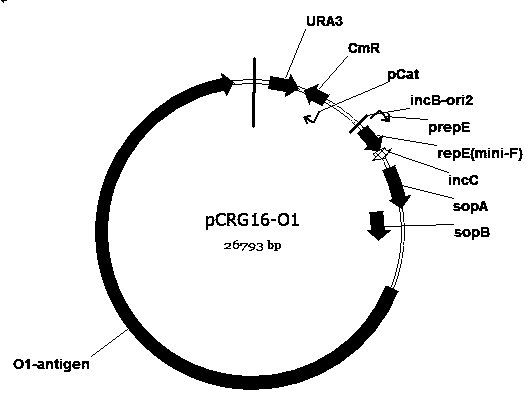
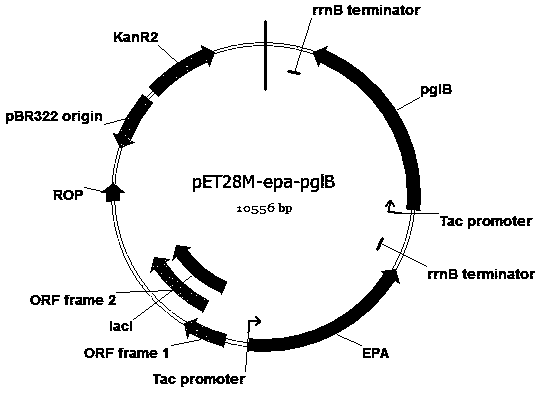
Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for synthesizing glycoprotein conjugate vaccines for neonatal meningitis escherichia coli and application
A technology of Escherichia coli and combined vaccine, applied in the field of synthetic biology, can solve the problem of less vaccine development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Gene acquisition
[0113] In the present embodiment, the acquisition derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa ( Pseudomonas aeruginosa ) from Escherichia coli codon-optimized exotoxin A gene (exotoxin A, GI: 877850); and from Campylobacter jejuni ( Campylobacter jejuni ) and the codon-optimized N-glycosyltransferase gene (undecaprenyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycotransferase, GI: 905417) of Escherichia coli.
Embodiment 2
[0115] Design of gene deletion primers
[0116] In this example, the λRed recombination system is used to knock out two genes of JM109. In this method, resistance is eliminated every time a gene is knocked out. Below to waaL Taking the gene as an example, the steps of gene knockout are explained in detail. wecA Gene deletion primer design is the same.
[0117] Find the nucleotide sequence of JM109waaL, design primers for deletion and identification of waaL. The deletion primer of waaL is waaL-FRT-chl-FRT-F / R, and the identification primer is S-waaL-F / R. Nucleotide sequences are shown in Table 1-8.
Embodiment 3
[0119] JM109Δ waaL build
[0120] 3.1 Transformation of plasmid pSim
[0121] Wild-type JM109 frozen at -80°C was picked and streaked on a non-resistant LB plate, and cultured overnight at 37°C. The next day, a single clone was picked, inoculated into 5 mL LB medium, and cultured overnight at 37° C., 220 rpm. The next day, transfer to 200ml LB medium according to the inoculum volume of 1%. 37°C, 220rpm, cultivate to OD 600 About 0.6-0.8, ice bath for 20min, 5500rpm, 5min, collect the bacteria in a sterilized 50ml centrifuge tube, 4℃, 5500rpm, centrifuge for 5min, discard the supernatant, and use 50ml ice-bathed sterile 10% Resuspend the bacteria in glycerol, 4°C, 5500rpm, and centrifuge for 5 minutes. Repeat the above operation 3 times. For the last time, use the residual liquid when the supernatant was discarded to resuspend the bacteria, and transfer 80 μL to a new sterile EP tube. Freeze at -80°C.
[0122] Thaw the competent cells frozen at -80°C in ice for 10 minutes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com