Method for producing L-sodium malate through direct enzymatic conversion
A technology of sodium malate and calcium malate, applied in fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of restricting the wide application of L-sodium malate, consumption of large sulfuric acid, low concentration, etc., achieving significant industrial application value and environmental benefits, and reducing the degree of reverse reaction. , the effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
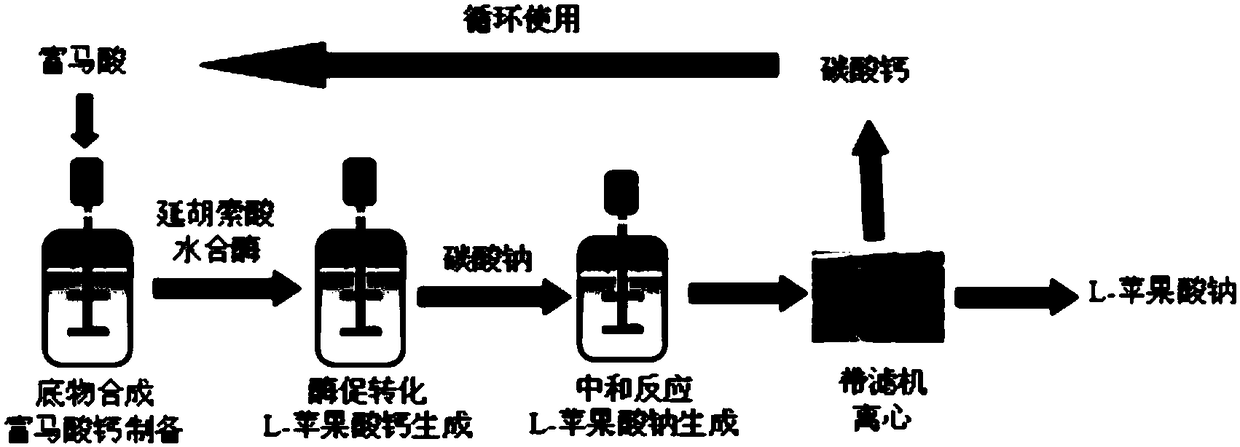
[0077] The preparation of embodiment 1 L-sodium malate
[0078] Preparation of Calcium Fumarate Suspension
[0079] Preheat 2.5L of pure water to 55°C, add 348g of fumaric acid, then slowly add 300g of calcium carbonate, stir and mix with a mechanical stirrer, keep warm to neutralize the two, and monitor the concentration of fumaric acid at any time during the reaction. Content, when its content is lower than 10g / L, reaction finishes, obtains 3L calcium fumarate suspension.
[0080] Enzymatic Transformation Production of Calcium L-Malate
[0081] According to the amount of 300U enzyme activity / 100mL substrate, add the recombinant Escherichia coli introduced and expressing fumc gene into the calcium fumarate suspension prepared in the previous step as fumarate hydratase (calculated by enzyme activity) to control the enzymatic reaction The temperature is 37° C., and the enzymatic reaction is carried out under stirring at a stirring speed of 200 rpm, and 3.5 L of calcium L-mala...
Embodiment 2
[0085] The preparation of embodiment 2 L-sodium malate
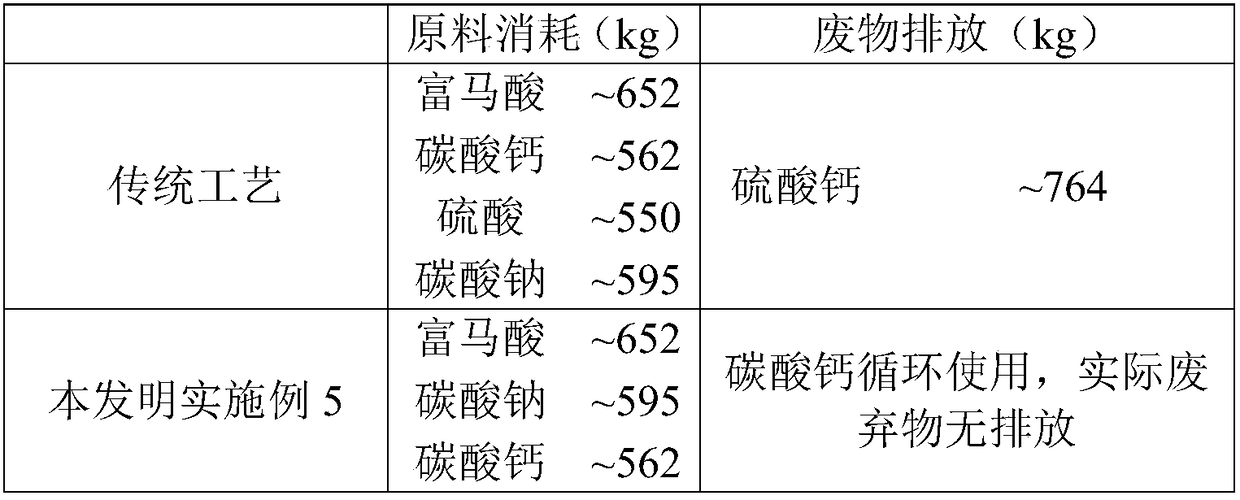
[0086] In this example, except adopting 348g fumaric acid and 138g calcium carbonate and adding calcium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 6.8, the method described in Example 1 was used to prepare L-sodium malate, wherein, as a solid precipitate The calcium carbonate of the product is recovered and recycled in the preparation of calcium fumarate suspension.
[0087] The average productive rate of the L-sodium malate of this embodiment is 28.34g / (L h), and the catalytic efficiency of fumaric acid hydratase is 8.54 * 10 -3 g / (U·h).
Embodiment 3
[0088] The preparation of embodiment 3 L-sodium malate
[0089] In this embodiment, in addition to adopting calcium bicarbonate to prepare calcium fumarate suspension at the beginning of the method and adopting the recombinant escherichia coli introduced and expressing the fuma gene as fumarate hydratase, prepare according to the method described in Example 1 This results in sodium L-malate, wherein the calcium carbonate as a solid precipitate is recovered and recycled in the preparation of the calcium fumarate suspension.
[0090] The average productive rate of the L-sodium malate of this embodiment is 28.45g / (L h), and the catalytic efficiency of fumaric acid hydratase is 8.56 * 10 -3 g / (U·h).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com