Method of separating and purifying phenyl lactic acid from lactobacillus plantarum
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and phenyllactic acid, applied in the field of food biology, can solve the problems of limited application scope and narrow antibacterial spectrum.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Activation of Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316 strain and preparation of fermentation supernatant
[0023] Activation of Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316 strain: take the strain out from -80°C, thaw at 4°C, streak on MRS solid medium, and culture at 37°C for 24 hours; pick a single colony and place it in MRS liquid medium at 37°C Cultured for 24 hours, successively subcultured twice to obtain seed solution. The seed liquid was inserted into the fermentation medium (MRS liquid) with an inoculation amount of 2% by volume for expansion cultivation, and cultured statically at 37° C. for 24 hours to obtain a fermentation liquid. The fermentation broth was centrifuged at 8000rpm for 15min (4°C) to obtain a supernatant, which was stored at 4°C until use.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2: Separation and purification of phenyllactic acid in the fermentation supernatant of Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316
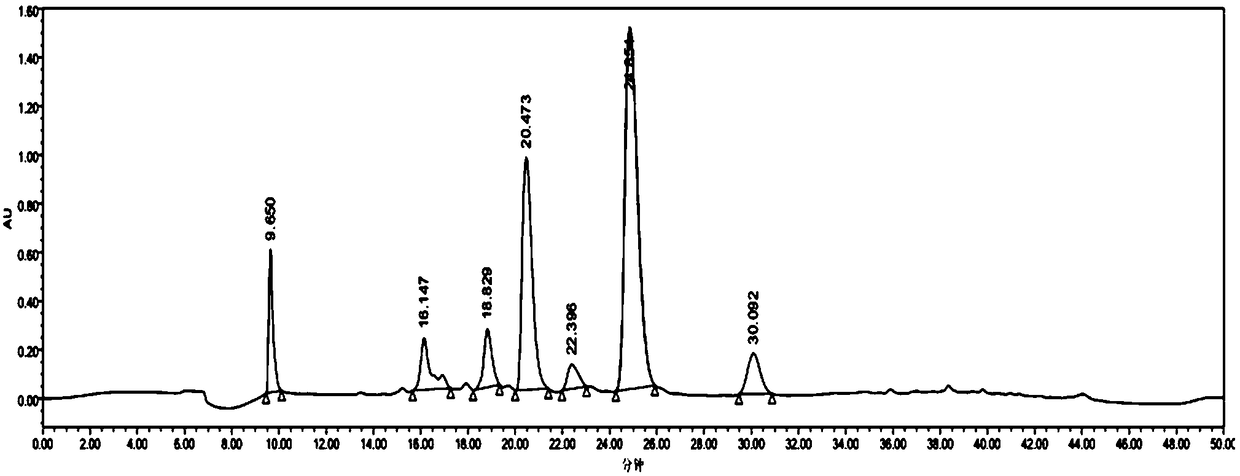
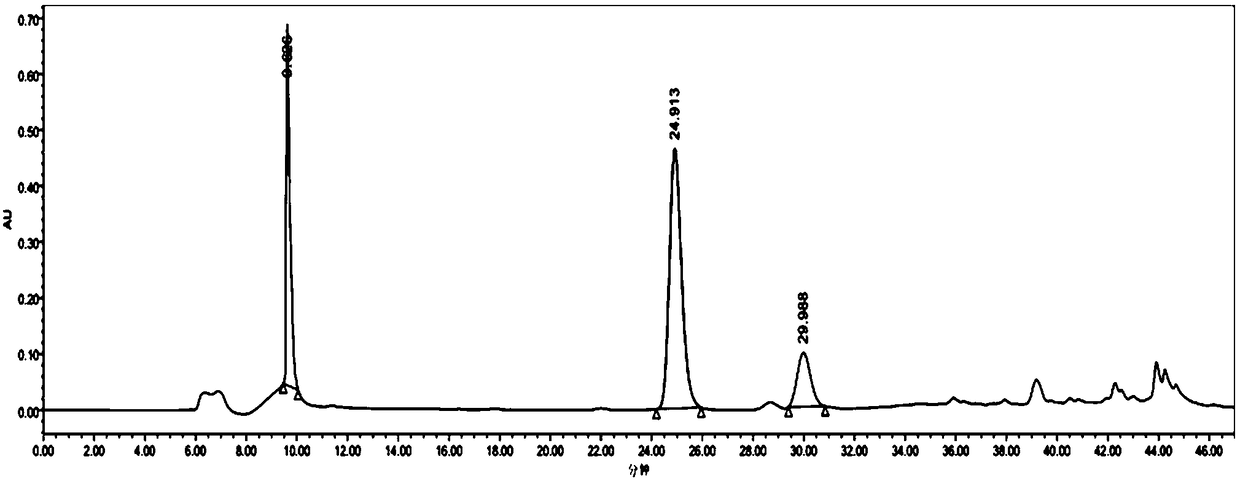
[0025] The centrifuged supernatant was adsorbed by XAD-2 macroporous resin, and the flow-through was collected and filtered through a microporous membrane (0.22 μm). The filtrate was separated and purified twice by high performance liquid chromatography. HPLC conditions for the