Method for real-time monitoring rare earth ion removing of fused salt by electrochemical means
A rare earth ion and real-time monitoring technology is applied in the field of real-time monitoring of molten salt to remove rare-earth ions, and electrochemical method of real-time monitoring of molten salt to remove rare-earth ions, which can solve the problems of tight energy supply, rapid growth rate, and large total energy demand. Achieve the effect of improving work efficiency, high sensitivity, and avoiding radiation hazards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
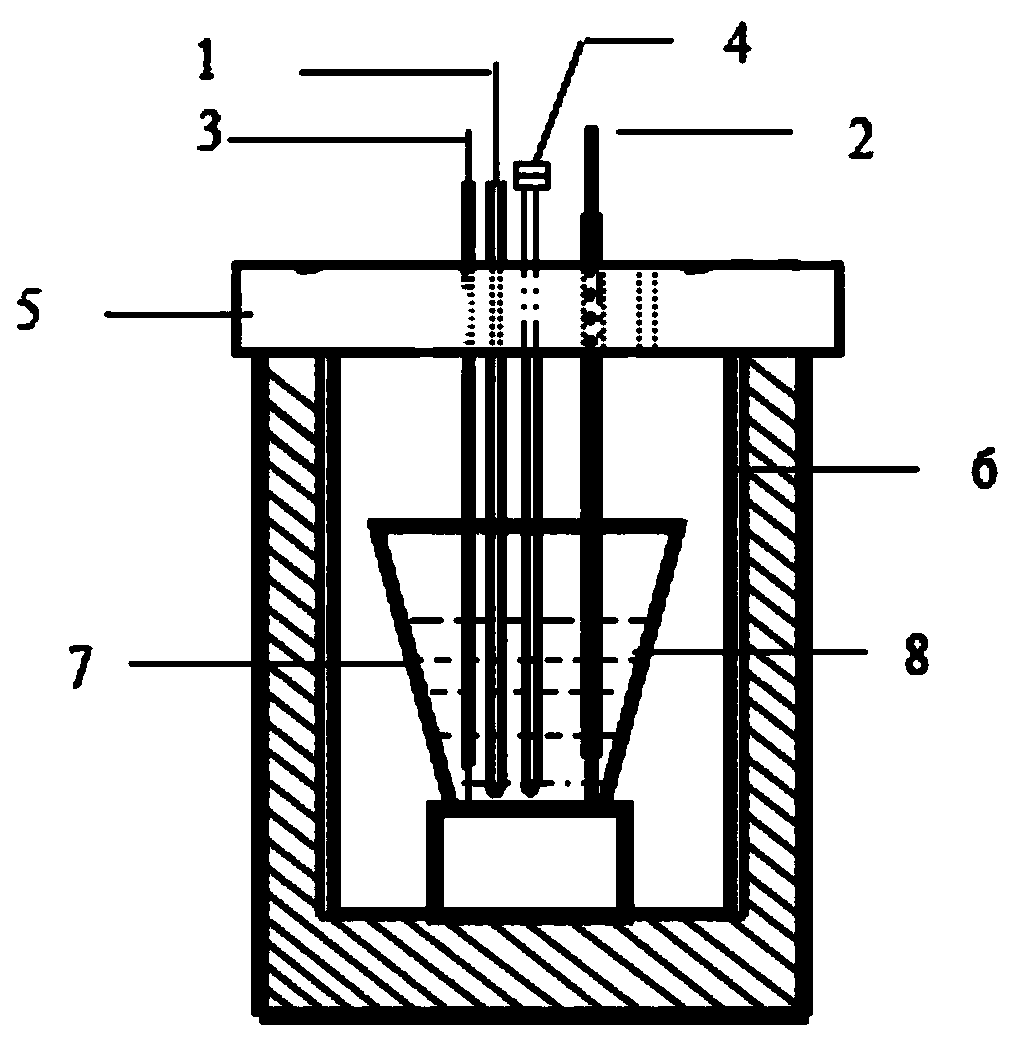
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Table 1 LiCl-KCl-(2.6wt.%)DyCl at 500℃ 3 In the molten salt system, the ICP data of the molten salt supernatant when anhydrous sodium phosphate is added in different amounts
[0042]
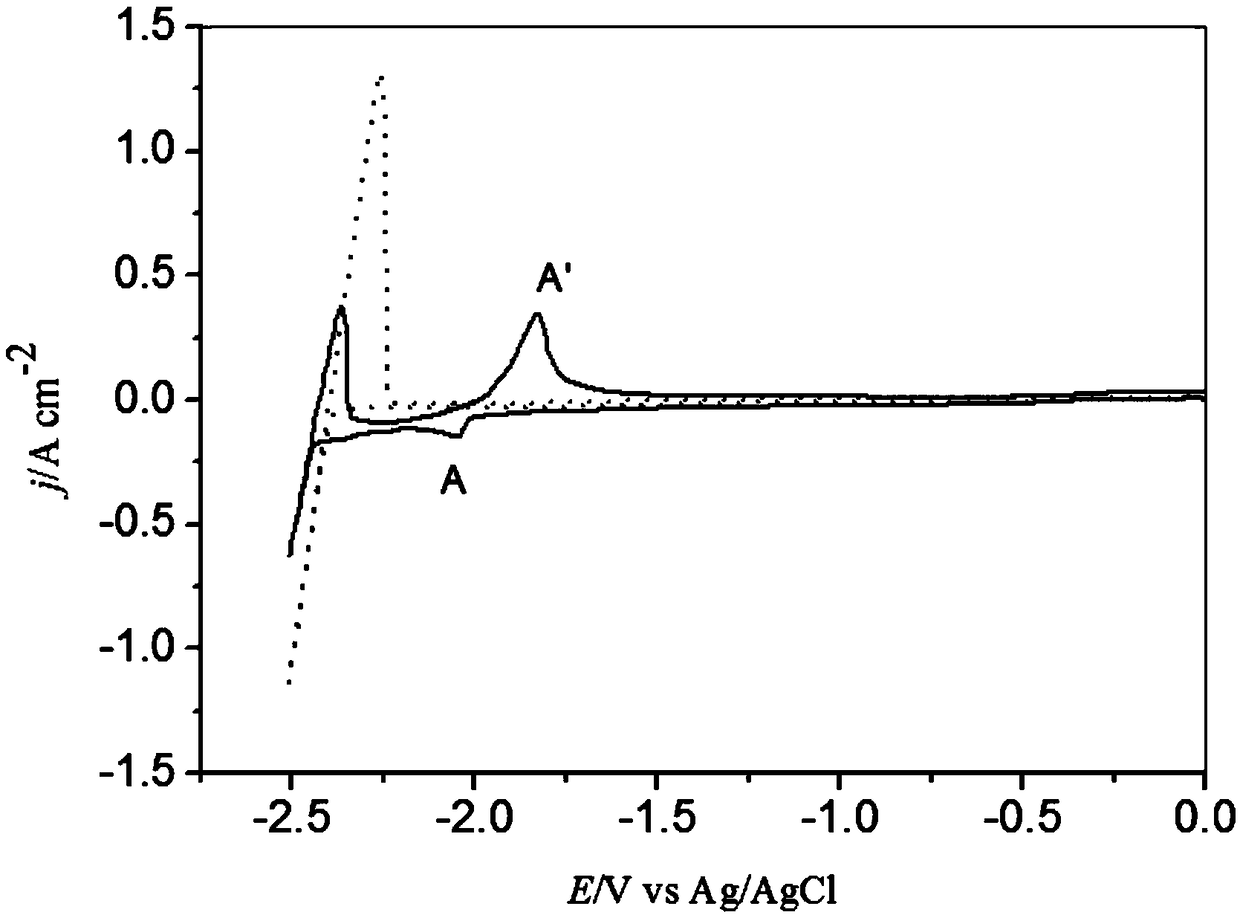
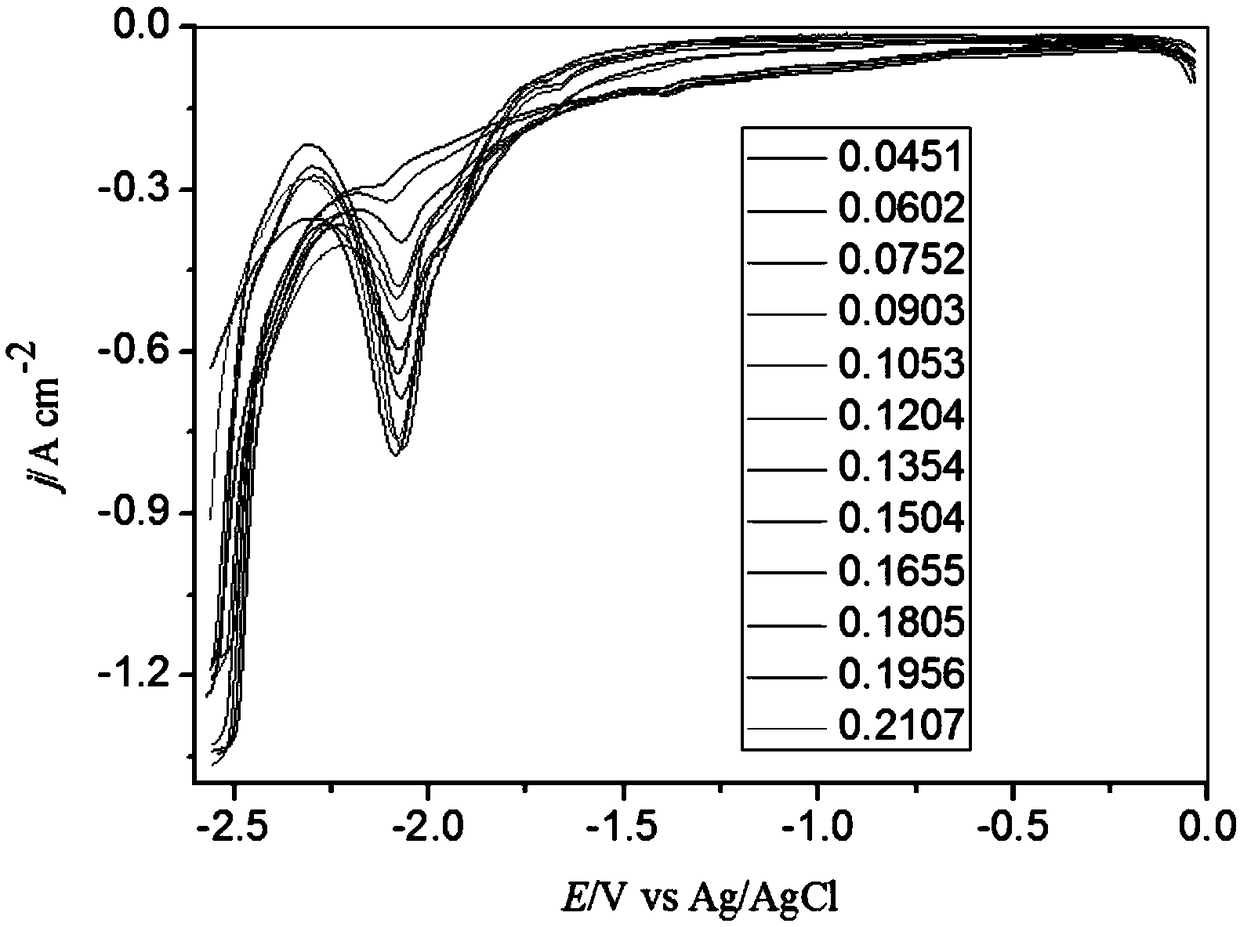
