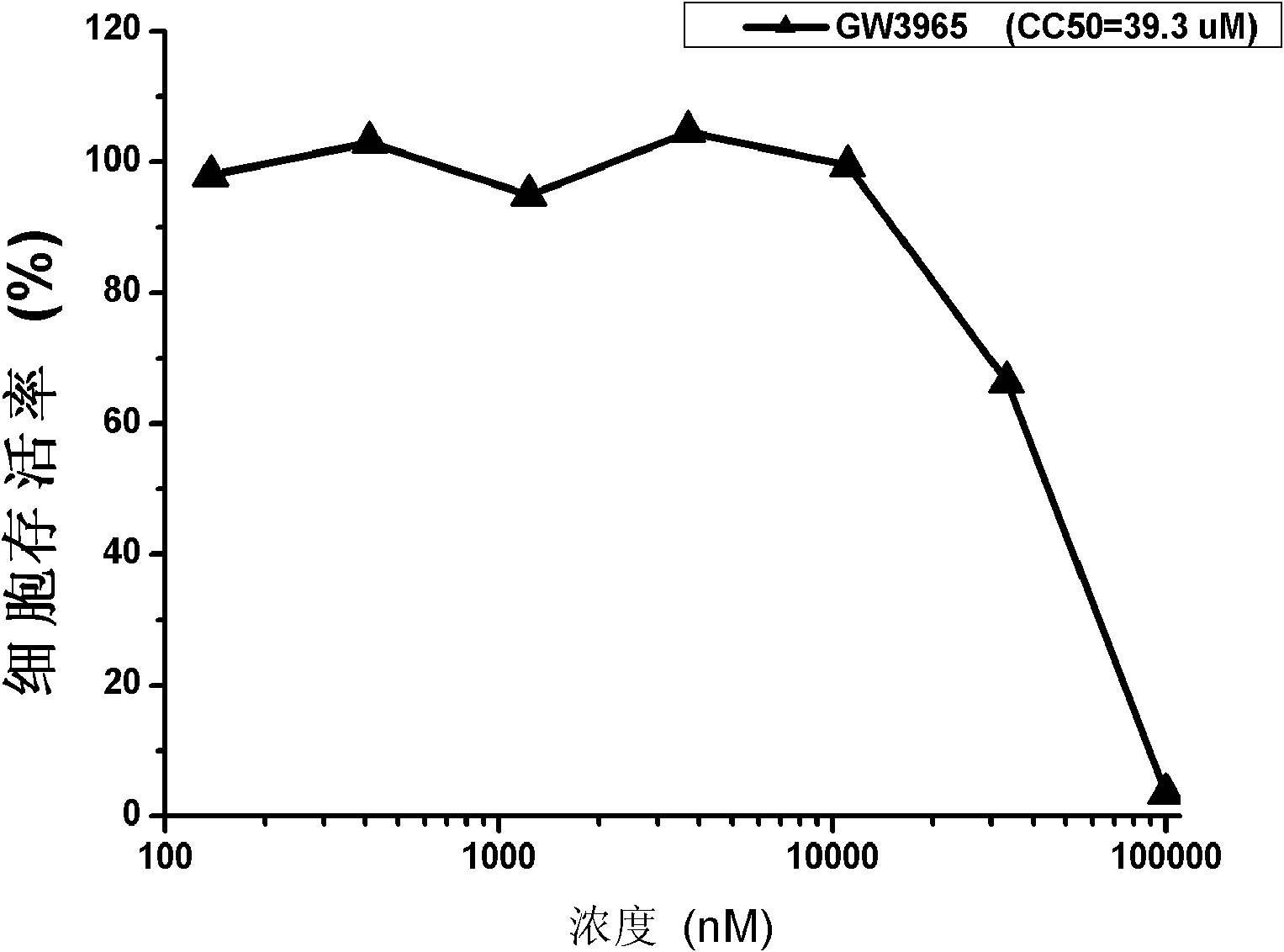
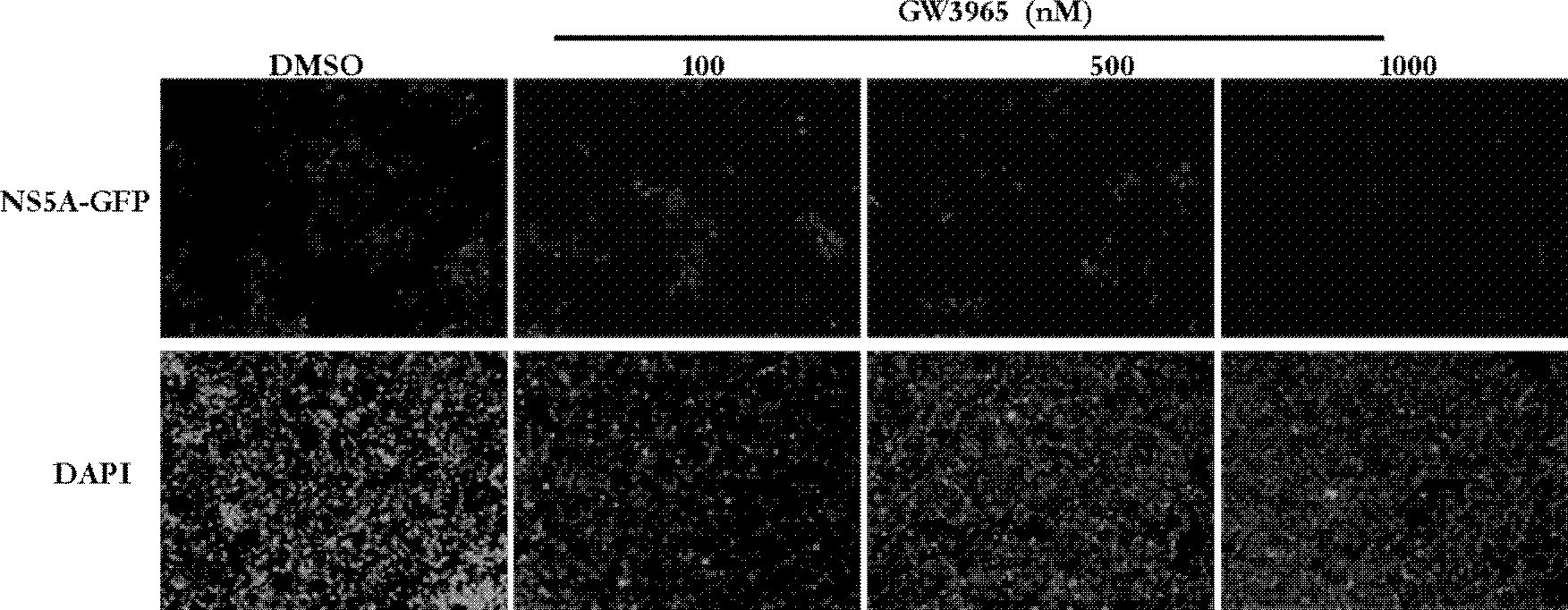
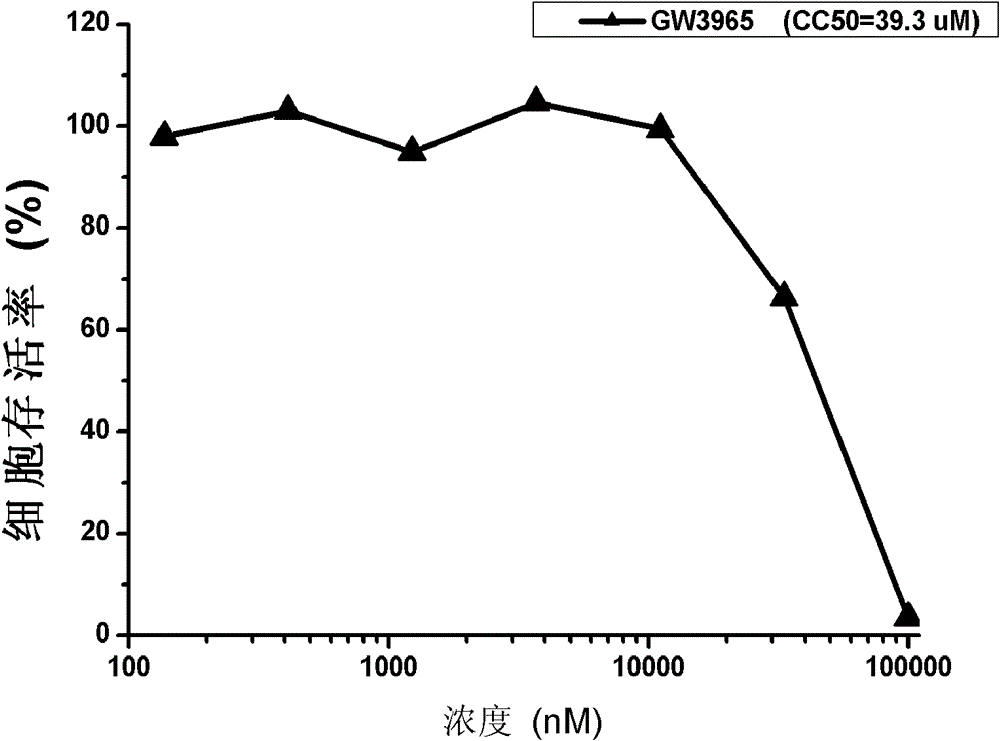
Application of GW3965 in preparation of drugs treating or preventing hepatitis C
InactiveCN103054844BAvoid infectionHigh selectivityPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemHcv hepatitis c virusPhenylacetic acid
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Gene sequence modification method based on codon synonymous mutation of codon and its application in vaccine preparation
InactiveCN110305880AIncreased probability of synthesis terminationHigh genetic stabilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsVirulent characteristicsVirus genetics
The invention discloses a gene sequence modification method based on codon synonymous mutation of codon and its application in vaccine preparation. The method is transformed into TTA, TTG, TCA or TCGby base mutation of a synonymous codon in a sequence. in the process of gene duplication, only one base needs to be mutated to form a stop codon (TAA, TGA, TAG), and the probability of termination ofpeptide chain synthesis by gene mutation is greatly increased, and the species or virus genetic stability thereby can be greatly increased. In the use of an attenuated live vaccine for viruses, safetyis the main problem, and the risk of virulence reversion of the attenuated live vaccine is always existed. In the design of the attenuated live vaccine, synonymous mutation of the codon of the viralgene can improve the fidelity of a vaccine sequence, and the risk of virulence reversion of vaccine poisons in the body is reduced, so that the safety of the attenuated live vaccine is increased.
