hot melt adhesive
A technology of hot-melt adhesives and symmetry, applied in the direction of adhesives, adhesive types, polyurea/polyurethane adhesives, etc., can solve the problems of low tensile breaking strength and low cohesion of hot-melt adhesives, Achieve the effects of small temperature dependence, stable adhesive force, and excellent tensile breaking strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
manufacture example 1
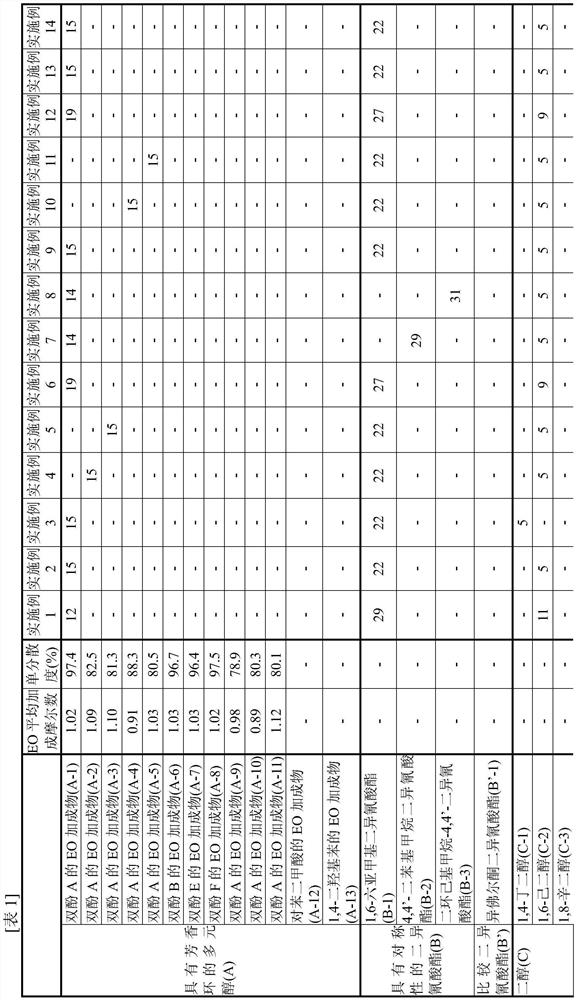
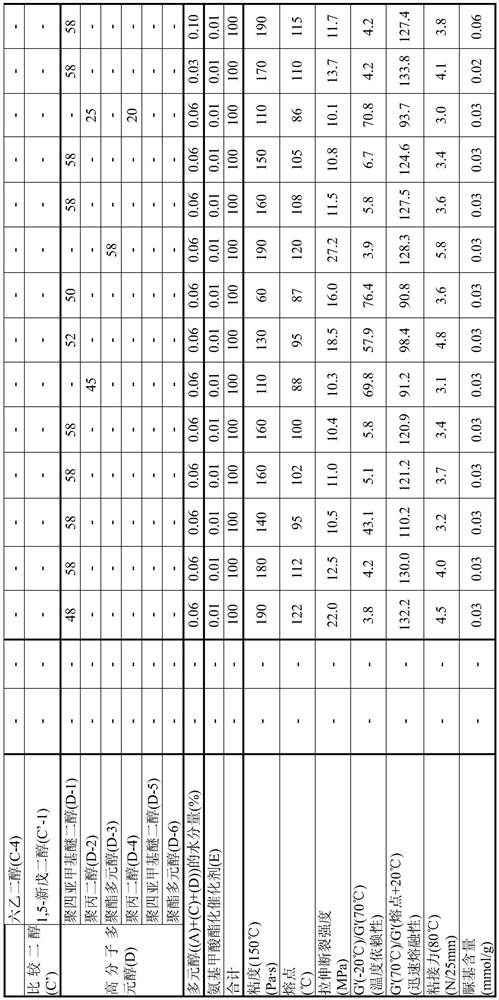
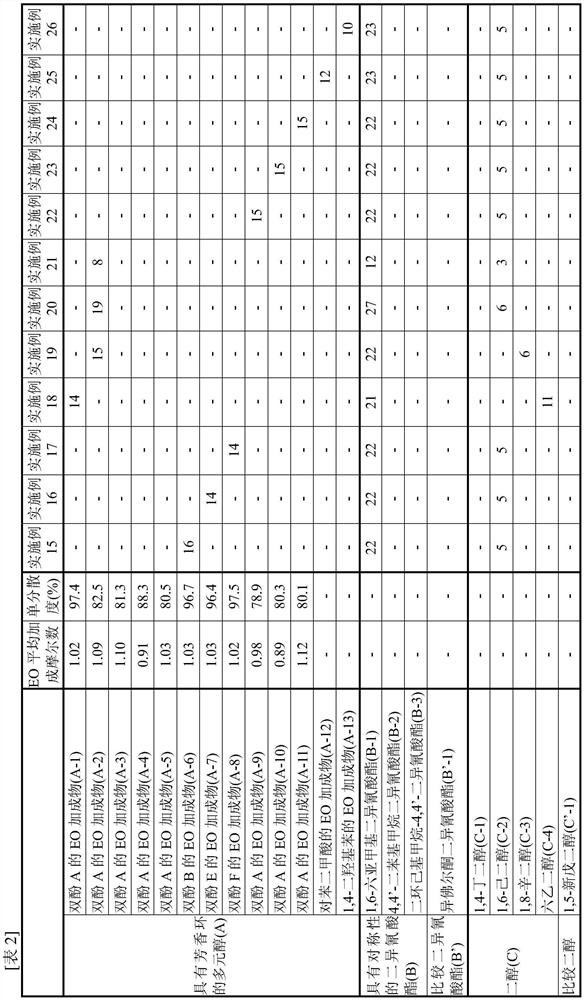
[0100] [Synthesis of EO adduct (A-1) of bisphenol A]
[0101] 137.0 g of toluene (40% relative to bisphenol) and 342.4 g (1.50 mol) of bisphenol A ("bisphenol A" manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation) were charged into a glass autoclave, and after replacing with nitrogen, the temperature was raised to At 75°C, bisphenol A was dispersed in toluene. To this was added 2.73 g of a 25% aqueous solution of tetramethylammonium hydroxide.
[0102] Nitrogen substitution was performed again, and EO was dripped and reacted in the range of 75-95 degreeC and reaction pressure 0.2 MPa or less. During the reaction, appropriate sampling was performed, and the addition mole distribution of the reactant to bisphenol was followed by GC, and the reaction was terminated when 1 mole of the addition product reached 0.1% or less. The EO required was 139.9 g (3.18 mol) and the reaction time was 7 hours.
[0103] After the reaction, unreacted EO, a catalyst, a solvent, etc. were distilled ...
manufacture example 2
[0106] [Synthesis of EO adduct (A-2) of bisphenol A]