[0043] Weigh 1 part of LiCl-KCl (the mass ratio of LiCl and KCl is 38:45) salt, mix well and put it into a corundum crucible, and bake it at 200°C for 12 hours to remove the water in it. Heat the eutectic salt to 500°C to fully melt. Connect the three-electrode system. Firstly, under the potential condition of -2.15V, pre-electrolysis was performed for 4 hours by chronoamperometry, and a new tungsten electrode was replaced. DyCl 3 Add to the molten salt several times, adding 0.00116mol DyCl each time 3 , adding DyCl each time 3 Finally, measure the square wave voltammetry after stirring evenly, until reaching the detection limit of the square wave voltammetry (the peak height of the square wave voltammetry no longer increases with the addition of dysprosium chloride). The relatio...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Table 2 LiCl-KCl-(2.6wt.%)DyCl at 450℃ 3 In the molten salt system, the ICP data of the molten salt supernatant when anhydrous sodium phosphate is added in different amounts
[0048]
[0049] Weigh 1 part of LiCl-KCl salt, mix well and put it into a corundum crucible, and bake it at 200°C for 12 hours to remove the water in it. The eutectic salt was heated up to 450°C to fully melt. Connect the three-electrode system. First, under the potential condition of -2.15V, pre-electrolyze with the method of chronoamperometry for 4 hours, and replace the tungsten electrode. DyCl 3 Add to the molten salt several times, adding 0.0012mol DyCl each time 3 , adding DyCl each time 3 Finally, measure the square wave voltammetry after stirring evenly, until reaching the detection limit of the square wave voltammetry (the peak height of the square wave voltammetry no longer increases with the addition of dysprosium chloride), arrange the experimental data to obtain the square wav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com