Carbon fiber recycling compositions and methods
A composition and fiber technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, plastic recycling, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of slow recovery of alkaline catalysis, incomplete removal of resin components, and danger.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
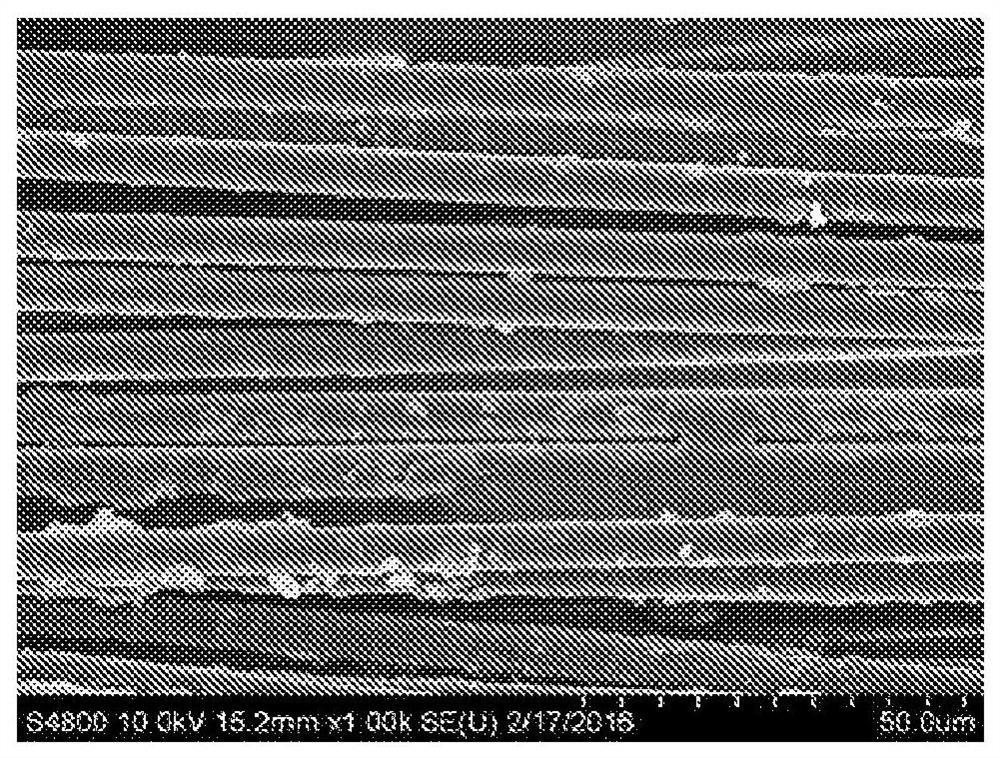
[0052] 5g PPh 4 -TFSI (tetraphenyl bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide) was heated to 350°C and mixed with a 1 cm 2 A 5-layer sheet of thick CFRP was incorporated. After 10 minutes, free carbon fibers were recovered from the mixture. The recovered carbon fibers were obtained as black and blue fibers and there was very little polymer residue on the recovered fibers. The ionic liquid was recrystallized and used to treat another 1 cm block under the same conditions 2 of 5-layer sheet-thick CFRP, again recovering free fibers from the mixture.
[0053] Then use 5g fresh PPh 4 -TFSI, use a piece of 1cm 2 Experiments were repeated with 16-layer slices of CFRP. Free fibers recovered from 16-ply thick CFRP included some residual resin particles. These experiments demonstrate that the exact ratio of ionic liquid to resin mass is not critical.
[0054] PPh before and after heating 4 - TFSI with CFRP 31 P NMR to observe material changes. Some ionic liquids degrade in the presen...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The cured resin decomposition mechanism is explored in this example to understand whether ionic liquids are heat transfer fluids or are chemically involved in cured resin decomposition in CFRP. A chemically similar material with a boiling point above the process temperature was heated at 350°C for 10 minutes with a 5-layer sheet of CFRP. None of the liquids behaved as well as PPh in terms of releasing fibers from CFRP. 4 -TFSI is just as good. Table 1 below shows the PPh 4 - TFSI promotes the decomposition of cured resin in CFRP. The data also show that ionic salts, which are liquid at processing temperatures, outperform other high temperature stable fluids.
[0058] Table 1
[0059]
[0060] The data in Table 1 indicate that PPh 4 - The role of TFSI ionic liquid in breaking down CFRP resin exceeds that of heat transfer fluid because it can react with the resin in CFRP or act like a catalyst to accelerate CFRP fracture. Heat transfer fluids such as triphenylmet...
Embodiment 3
[0062] To further explore the PPh 4 -Whether TFSI is a reactant or catalyst for the depolymerization of the cured resin, making the ionic liquid 20:1 (organic:PPh) in the other organic materials in Table 1 4 -TFSI) dilution. The catalysts or reactants still function at lower levels, but if the ionic liquid is simply a solvent to swell and dissolve the epoxy resin, we would expect carbon fiber recovery to fail due to dilution in less solvated materials. Table 2 shows that 1) the ionic liquid still depolymerizes CFRP in diluted form and 2) other organic materials must all decompose CFRP efficiently to some extent to support the process. figure 1 PPh is shown in 3 When with PPh 4 - Efficacy of TFSI upon merging to induce depolymerization, before and after photographs of a partially delaminated 16-layer sheet-thick CFRP layer after processing. The layered openings allow easier deep penetration of ionic liquids into CFRP. Diluted ionic liquid alone does not cause carbon fiber ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com