first separation and preparation: the chromatographic column model is YMC-Pack ODS-AQ 150×20mm L.D., the mobile phase: 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid / water (A) and 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid / methanol (B), and the ultraviolet detection conditions: Detector model Waters 2998, detector wavelength: 215nm, column temperature: 25°C, flow rate: 4mL / min, injection volume: 5mL. Gradient elution method: 0, 5, 25, 30, 40, 46 minutes eluent A / B volume ratio compositions are 95:5, 95:5, 5:95, 5:95, 95:5, 95, respectively :5. The chromatographic peak whose retention time is 24.854min is...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: Phenyllactic acid production and isolation purity in the supernatant of Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316
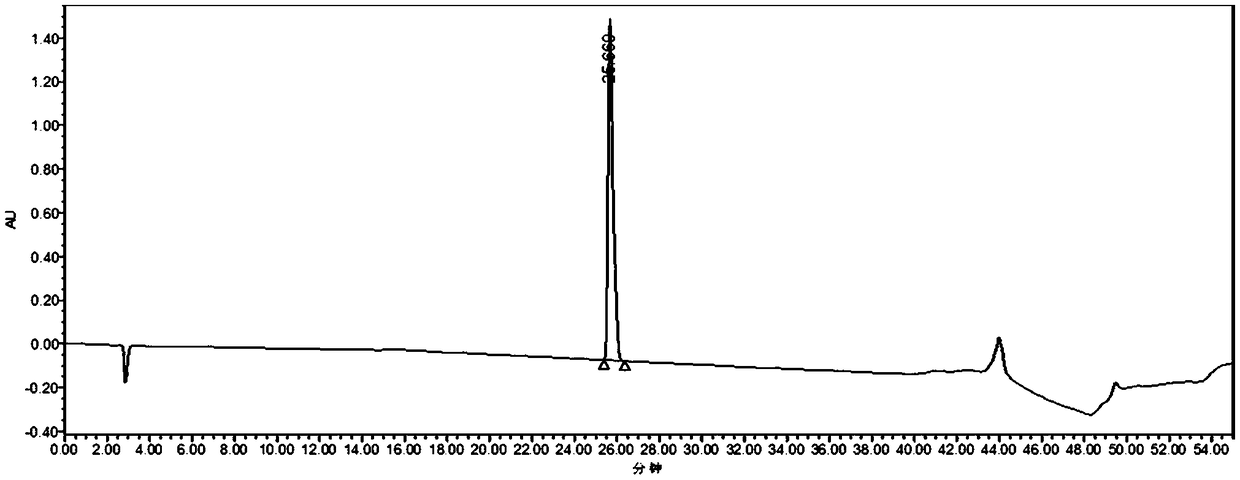
[0028] Test the purity of phenyl lactic acid (see image 3 ), analytical HPLC conditions: column model YMC-PackODS-AQ 150×4.6mm L.D., UV detection conditions: detector model Waters 2498, detector wavelength: 215nm, column temperature: 25°C, flow rate: 0.8mL / min, injection volume: 50 μL. The mobile phase and gradient elution method are the same as the second high performance liquid chromatography separation and purification in Example 2.
[0029] Using the same method, a series of concentration gradients (0, 0.05mg / mL, 0.10mg / mL, 0.25mg / mL, 0.50mg / mL, 0.75mg / mL) of phenyl lactic acid standard (purchased from Sigma company) Determination. Establish the standard curve of peak retention time and peak area, and calculate regression equation (see Figure 4 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com