Owner:安子琛
Methods, systems, and compositions for counting nucleic acid molecules
ActiveUS11186863B2Widen meansEasy to captureMicrobiological testing/measurementTrisomy 22Gene duplication
Compositions and methods, systems, and kits for detecting and quantifying variations in numbers of molecules, particularly variations in gene dosage, e.g., due to gene duplication, or to variations from the normal euploid complement of chromosomes, e.g., trisomy of one or more chromosomes that are normally found in diploid pairs, without digital sequencing.
Owner:ENUMERA MOLECULAR INC
Application of GW3965 in preparation of drugs treating or preventing hepatitis C
InactiveCN103054844ABroad-spectrum antiviral activityNovel targetPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAnti virusHepacivirus
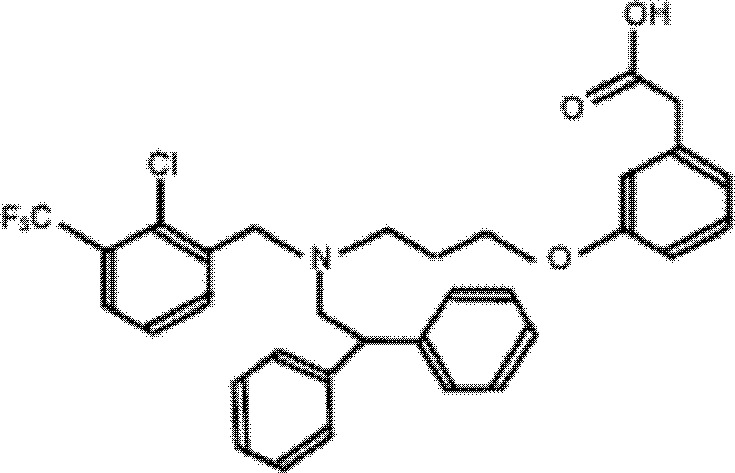
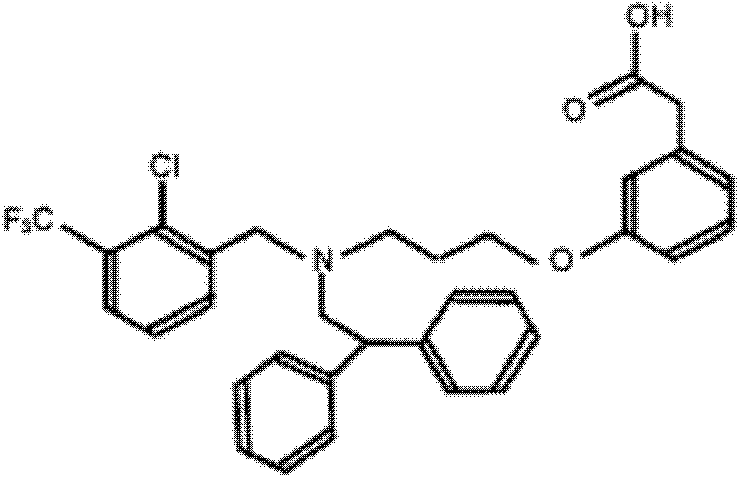
The invention discloses application of GW3965 (3-[3-[[[2-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methyl](2, 2)-biphenylethyl)amino]propoxy)phenylacetate hydrochloride) in preparation of drugs treating or preventing hepatitis C virus. A drug without any toxic concentration is chosen for an antiviral experiment, the influence of GW3965 on virus gene duplication is detected, and results show that the small molecule compound has significant antiviral activity and is dose dependent. Then, the GW3965 is employed to treat the hepatitis C pseudovirus system of different gene subtypes, and results show that the compound inhibits the virus entrance link at the early stage of a virus lifecycle. The anti-virus capability of drug combination of GW3965 and other anti-HCV drugs is detected, and results show that the compound has the potential of drug combination with other drugs. GW3965 can inhibit 1a, 1b, and 2a genotype virus entrance, and has broad-spectrum antiviral activity and a novel target, while there is no anti-hepatitis C virus drug with entrance as the target clinically. And drug combination can achieve a good effect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
