N-type organic semiconductor material as well as perpetration method and application thereof
An organic semiconductor, n-type technology, applied in the field of n-type organic semiconductor materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of limiting carrier mobility and absorption coefficient, and difficult to optimize photoelectric performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0217] This embodiment prepares the brominated monomer (compound 10) of the n-type organic semiconductor material having the structure shown in formula II through the following steps:
[0218] Step (1): Synthesis of Compound 2
[0219]
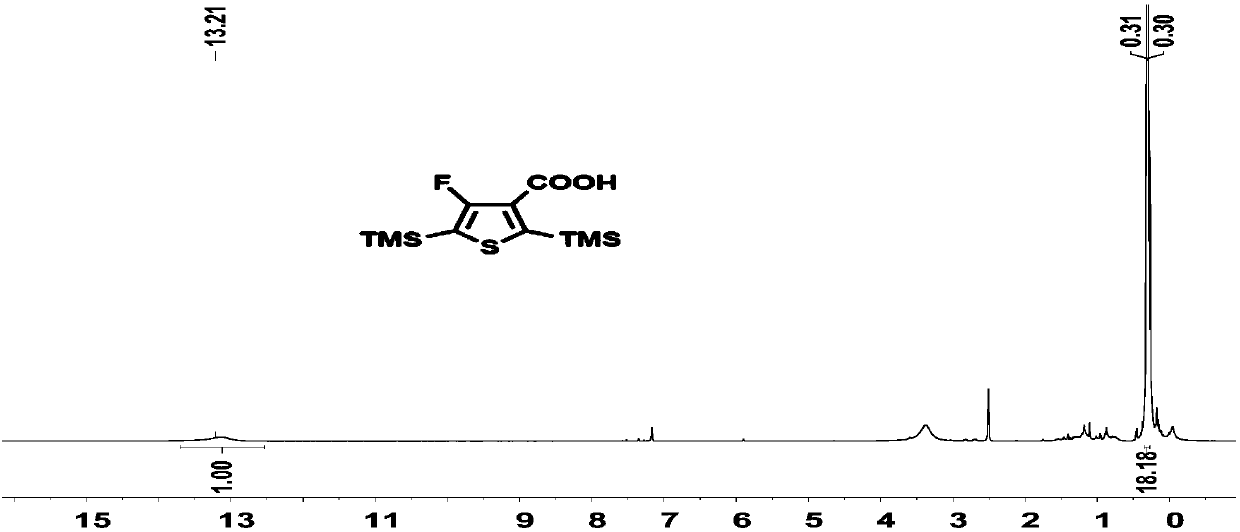
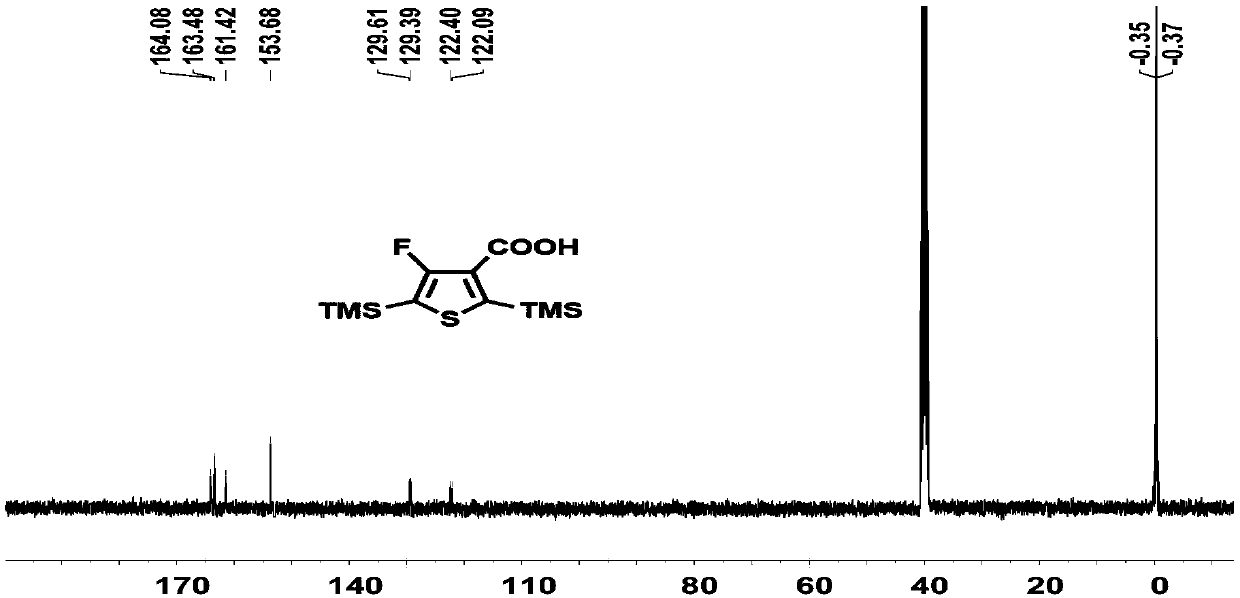
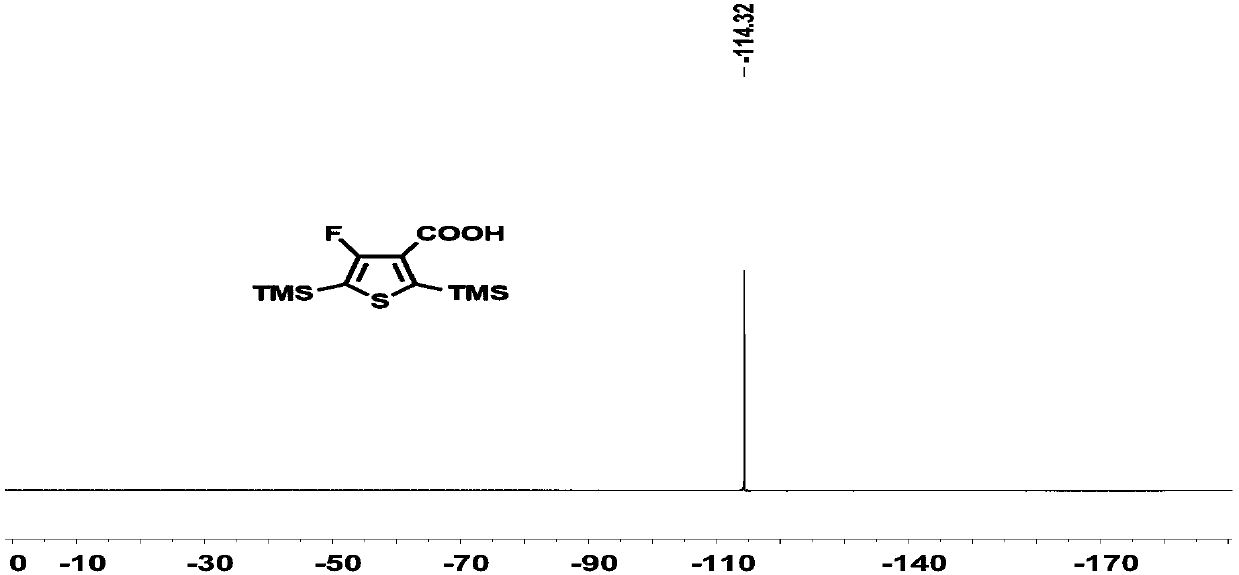
[0220] Compound 1 (4.1 g, 12.6 mmoL) was dissolved in 100 mL of ether solution. Add n-butyllithium (2.4M, 7.8mL, 1.05eq) at -78°C to react for 1 hour, and then pass excess carbon dioxide gas. Reaction 1h rose to room temperature. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, the remaining solid was dissolved in water, concentrated hydrochloric acid was added dropwise on an ice-water bath until a white solid precipitated, filtered and washed with water until neutral, and dried in a vacuum oven to obtain compound 2 (3.1 g, yield: 96%), directly for the next step. H NMR spectrum such as Figure 1A As shown, the carbon NMR spectrum is as Figure 1B As shown, the NMR fluorine spectrum is shown as Figure 1C As shown, high-resolution mass ...
Embodiment 2
[0255] In this embodiment, an n-type organic semiconductor material having a structure shown in formula II is prepared through the following steps:
[0256]
