Improvements to the manufacture and remanufacture of volatile anaesthetic agents using supercritical fluids
A supercritical fluid and anesthetic technology, which is applied in anesthetics, gas treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
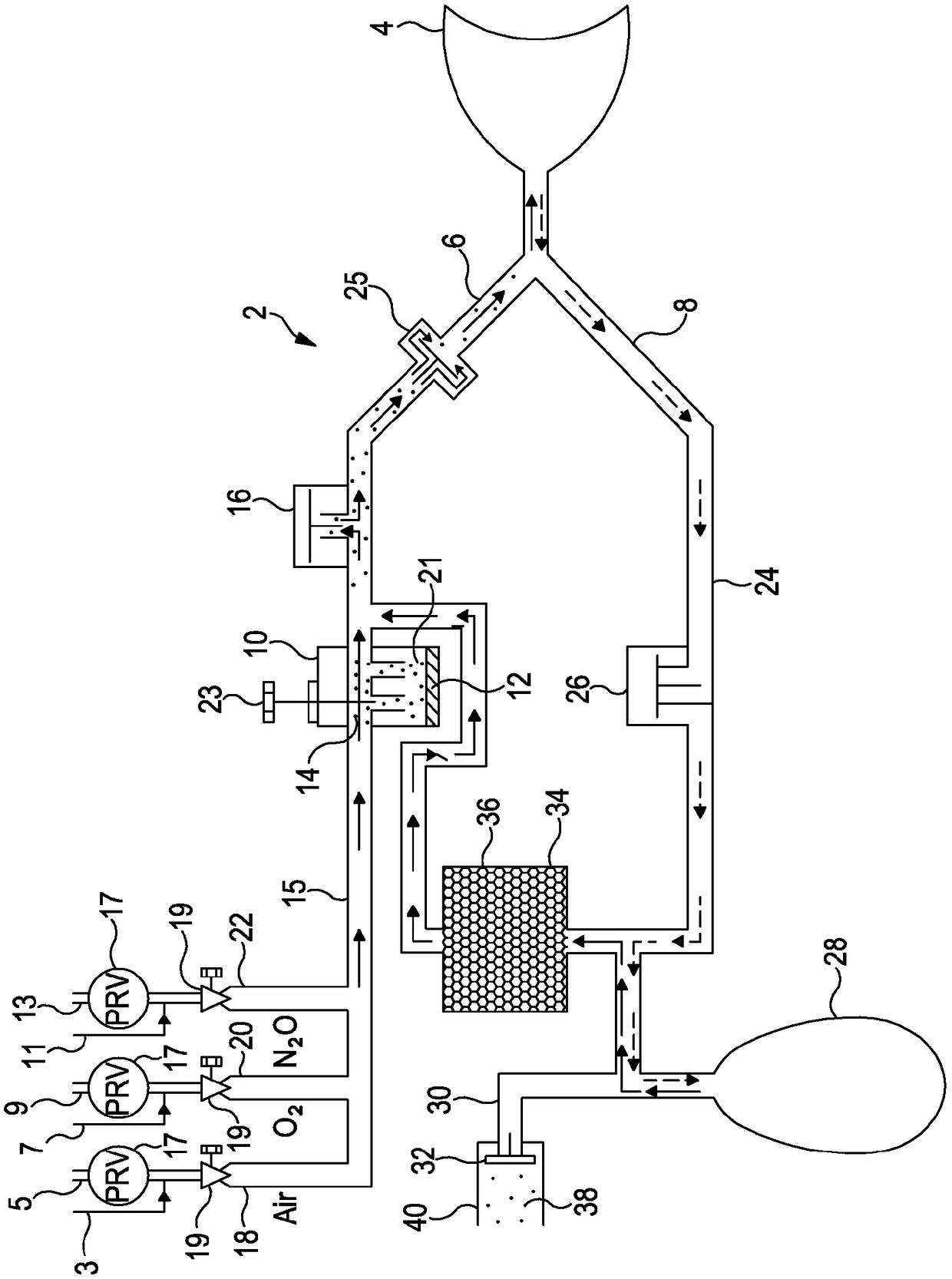
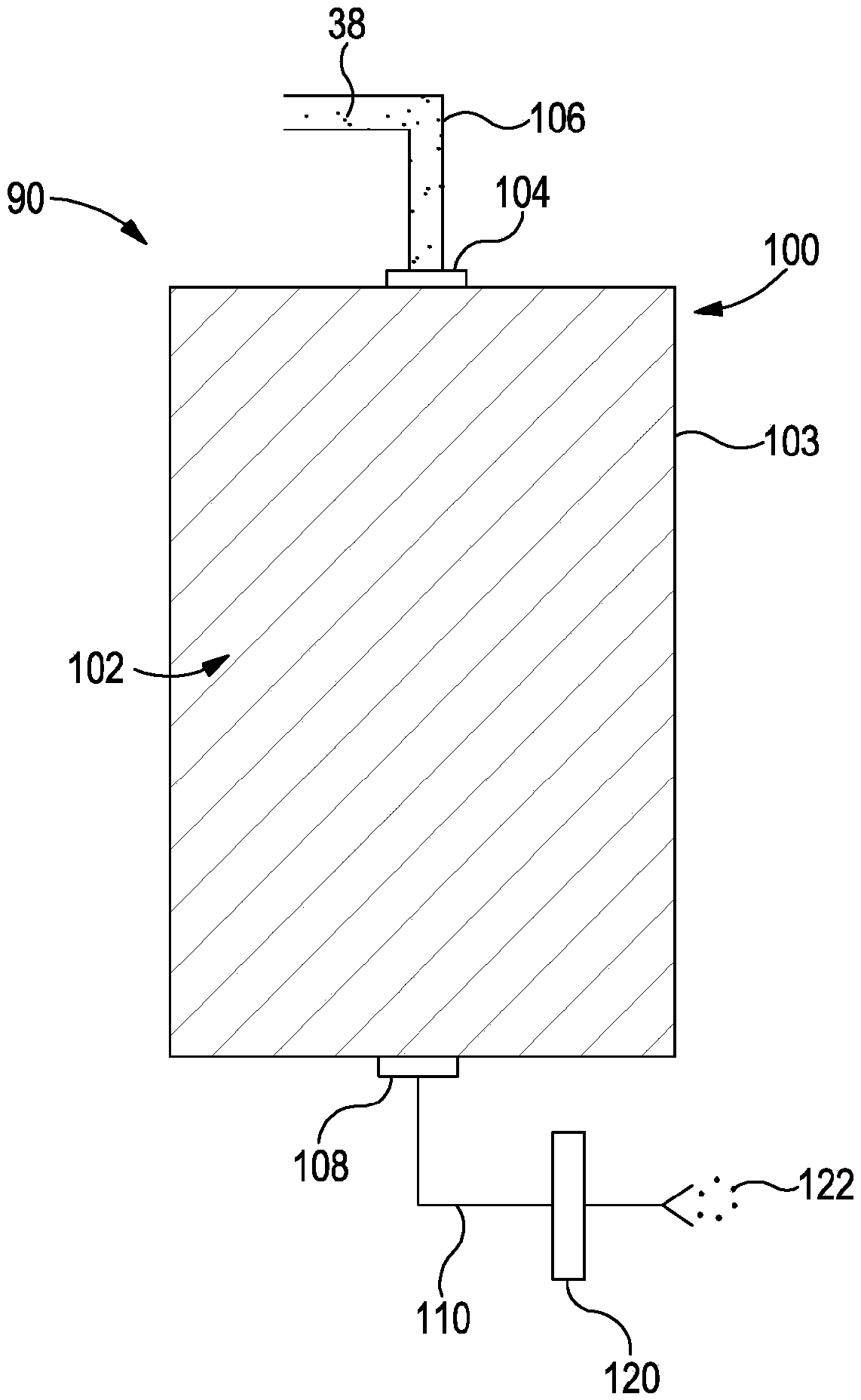
[0213] figure 2 A system 90 for capturing anesthetic halocarbons as detailed in P34906WO is shown.
[0214] Exhaust gas 38 from the anesthesia machine is passed via conduit 106 through connector 104 into tank 100 made of material resistant to supercritical pressure 103 . The canister 100 contains filter material 102 that captures the anesthetic agent from the exhaust 38 . The scrubbed gas then exits via exit conduit 108 and conduit 110 to pass through charcoal filter 120 before being vented to atmosphere 122 .