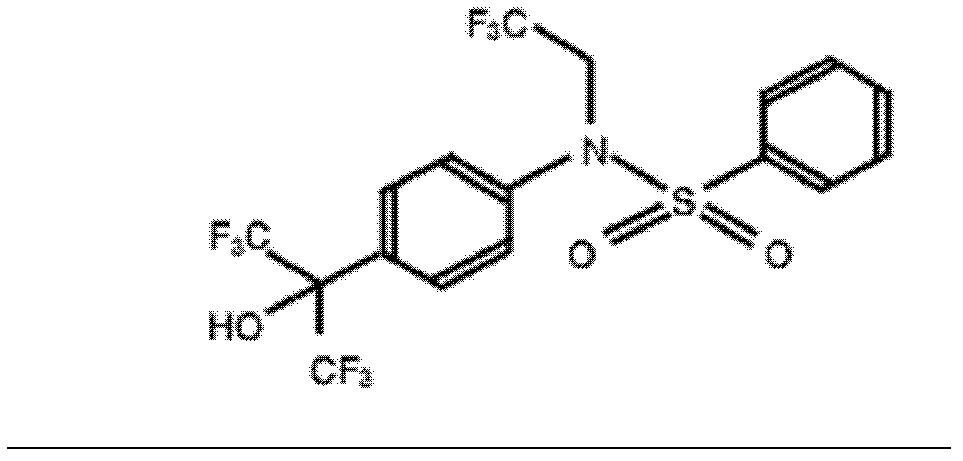
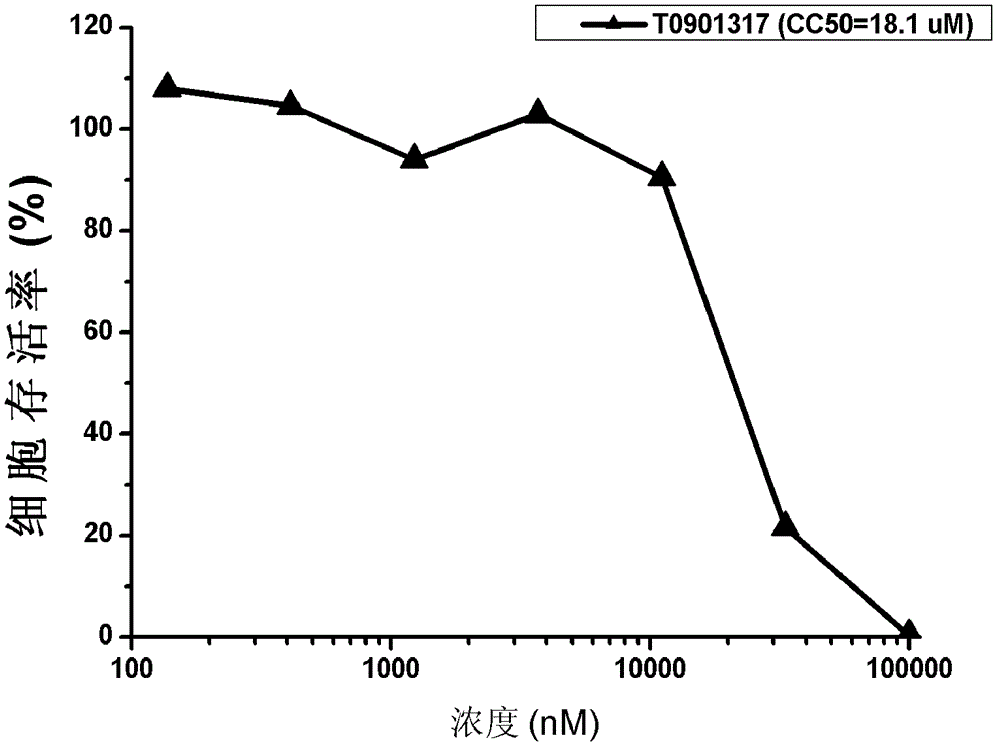
Application of T0901317 in preparation of drugs treating or preventing hepatitis C
InactiveCN103054841ABroad-spectrum antiviral activityNovel targetDigestive systemAntiviralsAnti virusHepatitis
The invention discloses application of T0901317 (N-(2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl)-N-[4-[2, 2, 2-trifluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(trifluoromethyl)ethyl]phenyl]-benzenesulfonamide) in preparation of drugs treating or preventing hepatitis C virus drugs. A drug without toxic concentration is chosen for an antiviral experiment, the influence of T0901317 on virus gene duplication is detected, and results show that the small molecule compound has significant antiviral activity and is dose dependent. Then, the T0901317 is employed to treat the hepatitis C pseudovirus system of different gene subtypes, and results show that the compound inhibits the virus entrance link at the early stage of a virus lifecycle. Also, the anti-virus capability of drug combination of T0901317 and other anti-HCV drugs is detected. T0901317 can inhibit 1a, 1b, and 2a genotype virus entrance, and has broad-spectrum antiviral activity and a novel target, while there is no anti-hepatitis C virus drug with entrance as the target yet clinically. And drug combination of T0901317 with other anti-hepatitis C virus drugs can achieve a good effect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
CYP2A enzymes and their use in therapeutic and diagnostic method
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as 'CYP2A6' for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
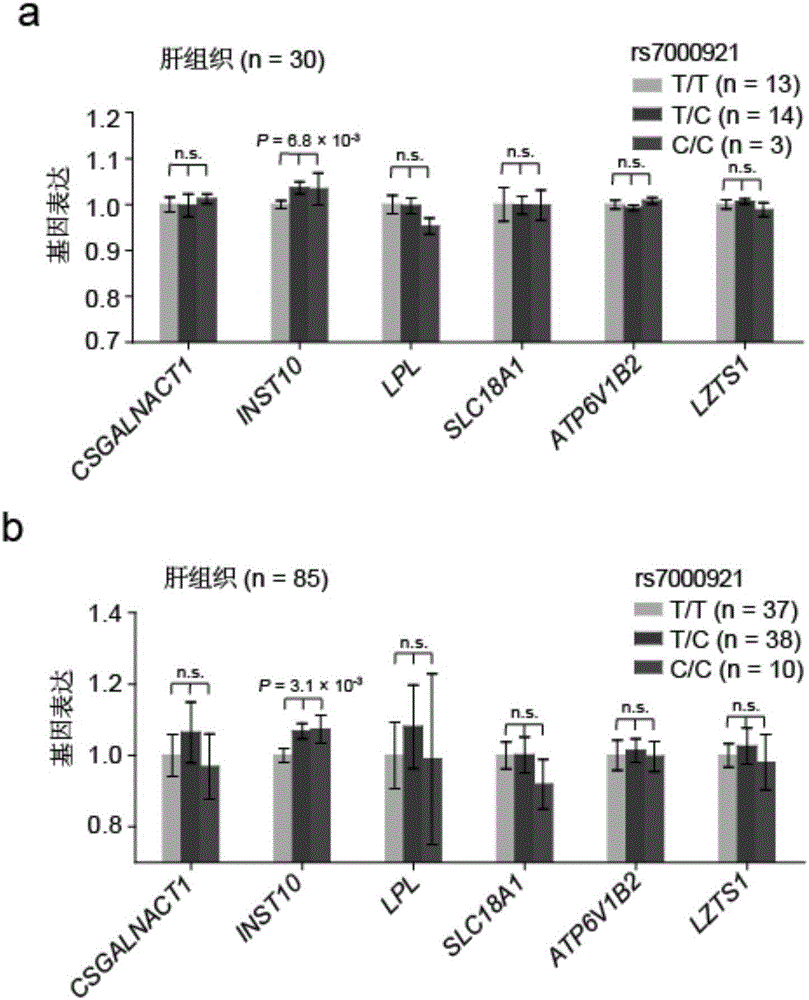