[0257] Add the tinned monomer (37.34, 0.083mmoL, 1.0eq) and the brominated monomer compound 4 (0.102g, 0.083mmoL) into a 5mL reaction tube, and at the same time add the catalyst Pd 2 (dba) 3 (1.09mg, 0.0012mmol, 1.5%eq), Ligand P(o-tolyl)3 (3.03 mg, 0.010 mmol, 12% eq) with argon sparging. Finally, 2.5 mL of anhydrous toluene was added. The reaction tube was placed in a microwave reactor and reacted at 140°C for 3 hours. After cooling to room temperature, 2-tributyltinthiophene was added, and capped at 100°C for 20 minutes. After cooling down to room temperature again, the reaction liquid was added into methanol, stirred for 3 hours, precipitated, filtered, and further extracted with methanol through a fat extractor to take out low molecular weight products. Finally, the product was concentrated, dropped into 5 mL...
Embodiment 3
[0261] UV absorption spectrum, electrochemical test and thermal stability characterization
[0262] UV-Vis absorption spectra and cyclic voltammetry of polymer s-FBTI2-FT in solution and film states Figure 10 and 11 As shown, the introduction of F atoms does not affect the energy level (E g opt =1.96eV), effectively lowering the molecular orbital energy level of the polymer molecule (HOMO=-5.54eV; LUMO=-3.57eV). It is more conducive to the injection and transmission of carriers in transistors, and has better energy level matching and spectral complementarity with polymer donors in all-polymer solar cells, which is conducive to the absorption of photons and the increase of current. In addition, polymers have good thermal stability, such as Figure 12 As shown, the mass loss of the polymer is 5% at over 400°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com