Cationic pressure sensitive adhesive UV cured by medium mercury bulbs
A pressure-sensitive adhesive, adhesive technology, applied in the direction of film/sheet adhesives, non-polymer adhesive additives, adhesive types, etc., can solve the problem of not yet obtained adhesives, etc., Achieve improved performance, high productivity, and less waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0127] Adhesive Coating Preparation
[0128] The adhesive was applied using a laboratory applicator with two heatable rolls. The adhesive was heated to 150°C and coated onto a 2 mil (51 μm) thick silicone-coated PET release liner. The adhesive on the liner was irradiated with a UV-C dose of 257 mJ / cm2 under H-lamps (Fusion Systems) at a line speed of 15 m / min. Then, the film was layered and transferred to a polyethylene terephthalate substrate ( DuPont) and conditioned at 23°C and 50% relative humidity. Adhesive film thickness was 3.5 mils (89 μm) unless otherwise stated.
[0129] UV curing
[0130] The adhesive film was cured using a medium pressure mercury arc lamp (using an IST UV curing laboratory unit). Use the EIT PowerPuck to measure and record the UV C dose. UV-C is the 200-280nm region.
[0131] Measurement methods:
[0132] AFERA 4001 (measurement of adhesion (peel) according to DIN EN ISO 11339:2010-06)
[0133] AFERA 4012 (measured by cohesion (shear)...
Embodiment 1
[0146] Example 1 (comparative): Standard example using an acrylic polymer containing 2-ethylhexyl acrylate.
[0147] Preparation of UV-curable polymers:
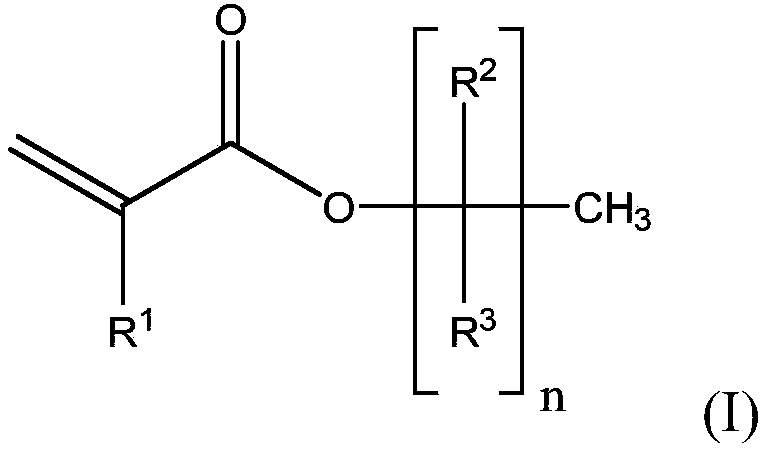
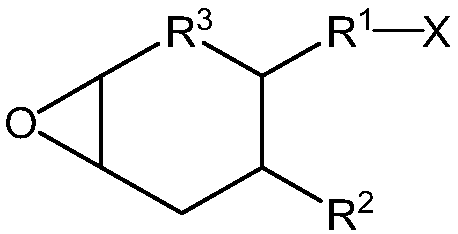
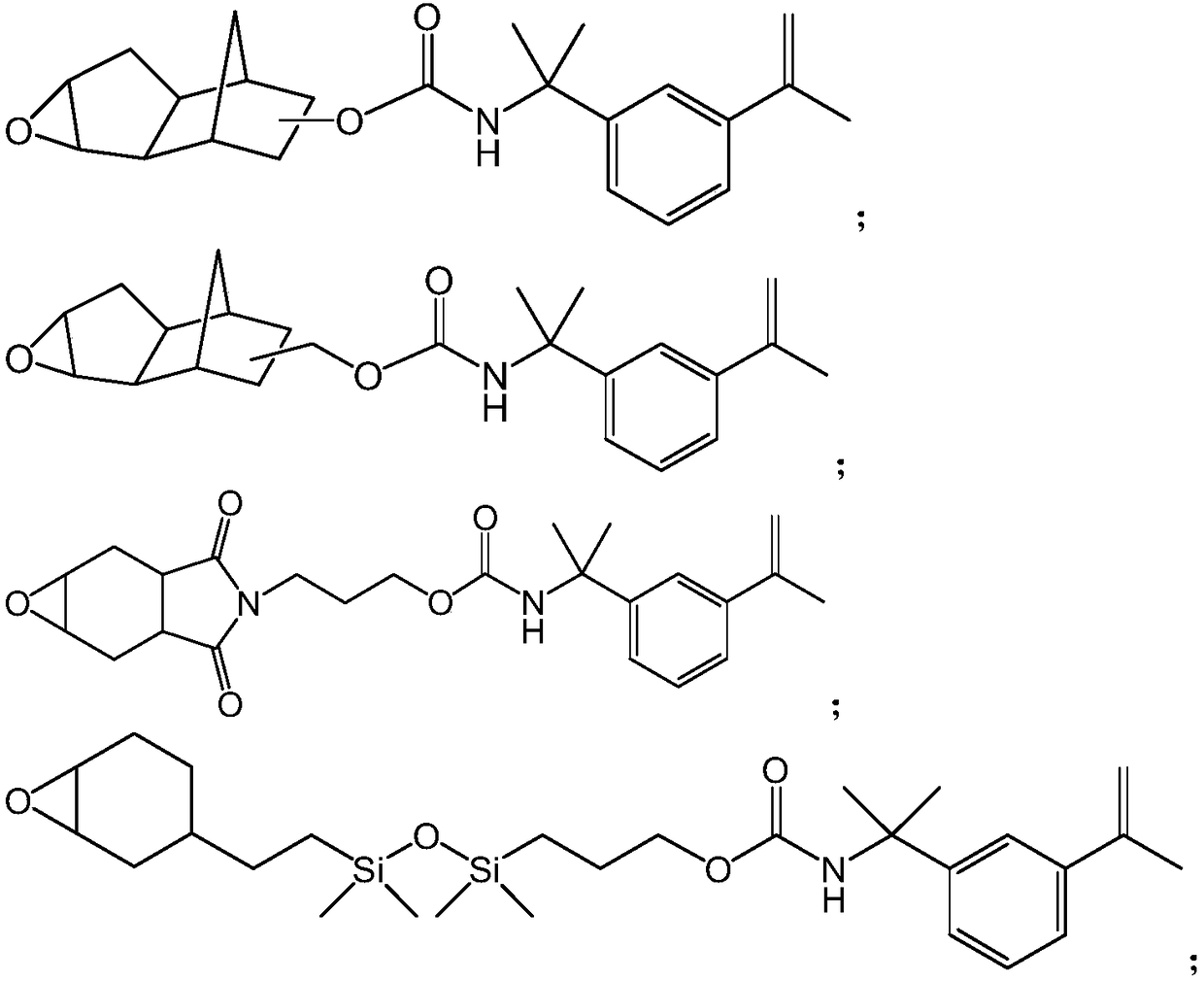