Use of INTS10 gene/protein in inhibiting HBV gene duplication or preventing or treating HBV associated diseases
InactiveCN105833290AEfficient screeningReliable resultsPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseFhit gene
The invention discloses a use of an INTS10 gene / protein in inhibiting HBV gene duplication or preventing or treating HBV associated diseases. Therefore, target cells such as liver cells or liver cancer cells excessively express the INTS10 gene, so that the duplication of the HBV gene in the liver cells or the liver cancer cells can be effectively inhibited, and therefore, the HBV associated diseases are effectively prevented or treated.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
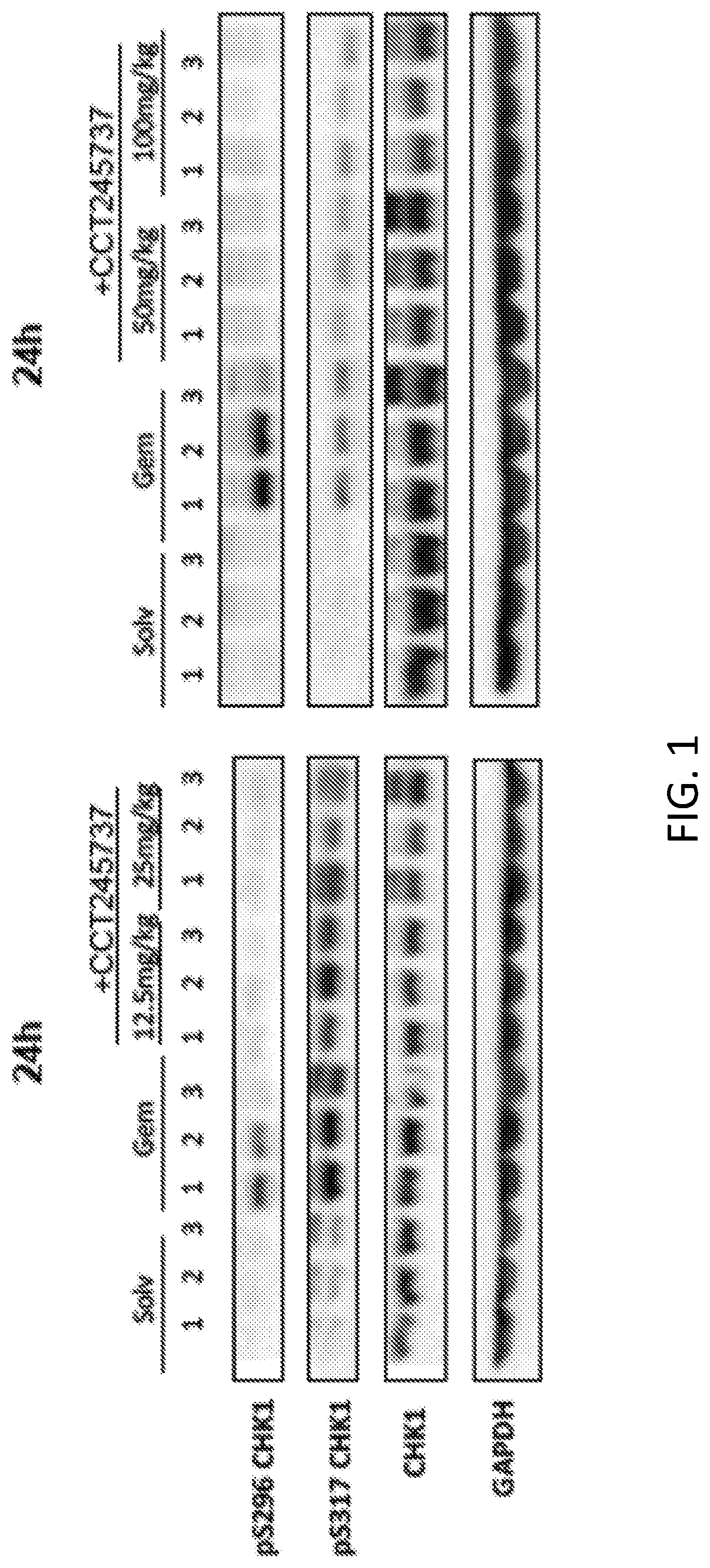
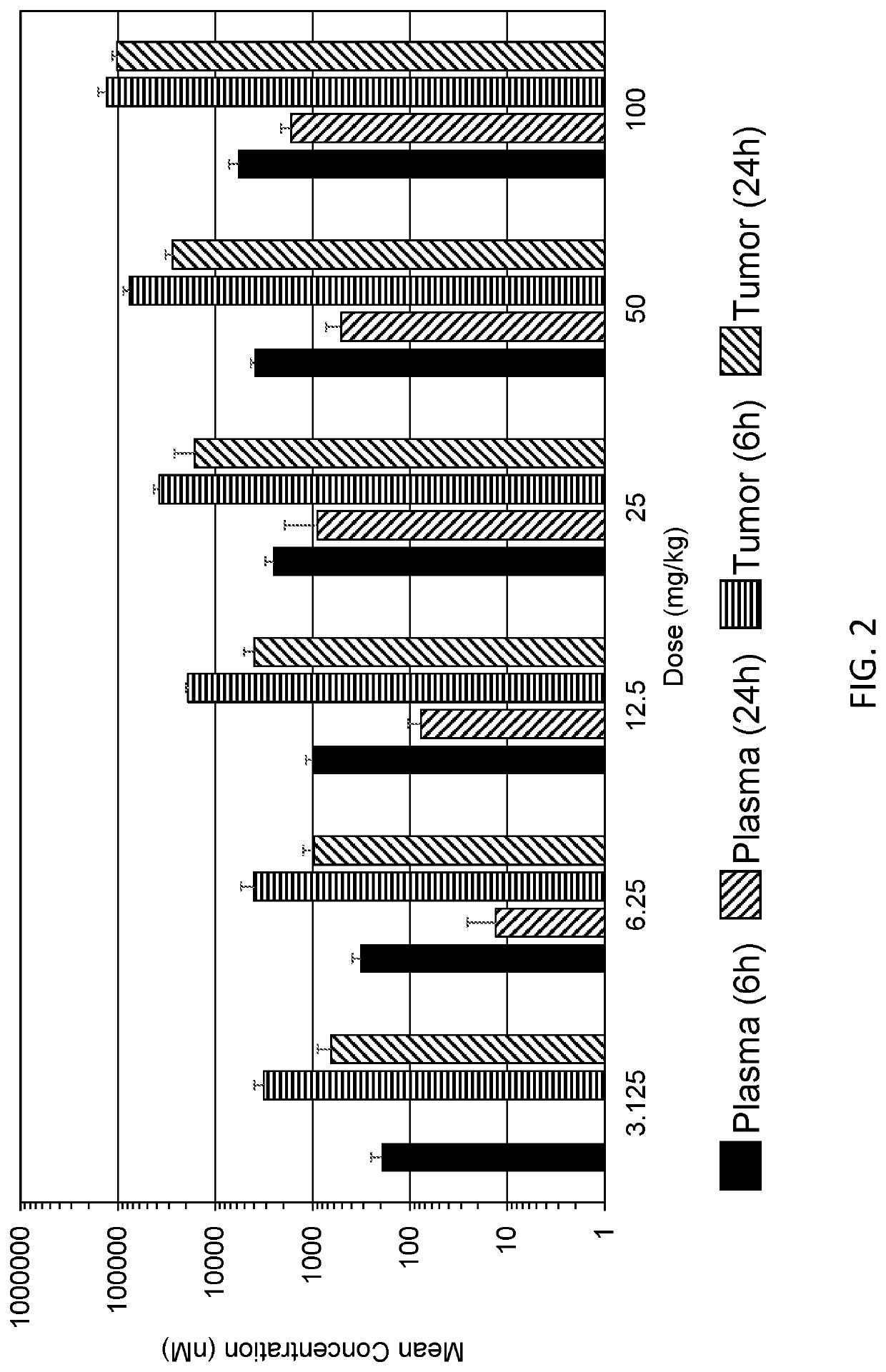
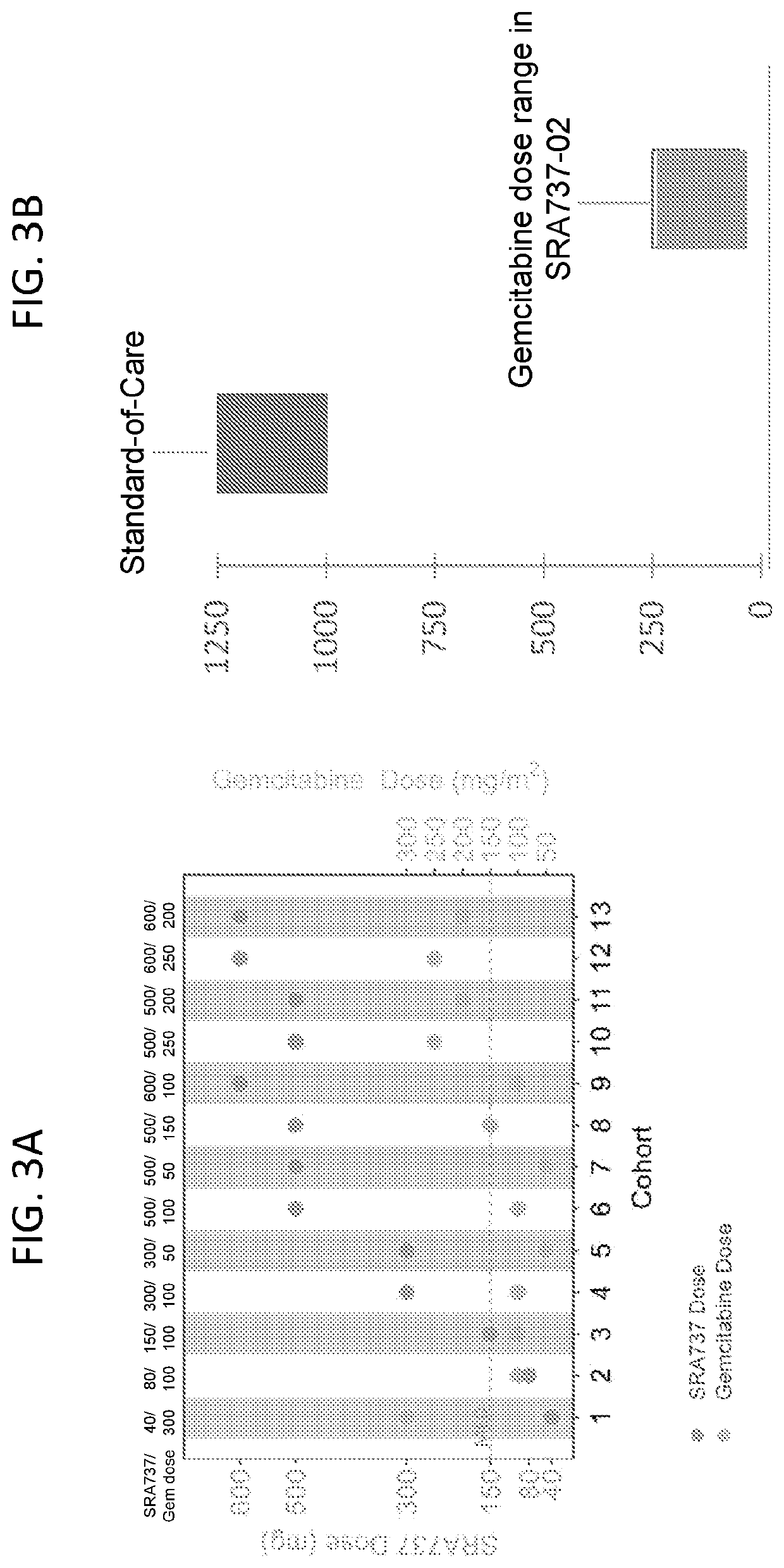
Methods of Treating Cancer Using CHK1 Inhibitors
PendingUS20220226338A1Lower requirementOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOncologyDNA damage
This disclosure provides methods of using a checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) inhibitor in the treatment of cancer in a subject having at least an intermediate tumor mutational burden (TMB), or a genetic abnormality in one or more particular genes associated with replicative stress. Accordingly, methods of treating cancer in a subject having at least an intermediate tumor mutational burden (TMB-I) are provided. Also provided are methods of treating cancer in a subject having a genetic abnormality in one or more particular genes selected from cell cycle regulation genes, replication stress genes, oncogenic driver mutations and DNA damage response and repair network genes. Methods of selecting subjects for Chk1 inhibition therapy are provided. The methods can include administering to the subject an effective amount of a SRA737 compound, in some cases in combination with low dose gemcitabine.