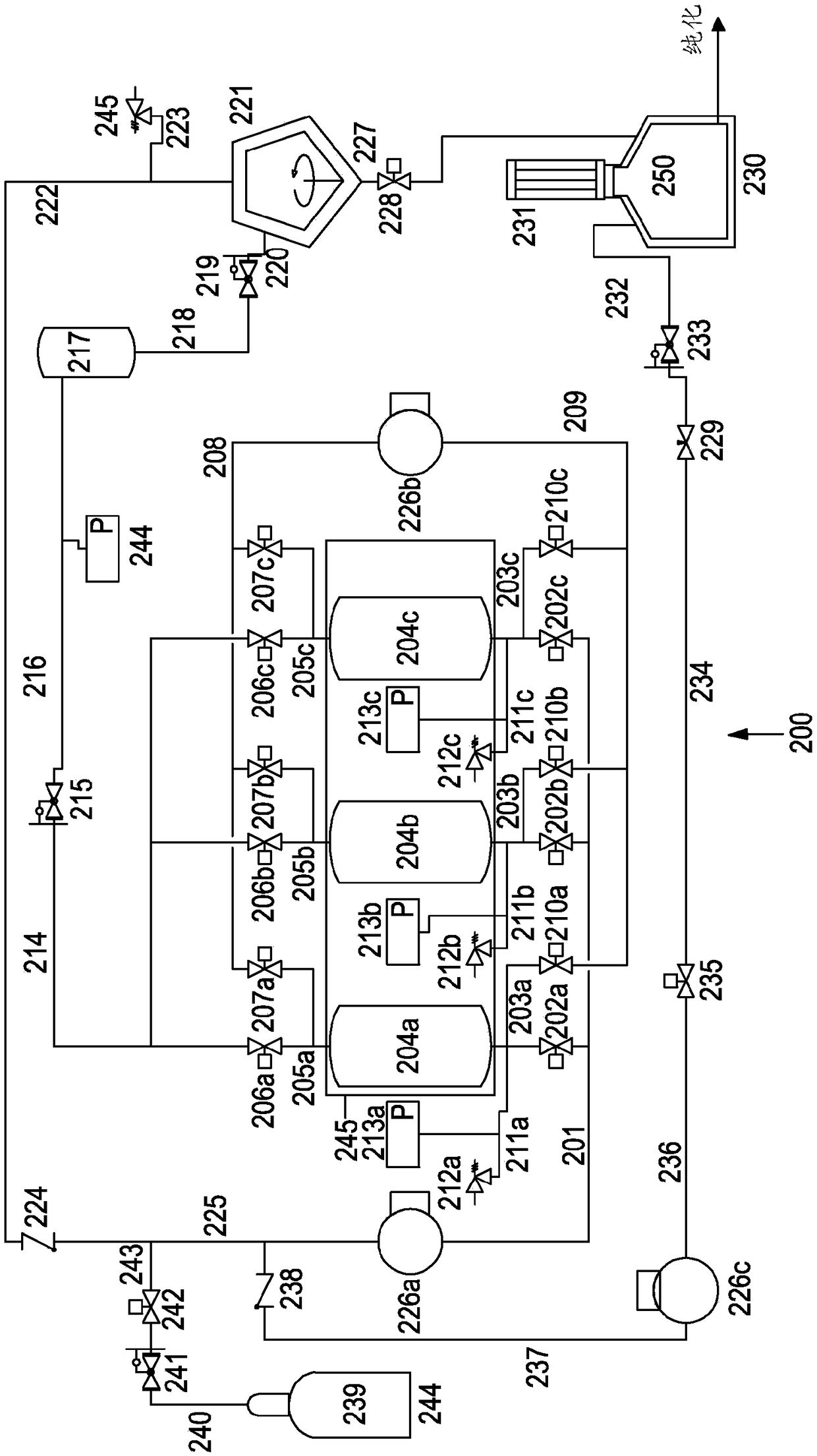
[0215] image 3 A system 200 for extracting and condensing anesthetic halocarbons trapped on a filter material using a supercritical fluid is shown in .
[0216] Trapping the anesthetic halocarbon onto the filter material 102, as in figure 2 or Figure 5 and Figure 6 as detailed in . exist figure 2 In , the tank is pressure-resistant and can therefore be connected directly to a supply of supercritical fluid. exist Figure 5 and Figure 6 In , the filter ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com