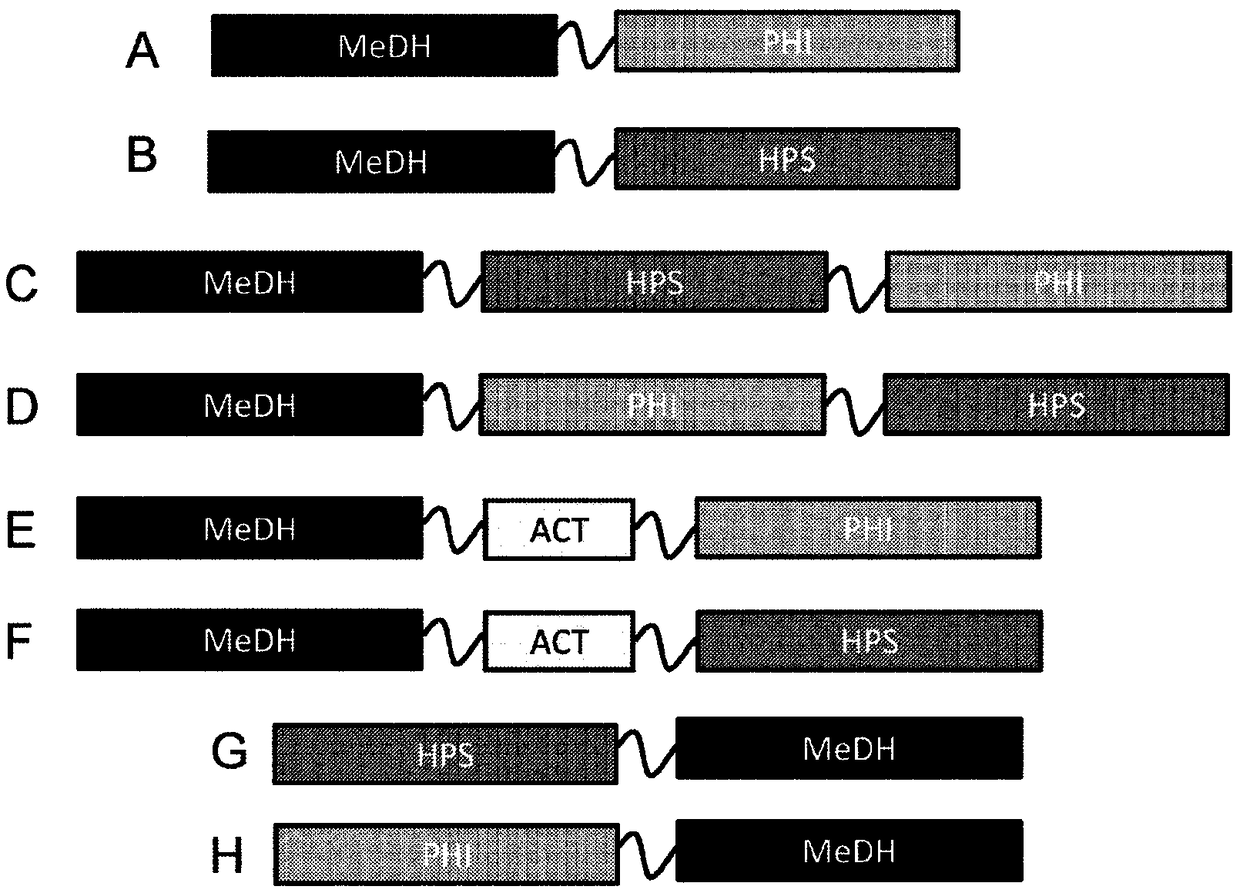
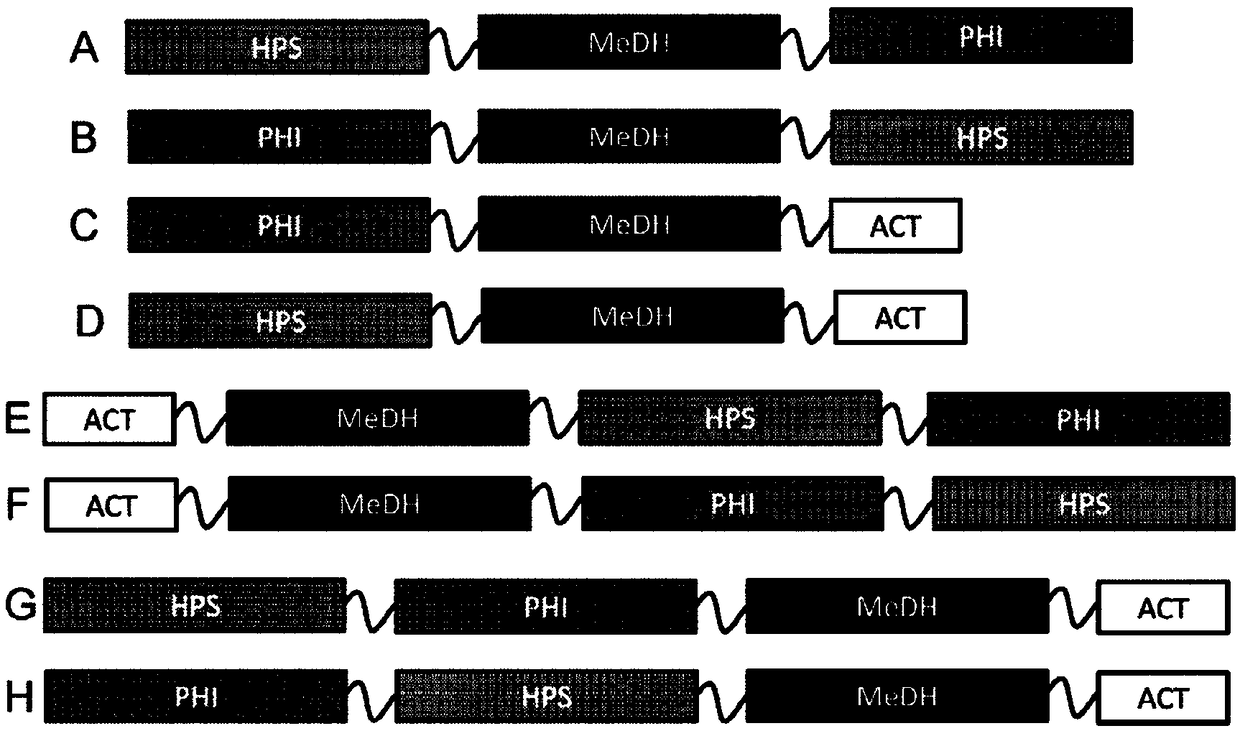
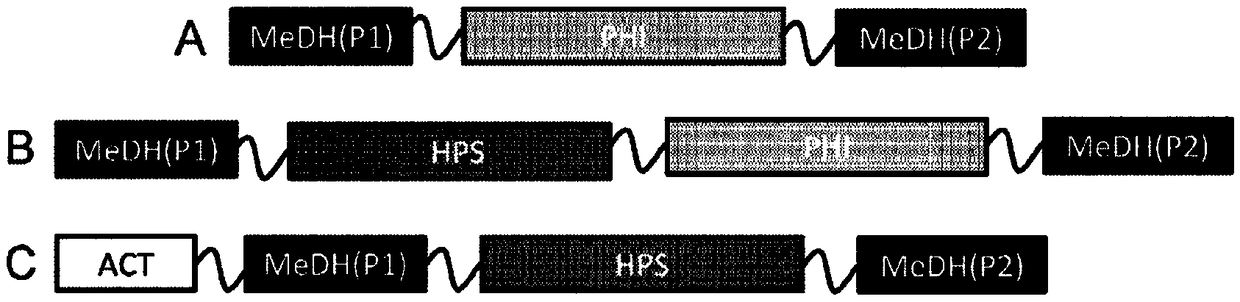
Methanol dehydrogenase fusion proteins
A methanol dehydrogenase and fusion protein technology, applied in the direction of fusion polypeptide, enzyme, lyase, etc., can solve problems such as increased concentration, adverse effects on cells, and adverse effects on cell health
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0239] Embodiment 1: Preparation of MeDH fusion protein construct
[0240] Nucleic acid constructs were prepared for expression of various MeDH-containing fusion proteins, as well as no-fusion control constructs and no-insertion controls. Table 7 is a list of nucleic acid constructs and Table 8 provides details of the genes used in the fusion protein constructs.
[0241] Table 7
[0242] pZS13S-p100-2315LS-linker-hps-phi
pZS13S-p100-2435A-linker-hps-phi
pZS13S-p100-2451A-linker-hps-phi
pZS13S-p108-2315LS-linker-hps-phi
pZS13S-p108-2435A-linker-hps-phi
pZS13S-p108-2451A-linker-hps-phi
pZS13S-p100-2435A-hps-phi
pZS13S-p100-2451A-hps-phi
pZS13S-p108-2315LS-hps-phi
pZS13S-p108-2435A-hps-phi
pZS13S-p108-2451A-hps-phi
[0243] Table 8
[0244]
Embodiment 2
[0246] Example 2: Preparation and Analysis of Engineering Escherichia coli Expressing MeDH Fusion Protein
[0247] The nucleic acid constructs listed in Table 7 were transformed into E. coli. E. coli transformants expressing the MeDH-2616A fusion were evaluated for soluble protein expression, methanol dehydrogenase activity in E. coli cell lysates, and the ability to confer growth on methanol as a carbon source to an engineered E. coli strain (ECKh-8665) Ability. Several variables were tested to identify combinations that conferred improved activity, including: promoter strength, different MeDH variants, and the peptide linker in the MeDH and 2616 fusion.
[0248] The nucleic acid constructs were transformed into E. coli strain 7539 and grown overnight at 37°C in 5 mL of LB+carb100 broth.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com