Owner:SIERRA ONCOLOGY INC
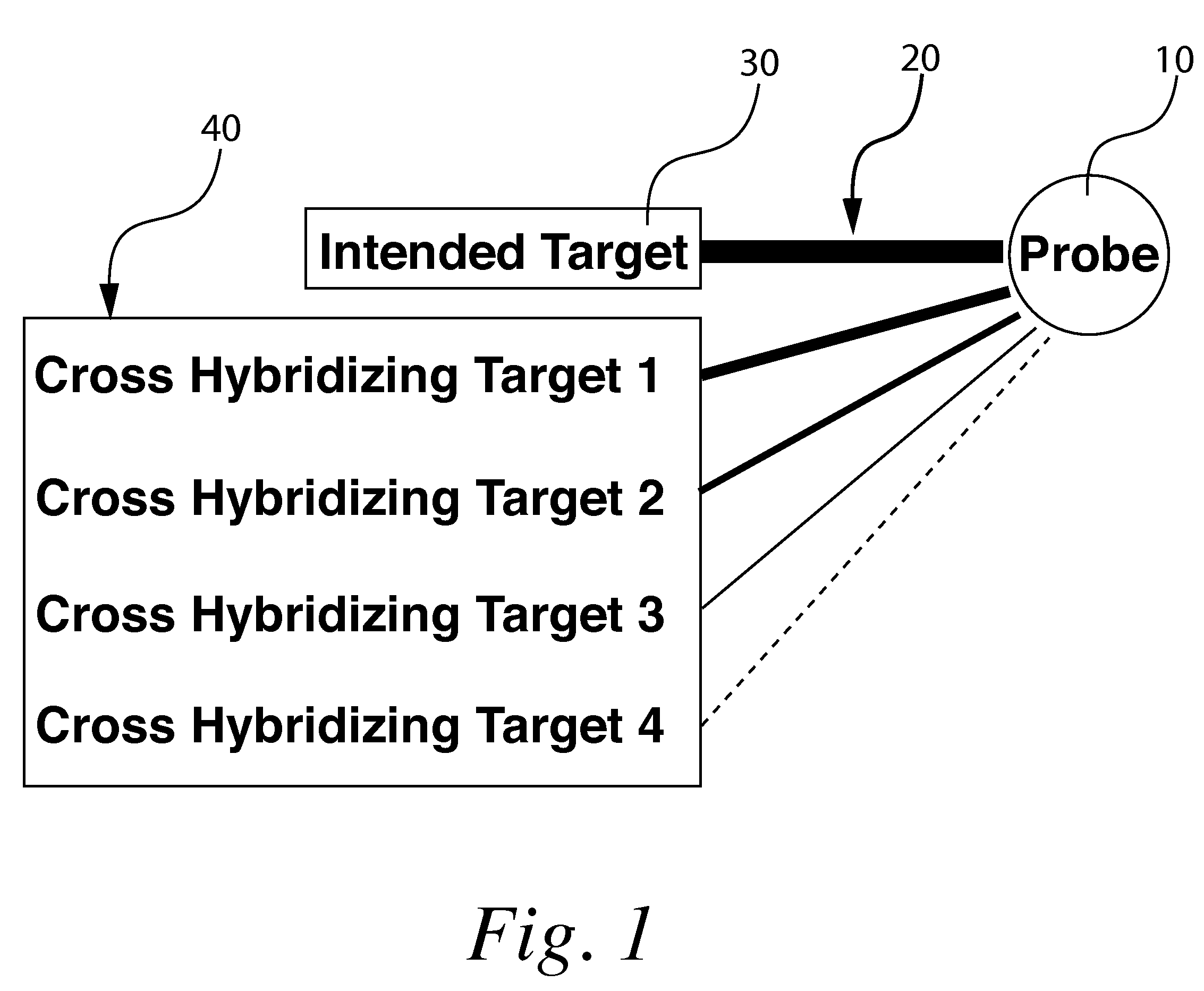
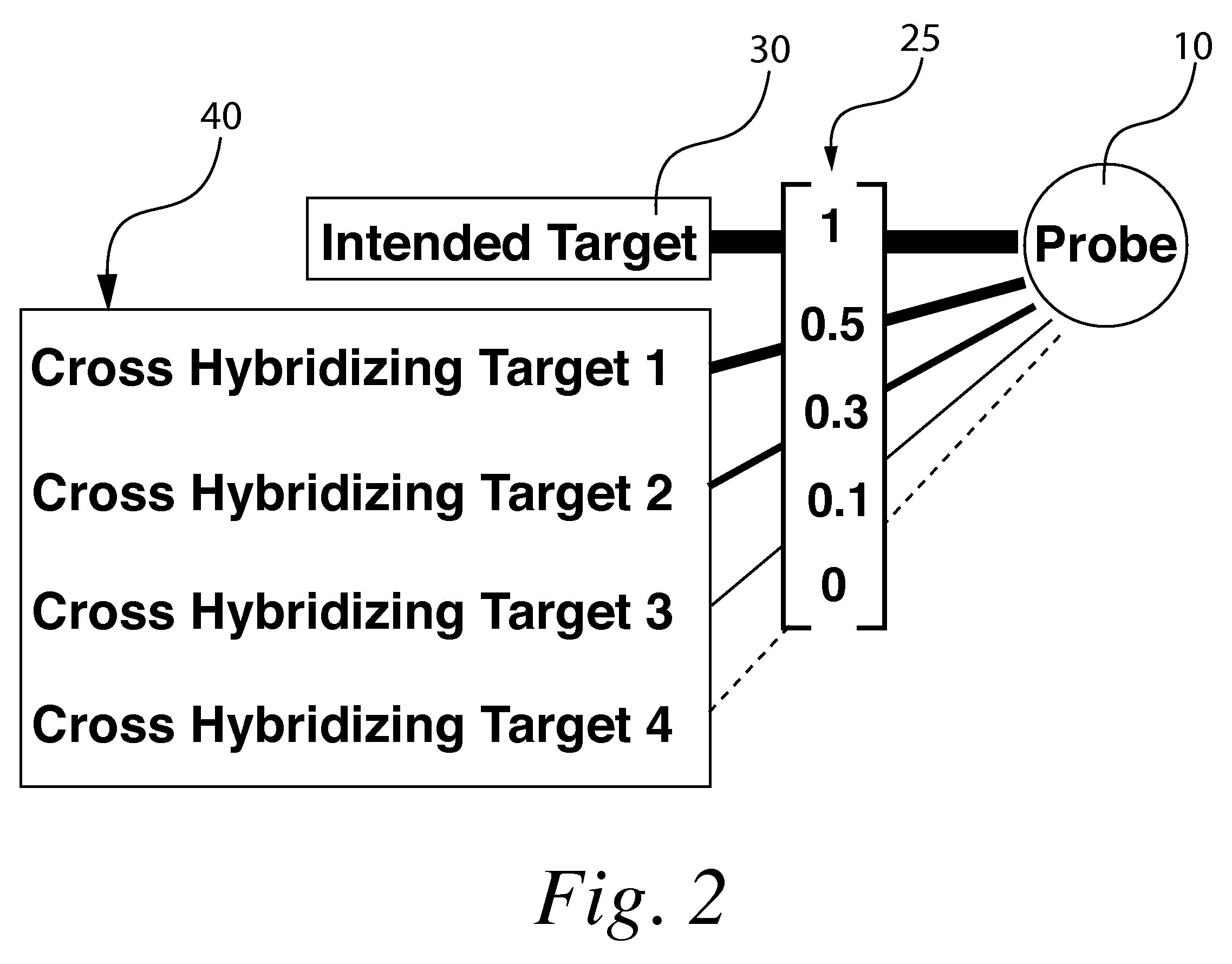
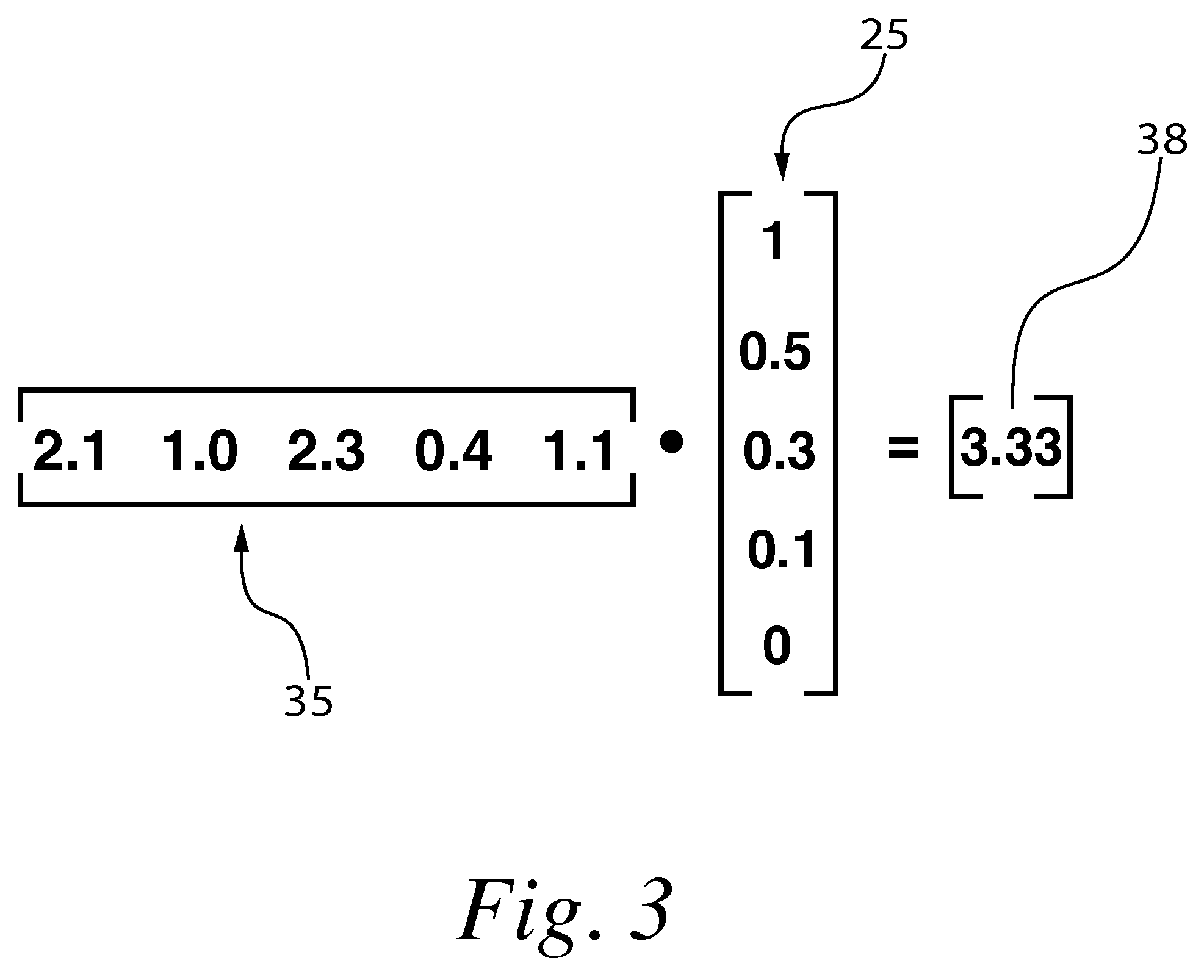
Microarray Method
A method for correcting microarray data for the effects of cross-hybridization comprising multiplication of microarray probe hybridization intensities with the inverse or pseudoinverse of a matrix of cross-hybridization potentials between probes and targets. This matrix of cross-hybridization potentials may be determined experimentally by repeating a microarray experiment with each of the targeted genes individually present to determine the cross-hybridization of that targeted gene to each probe, or alternatively, computational models of hybridization may be employed. This represents a new paradigm for handling the problem of cross-hybridization and also can be used in probe-set design strategies.
