A kind of process of arsenic trioxide melting and electrolysis of elemental arsenic
A technology of arsenic trioxide and molten electrolysis, which is applied in metallurgical technology and environmental protection, can solve problems such as waste of energy and equipment capacity, hidden dangers of operation and production safety, environmental protection pressure, etc., and achieve the effects of saving energy consumption, improving the operating environment, and saving energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
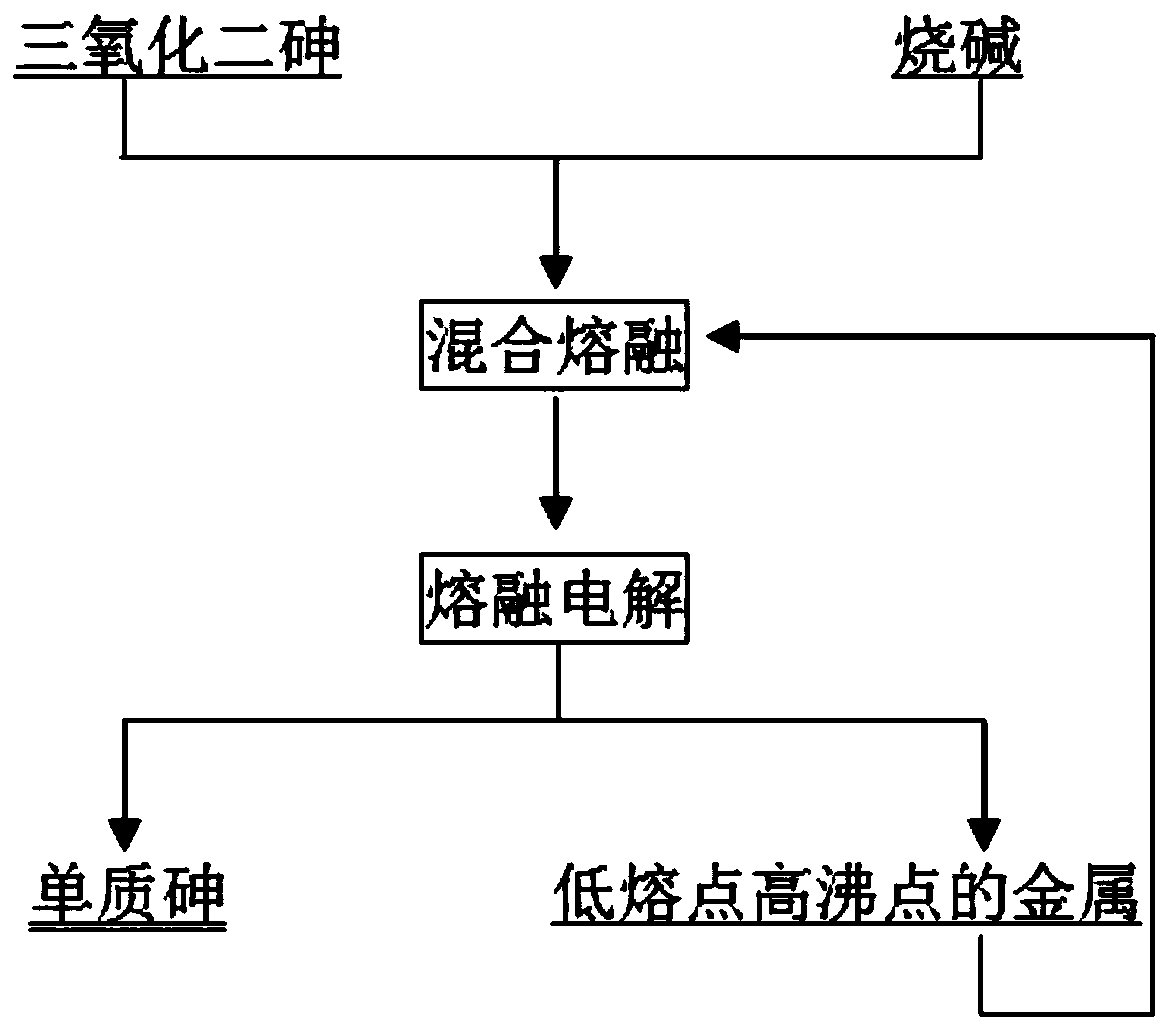
[0032] A process for melting and electrolyzing elemental arsenic with diarsenic trioxide, the process includes the following steps:
[0033] (1) Diarsenic trioxide and caustic soda are mixed and melted at a mass ratio of 1:1. The melting temperature is 800°C and the melting time is 40 minutes to obtain molten sodium arsenate. Graphite is used as the electrolytic positive electrode and lead is used as the electrolytic negative electrode. The tank pressure is 8v and the current is Density 20A / dm 2 Electrolysis to obtain elemental arsenic and low-melting-point arsenic alloys. Elemental arsenic is deposited at the bottom of the electrolytic cell in the form of molten arsenic and released from the chute at the bottom of the cell;
[0034] (2) The above-mentioned low-melting-point arsenic alloy is subjected to vacuum distillation, and the conditions for vacuum recovery are: vacuum degree 40Pa, temperature 700°C, steaming for 30min, to obtain elemental arsenic and lead;
[0035] (3)...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A process for melting and electrolyzing elemental arsenic with diarsenic trioxide, the process includes the following steps:
[0038] (1) Diarsenic trioxide and caustic soda are mixed and melted at a mass ratio of 1:1. The melting temperature is 730°C and the time is 50 minutes to obtain molten sodium arsenate. Graphite is used as the electrolytic positive electrode and bismuth is used as the electrolytic negative electrode. The cell pressure is 6v and the current is Density 25A / dm 2 Electrolysis to obtain elemental arsenic and low-melting-point arsenic alloys. Elemental arsenic is deposited at the bottom of the electrolytic cell in the form of molten arsenic and released from the chute at the bottom of the cell;
[0039] (2) The above-mentioned low-melting-point arsenic alloy is subjected to vacuum distillation, and the conditions for vacuum recovery are: vacuum degree 30Pa, temperature 800°C, and steaming for 30 minutes to obtain elemental arsenic and bismuth;
[004...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A process for melting and electrolyzing elemental arsenic with diarsenic trioxide, the process includes the following steps:
[0043] (1) Diarsenic trioxide and caustic soda are mixed and melted at a mass ratio of 1:1. The melting temperature is 900°C and the time is 50 minutes to obtain molten sodium arsenate. Graphite is used as the electrolytic positive electrode and tin is used as the electrolytic negative electrode. The cell pressure is 6v and the current is Density 30A / dm 2 Electrolysis to obtain elemental arsenic and low-melting-point arsenic alloys. Elemental arsenic is deposited at the bottom of the electrolytic cell in the form of molten arsenic and released from the chute at the bottom of the cell;
[0044] (2) The above-mentioned low-melting-point arsenic alloy is subjected to vacuum distillation, and the conditions for vacuum recovery are: vacuum degree 30Pa, temperature 740°C, and steaming for 30 minutes to obtain elemental arsenic and tin;
[0045] (3) T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com