[0148] A four-neck 1 L round bottom polymerization flask was equipped with a thermometer connected to a temperature control unit, a condenser, an overhead mechanical stirrer, two addition funnels, and nitrogen inlet / outlet. The apparatus was purged with nitrogen for 15 minutes. A mixture of the following monomers was prepared: 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (2-EHA, 99.8 g), methyl acrylate (MA, 96.2 g), 1-acryloylmethyl-3,4-cyclohexene epoxide (M100, 1.0g). Into a funnel was added 160 g of the monomer mixture. Into another funnel was added the initiator 2,2'-azobis-(2-methylpropionitrile) (AIBN, 0.5 g) and ethyl acetate (60 mL). The remaining monomer mixture (40 g), initiator AIBN (0.27 g) and ethyl acetate (100 mL) were added to the polymerization flask. The mixture was heated to vigorous reflux (76-80°C) for 15 minutes. The m...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Example 2: An example of using only butyl acrylate and methyl acrylate in the acrylic polymer.
[0154] Preparation of UV-curable polymer: Same as the polymer prepared in Example 1, except that butyl acrylate was used instead of 2-ethylhexyl acrylate. The properties of this polymer can be seen in Table 2 below. Most important are the ball rolling values for two different curing conditions: at 20mJ UV-C: 20cm and 21cm on both sides. At the higher cure doses: 26cm and 28cm, there was no significant difference.
[0155] Table 2: Performance measurements of tackifying polymers using only butyl and methyl acrylate
[0156]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight-average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com