Owner:DOTAN NATAN
Business method by preserving genes and storing records during lifetime
InactiveCN103260399ABiology History BenefitSolve the burialAnimal cellsDead animal preservationChemical reactionUltraviolet
[Technical Field] The present invention relates to a method for putting the genes (DNA) of a dead person in rosin and sealing the same with lead to preserve the genes, and a method for marking an identification number on the sealed lead to allow the lifetime records of the person to be searched on a homepage. [Problem To Be Solved] The present invention can make someone expect the possibility of rebirth depending on the gene duplication will of the mankind in the future and perpetuate the meaning of birth and life by semi-permanently preserving DNA of which the characteristics are different among people and the lifetime records, thereby easing the fear of inevitable death and remarkably solving the problem of burial ground shortage as a concomitant effect. [Solution to Problem] The blood and body tissue (gene) of the dead person are put into rosin, which can block air and water and is stable against organic-chemical reaction, and are sealed with the lead through which ultraviolet rays and radioactive rays cannot penetrate. [Effects of Invention] Since gene duplication is possible, mankind can achieve their long time aspiration of rebirth, and to simultaneously solve the problems concerning a burial plot and charnel house.
Owner:崔敏成
Method, vectors, cells, seeds and kits for stacking genes into a single genomic site
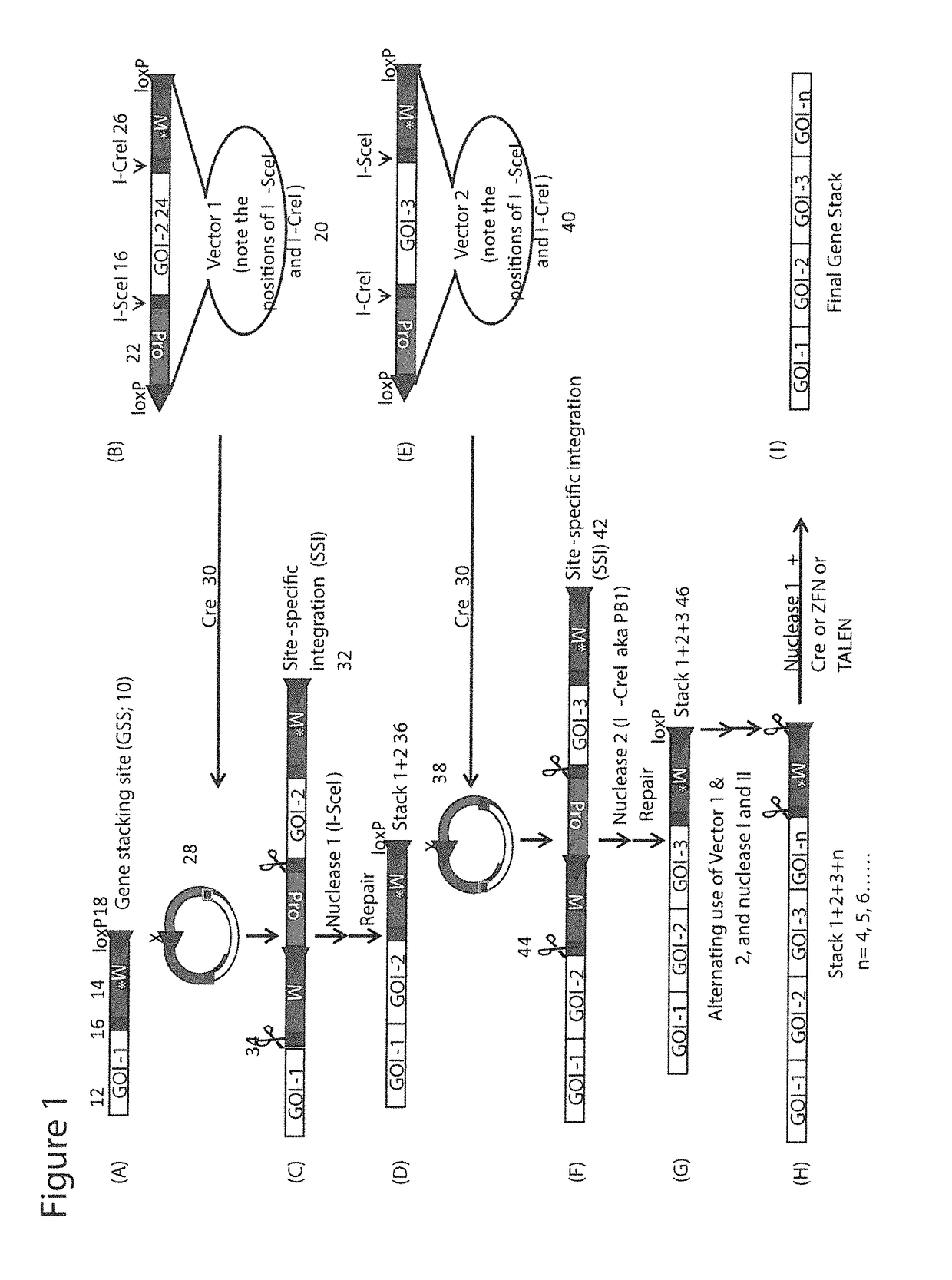
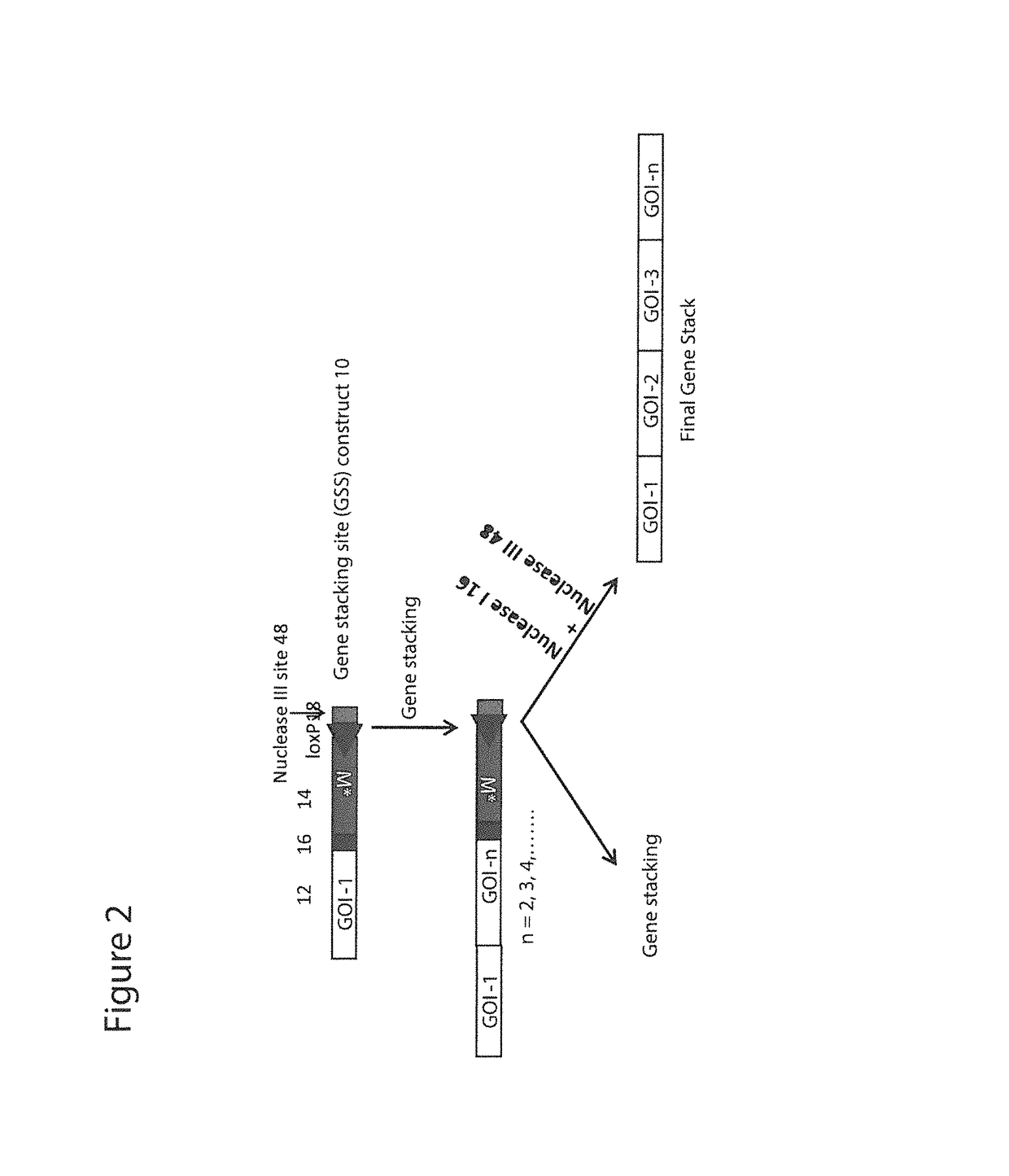
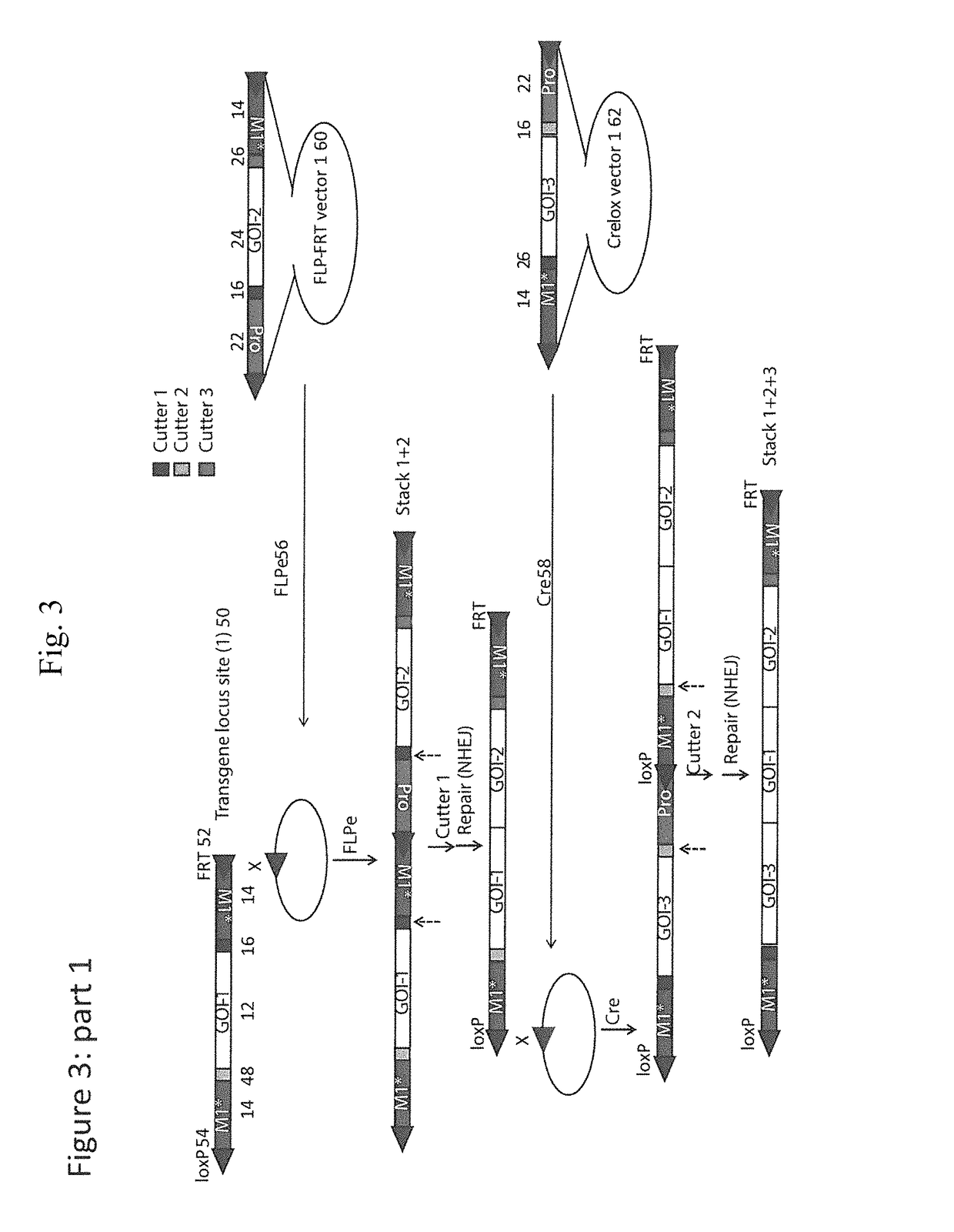
InactiveUS10233456B2Improve stabilityImprove performanceVector-based foreign material introductionCo segregationGenome
Methods of gene stacking are described herein. The methods can be used to repeatedly add genes into a chosen locus in a precise manner, which ensures co-segregation of all introduced genes and contributes to the stabilization of gene expression. In addition, methods of removing any additional foreign DNA elements such as selectable markers are provided. Seed stocks or cell lines comprising a gene stacking site, vectors containing an insert flanked by target sites for a site-specific DNA recombinase for use in the methods and kits for carrying out the methods are also provided herein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Eucaryon expression system using jiadi flagllate virus as gene expression carrier
InactiveCN100351384CEffective infectionActiveFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDna transfectionCytotoxicity
An eucaryotic expression system using Giardia virus as gene expression carrier is disclosed, which can be the one using DNA transfection mode and the other using RNA transfection mode. Said Giardia virus can effectively infect its trophont and has lower toxin and more number of copies in gene duplication. Said Giardia is easily cultured. Its advantages are high expression efficiency and no pollution to gene.