[0107] 85.6 g (A-1) obtained in Example 1 (25 weight% with respect to the bisphenol A added later) was added to the glass autoclave, and it melt|dissolved as the solvent of a reaction system. After heating and melting at 110° C., 342.4 g (1.50 mol) of bisphenol A was charged and replaced with nitrogen, and then cooled to 95° C. to disperse bisphenol A. 0.30 g of sodium hydroxide was added thereto.
[0108] Nitrogen substitution was performed again, and EO was dripped and reacted in the range of 75-95 degreeC and reaction pressure 0.2 MPa or less. During the reaction, appropriate sampling was carried out, and the molar distribution of addition of reactants to bisphenol was traced by GC. The reaction was terminated when 1 mole of the adduct reached 0.1% or less. The EO required was 150.5 g (3.42 mol) and the reaction time was 7 hours.
[0109] After the reaction, the catalyst was neutralized with phosphoric acid, and unr...
manufacture example 3
[0112] [Synthesis of EO adduct (A-3) of bisphenol A]
[0113] The reaction was carried out in the same manner as in Production Example 2, except that the amount of EO to be added dropwise in Production Example 2 was 154.0 g (3.50 mol), and the reaction was terminated when 1 mol of the adduct became 0.1% or less.
[0114] After the reaction, the catalyst was neutralized with phosphoric acid, and unreacted EO was distilled off at 130 to 160° C. under reduced pressure to obtain an EO adduct of bisphenol A (A-3).
[0115] This (A-3) was analyzed by GC, and the obtained (A-3) had an average added mole number of EO per hydroxyl group of 1.10 and a monodispersity of 81.3%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com