Owner:MILITARY SUPPLIES UNIV THE CHINESE PLA
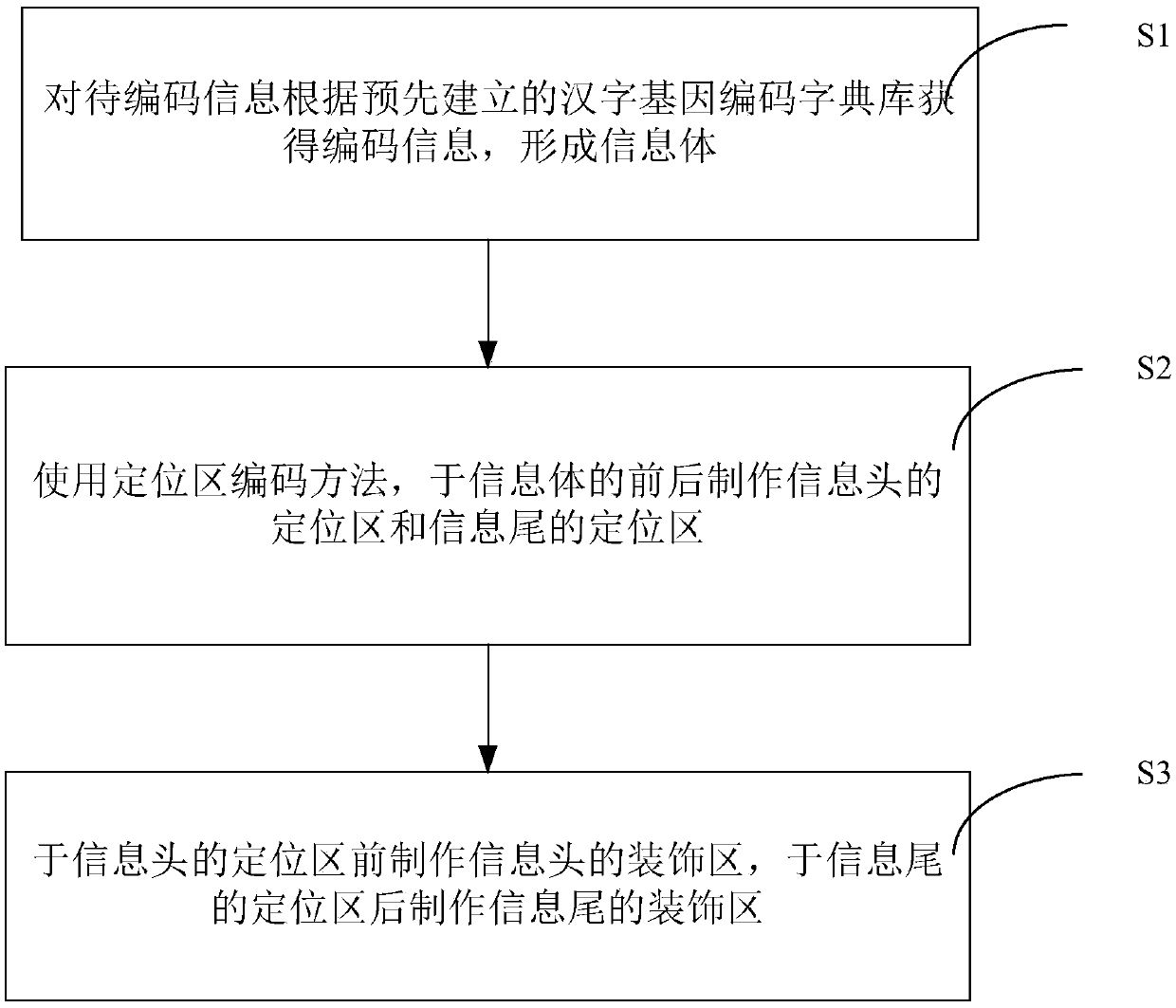
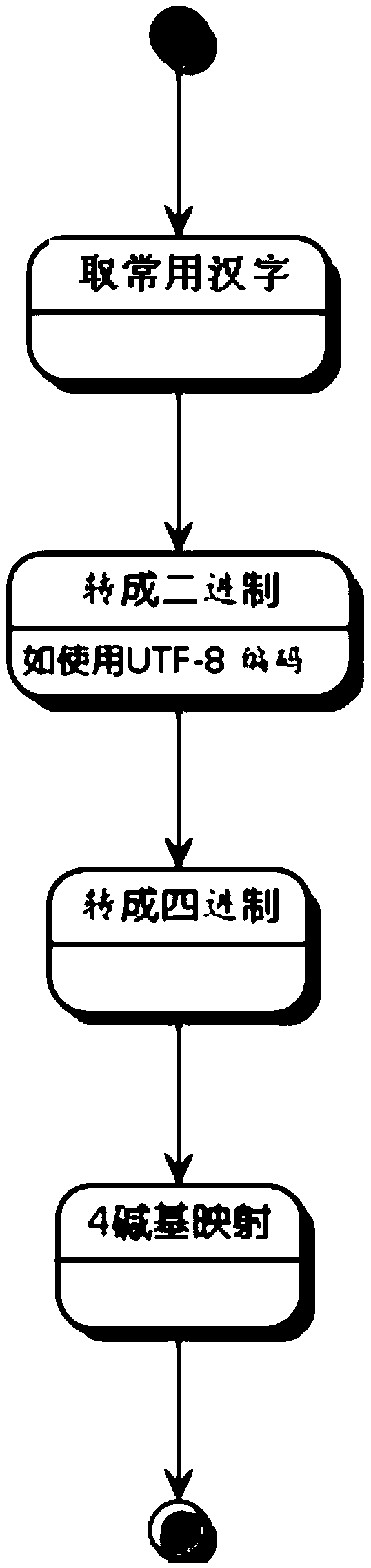
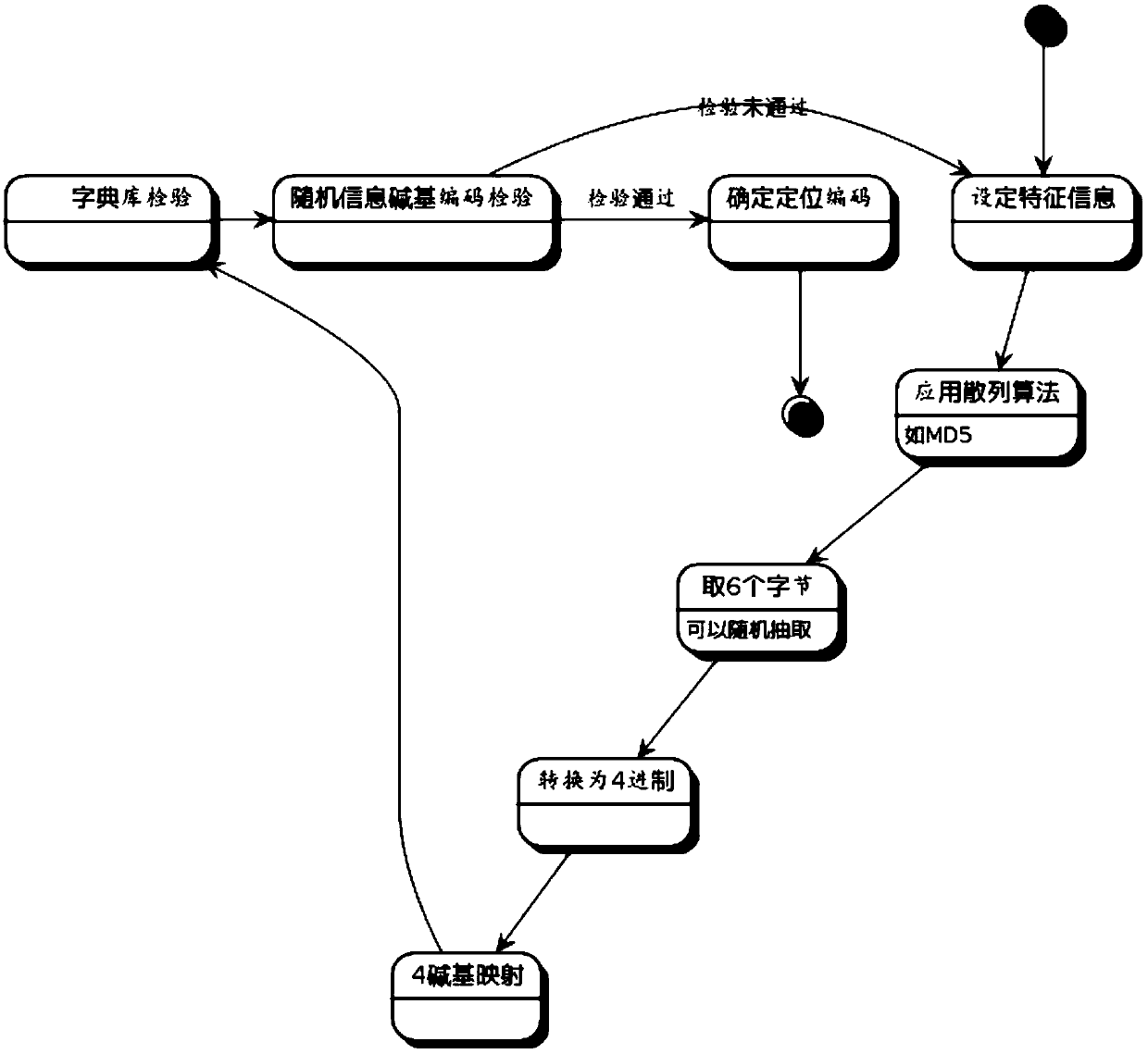
A method and system for gene encoding and decoding of Chinese characters
The invention discloses a Chinese character gene coding method and system, and a Chinese character gene decoding method and system. The coding method comprises the following steps: obtaining coded information from information to be coded according to a pre-established Chinese character gene coding dictionary database, so that an informosome is generated; respectively producing a positioning zone of an information header and a positioning zone of an information trailer in front of and behind the informosome through a positioning zone coding method; and producing a decoration zone of the information header in front of the positioning zone of the information header, and producing a decoration zone of the information trailer behind the positioning zone of the information trailer. The coding method and system and the decoding method and system provided by the invention have the advantages that commonly-used Chinese character information is stored in biological genes, and can be decoded in ahighly fault-tolerant manner during gene duplication for biological information labeling and tracking, so that the tracking and identification precision and efficiency for plant biological information are improved, and time for analysis and identification can be further greatly reduced.
Owner:北京农科院种业科技有限公司 +1
Multiplex PCR rapid identification method for salmonella and listeria monocytogenes
The invention discloses a kind of appraisal bacterium, specially appraises the monk fungus (Salmonella), produces the uninuclear cell Liszt fungus (Listeria monocytogenes) the examination method. First (YAU_DSL1) separately uses the monk fungus and the backwoods coli the thermal crack solution to withdraw respective DNA template, produces the uninuclear cell Liszt fungus to use the enzyme solution to withdraw the DNA template, then carries on disposable PCR to expand increases the specific many genes, finally passes through the electricity to swim the appraisal. The invention through sample DNA, disposable at the same time to the monk fungus histidine transportation operon gene which possibly has, produces the uninuclear cell hemolysin gene to expand increases (YZU_DSL1) the material particle carries on with the certain existence backwoods coli expands increases, forms the massive genes duplication fragment, quite is convenient, can appraise whether for the monk fungus, produces the uninuclear cell Liszt fungus, and makes the judgement to the negative result reacting system accuracy. The invention more classical method bacterium separation, the appraisal and the blood serum school grades testing method fast, is accurate.
Owner:江苏瑞邦生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com